![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lens |
A transparent optical medium bound by two polished surfaces, at least one of which must be curved. |
|
|
What are 3 examples of optical media/materials? |
1. Natural - Quartz/Rock Crystals 2. Glass 3. Plastic |
|
|
Dioptre |
The unit used to denote power. It is the reciprocal of a given focal length in metres. |
|
|
Optically thin lens |
A lens where the centre thickness is not considered in calculations. The total power is the surface powers combined.
|
|
|
Total Lens Power (Equation) |
F = F1 + F2 |
|
|
Focal Length (Definition and Equation) |
The reciprocal of a focal power in metres. f = 1/F |
|
|
Spherical Lens |
A lens where only spherical power is exerted. |
|
|
Flat |
Considered as a lens that is not meniscus or curved. |
|
|
Curved |
A lens that has one convex surface and one concave. Also known as meniscus. |
|
|
Base Curve |
The lower surface power of the two surfaces. |
|
|
The power of a lens is the reciprocal of the focal length in metres. What is the formula for this? |
F = 1/f’ Where: F = total power of lens f = first principal focus of the lens f’ = second principal focus of the lens (after refraction) |
|
|
Positive Lens Diagram |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Negative Lens Diagram |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the formula for the total power of a thin lens? |
F = F1 + F2 Where F1 is the front surface power and F2 is the back surface power. |
|
|
Bi-Convex Lens Form |
Both surfaces are positive but of different power |
|
|
Equi-Convex Lens Form |
Both surfaces positive and of equal power |
|
|
Plano-Convex Lens Form |
Power on one surface only. Other surface is Plano |
|
|
Curved/Meniscus Lens Form |
Front surface is positive, back surface is negative |
|
|
Simple Transposition |
The process of changing a lens from one form to another without changing the overall power. |
|
|
The surface nearest to the eye is the… |
… back surface, and is always the most negative surface |
|
|
Are focal lengths additive? |
NO |
|
|
Focal Length (COMMON EXAM Q) |
The reciprocal of focal power in metres, however the answer can be expressed in cm, mm or m. f = 1/F |
|
|
Radius of Curvature |
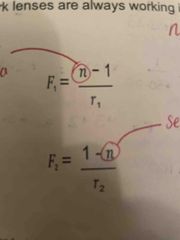
The radius of a full circle of which the curve forms a part. Measured FROM the surface TO the centre of curvature. MUST have sign and be measured in mm in OL rmm = multiply answer by 1000 |

