![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chapter 1 |
. |
|
|
Management in a Diverse Workplace |
. |
|
|
Define the management ? |
The process of deciding the best way to use an organization's resources to produce goods or provide services. |
|
|
What the resources of any organization ? |
1. Employees 2. Equipment. 3. Money. |
|
|
Umbrella of Management Encompasses |
1. Sound decisions 2. Good Communication Skills 3. Delegation of plans 4. Training and motivationg people 5. Apprasial of employees' job performance |
|
|
What are the levels of business management ? |
1. Senior management 2. Middle managment 3. Supervisory management |
|
|
Senior Managment |
Responsible for setting goals for business, deciding what actions are necessary to meet them and determining how best to use resources. |
|
|
Middle Management |
Responsible fot achieving the goals set by senior managment. |
|
|
Supervisory Management |
Responsible for the people who physically produce the company's products or provide its services. |
|
|
Management pyramid slide no.6 |
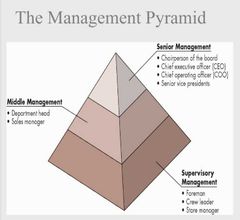
|
|
|
Management Tasks |
1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Staffing 4. Leading 5. Controling |
|
|
Planing |
Deciding what objectives to pursue and what to do to achieve those objectives. |
|
|
Organizing |
Grouping activities, assigning activities, and providing the authority necessary to carry out the activities. |
|
|
Staffing |
Determing human resource needs and recruiting, selecting, training, hence and developing human resources. |
|
|
Leading |
Dircting and channeling employee human behavior toward the accomplishment of objectives. |
|
|
Controling |
Measuring performance against objectives, determining the causes of deviations, and taking corrective action where necessary. |
|

|
. |
|
|
Management Roles |
1. Interpersonal Roles 2. Information-Related Roles 3. Decision-Making Roles |
|
|
Interpersonal Roles |
1. Figuregead 2. Relationship builder 3. Leader |
|
|
Figurehead |
Manager serves as official representative of the organization or unit. |
|
|
Relationship builder |
Manager interacts with peers and with people outside the organization to gain information. |
|
|
Leader |
Manager guides and motivates staff and acts as a positive influence in the workplace. |
|
|
Information-related roles |
1. Monitor 2. Communicator 3. Spokesperson |
|
|
Monitor |
Manager receives and collects information. |
|
|
Communicator |
Manager distrbutes information within the organization. |
|
|
Spokesperson |
Manager distributes information outside the organization. |
|
|
Decision-Making Roles |
1. Enterpreneur 2. Distrbance handler 3. Resource directer 4. Negotiator |
|
|
Enterpreneur |
Manager initates change. |
|
|
Distrbance handler |
Manager decides how conflicts between subordinates should be resolved and steps in when a subordinates suddenly leaves or an important customer is lost. Q |
|
|
Resource dirctor |
Managger decides how the organization will use its resources. |
|
|
Negotiator |
Manager decides to negotiate major contracts with other organization or individuals. |
|
|
Management Skills |
1. Conceptual skills 2. Human relations skills 3. Technical skills |
|
|
Conceptual skills |
Help managers understand how different parts of an organization relates to one another and to the business as a whole. Decision making, planning and organization require conceptual skills. |
|
|
Human relation skills |
Needed by managers to understand and work well with people. Interviewing job applicants, forming partnerships with other organization and resoloving conflict require human relations skills. |
|
|
Technical Skills |
Specificabilities that people use to perform their jobs.
Operating a word processing program,designing a brochure and training people in using a new budgeting system require technical skills. |
|

|
. |
|
|
Principles of Management |
•Management principles are more likely to change than physical principles, hence are more effective used as guidelines to actions.
•A principle is a basic truth or law.
•Hypothesis are conducted to prove a principle.
•Deduction is the process of drawing a general conclusion from specific examples. |
|
|
Changes in Information Availability |
•Increasing sophistication of communication systems and the rapid increase in the use of computers, new data and information are being provided at an accelerating rate. •These changes require managers to have increased technical skills. •Higher levels of skill and training require new approaches to motivation and leadership. |
|
|
Factors that can improve quality of life |
•Safe and healthy working conditions. •Opportunity to use and develop individual capabilities. •Opportunity for personal and professional growth. •Work schedules, career demands and traveltime that do not regularly take up family and leisure time. •Right to personal privacy, free speech,equitable treatment and due process. |
|
|
Glassceiling |
A level within the management hierarchy beyond which few women and minorities advance. |
|
|
Diversity |
Diversity in the workforce means including people of different genders, races, religions,nationalities, ethnic groups and physical abilities. |
|
|
Advantages of Diversity |
1. Can improve decision making. 2. Increasing globalization. 3. Presents stimulating challenges to both employees and supervisors. 4. Createsan organization culture that is tolerant, hence leading to better business decisions. |
|
|
Entrepreneurship and Management |
•Professional managers are paid to perform functions within a company.
•Senior, middle and supervisory managers are all professional managers. |
|
|
Entrepreneurs
|
Entrepreneursare people that launch and run their own businesses.
|
|
|
Entrepreneurship and Management |
•Entrepreneurs may hire professional managers as their organization grows.
•Being a entrepreneur is more riskier than being a professional manager.
•Entrepreneurs are more independent and possess less formal education. |
|
|
Types of Entrepreneurial Ownership |
•Soleproprietors run the business single-handedly.
•Partnershipsare usually made when large investments over the business are made. •One or more partners can provide money,while the other runs the business. •Two or more partners might also run the business together.
•Incorporates involves people forming a corporation to avoid being held personally liable for financial losses.
•Franchiseescan also be owned by some entrepreneurs. |
|
|
Small Businesses |
A small business is a company that is independently owned and operated. |
|
|
Owners of small businesses often perform all management tasks. |
. |
|
|
According to the Small Business administration (SBA), a company is a small business if it has less than 100 employees. |
. |
|
|
Small businesses generally tend to be more innovative than larger businesses. |
. |
|
|
Encouraging Entrepreneurship |
•To encourage intrapreneurship (entrepreneurship within an organization), many medium-sized and large organizations must:
|

