![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
126 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Follow up of cystic ovarian structures is recommended if |
They exceed 3 cm |
|
|
|
Simple cyst |
Anechoic Thin wall Post enhancement Unilocular |
|
|
|
Most common cause of ovarian enlargement in young women |
Functional cysts |
|
|
|
Functional cysts |
Result from gonadotrophins stimulation |
|
|
|
Functional cysts types |
Follicular cysts Corpus luteum cysts Theca lutein cysts |
|
|
|
Follicular cysts |
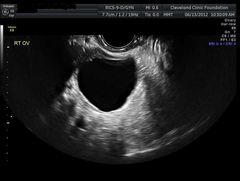
Non ruptured follicle 3-8 cm |
|
|
|
Corpus luteal cysts |
After ovulation Secrete progesterone and a bit of estro Rarely exeed 4cm |
|
|
|
If pregnant what happen to corpus luteum cyst |
Persists until 16 wks Produces progesterone |
|
|
|
If not pregnant what happens to corpus luteum cyst? |
Grow and hemorrage into lumen |
|
|
|
Theca lutein cysts |
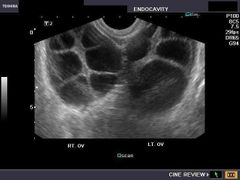
Multilocular Bilateral
|
|
|
|
Causes of theca lutein cyst |
High levels of hCG (Molar or fertility hcg) |
|
|
|
Do theca lutein cyst secrete hormones? |
Nope |
|
|
|
Largest of functional cysts? |
Theca lutein cysts |
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst |
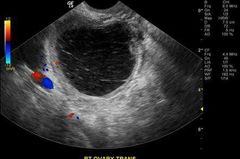
Subacute |
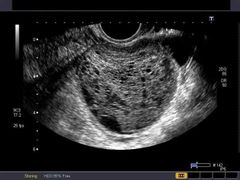
Acute |
|
|
Clinical sign of hemorragic cyst |
Acute pain |
|
|
|
Ovarian torsion |
Complete or partial rotation of the ovarian pedicle |
|
|
|
Ovarian torsion compromises |
Lymphatic and venous drainage causing congestion and edema Leading to loss of arterial flow |
|
|
|
Clinical sign of ovarian torsion |
Sudden pelvic pain May be confused with appendicitis |
|
|
|
Risk factors for ovarian torsion |
Mobile adnexa- children Pregnancy Ovarian mass or cyst |
|
|
|
Ovarian torsion is most common in |
Children |
|
|
|
Ovarian torsion ultrasound |
Enlarged ovary- more midline positioned Multiple follicles Affected flow Wirlpool sign-twisted ovarian vessels
|
|
|
|
Venous flow in ovarian torsion |
Lost first Absent |
|
|
|
Arterial flow in ovarian torsion |
Lost second May be present ,dampened ,or absent Compare both ovaries |
|
|
|
Ovarian torsion |
|
|
|
|
Polycystic ovarian syndrome |
Stein-Leventhal Syndrome Chronic anovulation |
|
|
|
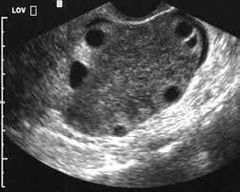
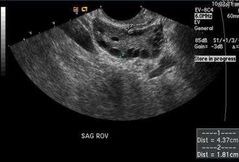
PCOS diagnosed |
Through Clinical and serologic findings |
|
|
|
Clinical sign of PCOS |
Infertility Obesity Hirutism Amenorrhea |
|
|
|
How many follicles in one PCOS ovary |
More than 12-19 follicles |
|
|
|
Ovarian volume in PCOS |
More than 10 cm3 |
|
|
|
PCOS is uni or bilateral? |
Always BILATERAL |
|
|
|
PCOS |
|
|
|
|
Make up 90% of all ovarian malignancies |
Epithelial tumors |
|
|
|
Epithelial ovarian tumors derive from |
Surface epithelium that covers the ovary |
|
|
|
Epithelial tumors |
Serous Mucinous Endometroid Clear cell Transitional cell -brenner Think about layers ;serosa mucosa endometrioum |
|
|
|
Serous tumors |
Serous cystadenomas-benign Serous cystadenocarcinomas-malign |
|
|
|
Most common ovarian carcinoma |
Serous cystadenocarcinoma |
|
|
|
Serous cystadenoma |
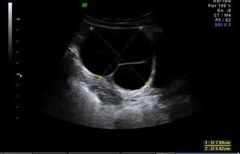
Large Anechoic Thin septations Unilocular |
|
|
|
Serous cystadenocarcinoma |
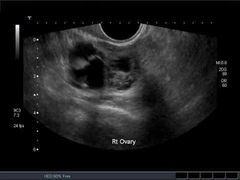
Multilocular Papillary projection Echogenic foci Ascites |
|
|
|
Mucinous tumors |
Mucinous cystadenoma- benign Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma-malig |
|
|
|
Mucinous tumors cause |
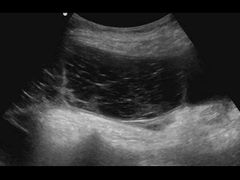
Pseudomyxoma peritonei |
|
|
|
Mucinous cystadenomas are |
Unilateral 30-50 |
|
|
|
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma |

20% bilateral Large multilocular cysts up to 30 cm Echogenic material and papillary extensions |
|
|
|
Mucinous cystadenoma |
Multiloculated thicker septation cysts up to 50 cm Gravity dependent echoes |
|
|
|
Transitional cell tumors |
Brenner Fibroepithelioma BENIGN TUMORS |
|
|
|
Endometroid tumors |
80% malignant but better prognosis than other epithelial cancers |
|
|
|
Endometroid tumors |
Make up 25% of ovarian cancer |
|
|
|
Endometroid tumors are identical to |
Endometrial adenocarcinoma |
|
|
|
30% of ovarian endometroid tumors pt will have |
Endometrial cancer |
|
|
|
Clear cell tumors |
Malignant |
|
|
|
Histological variant of endometroid and serous carcinomas |
Clear cell tumors |
|
|
|
Mets make up |
10% of ovarian tumors |
|
|
|
Most comon sites of ovarian mets are |
Breast GI |
|
|
|
Ovarian cancer that arises from GI |
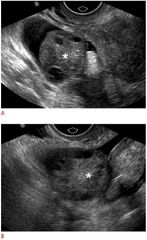
Krukeberg tumor
|
|
|
|
Ovarian mets are usually |
Bilateral |
|
|
|
Krukenberg tumor are usually bi but if uni are most common in |
Rt side |
|
|
|
The fifth leading cause of cancer death |
Ovarian cancer |
|
|
|
The fifth most frequent cancer in women |
Ovarian cancer |
|
|
|
Ovarian cancer is |
Silent Most will habe late stages when discovered and 5yrs survival rate is 30-50% |
|
|
|
Risk for ovarian ca |
Family hx of breast or ovarian ca Nulliparity or unsuccessful pregnancies 50+ Early menses/ late meno |
|
|
|
Screening for ovarian ca |
CA-125 SONOGRAPHY |
|
|
|
For pt with suspected ovarian mass check |
Peritoneum Liver Pleural space |
|
|
|
Highly suggestive of ovarian carcinoma |
Ovarian mass Elevated CA -125 |
|
|
|
Paraovarian cysts |
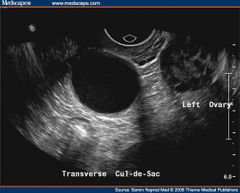
Parovarian cysts Remnants of Wolfian ducts Adjacent to ovary |
|
|
|
Bladder abnormalities |
Distal ureteral stone Cystitis Bladder wall neoplasm Bladder diverticulum Neurogenic bladder |
|
|
|
Neurogenic bladder |
Malfunction Enlarged bladder with/w/o debris |
|
|
|
Distal ureteral stone in tvag |
|
|
|
|
PID |
Inflamation of pelvic and adnx structure |
|
|
|
PID is |
An ascending infection from cervix to fallopian tubes and adnexa |
|
|
|
Most common cause of PID |
sexually transmited infections and polymicrobial Chlamydia Gonorrhea E.coli |
|
|
|
PID may also be caused from |
D & C , HSG, ruptured app, abortion etc |
|
|
|
Stages of PID |
I- endometritis II- salpingitis III- TOA (SEVERE) |
|
|
|
Chronic PID |
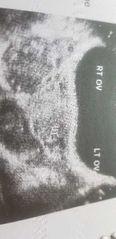
Indefinite uterus sign= lobster claw sign
Adhesion causes pelvic organs to merge centrally |
|
|
|
Endometritis in early PID |
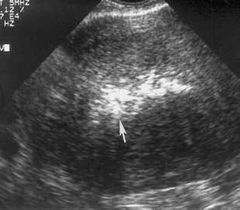
Air bubbles in endo |
|
|
|
Pyosalpinx in stage II PID |
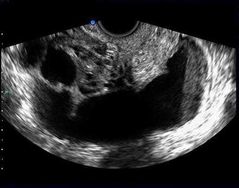
|
|
|
|
Stage III PID |
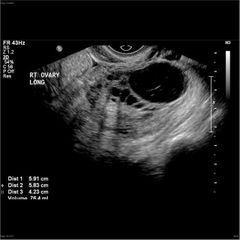
TOA |
|
|
|
Hydrosalpinx |
Chronic PID- resolved pyosalpinx |
|
|
|
Clinical signs with PID |
Fever Leukocytosis Pain Dyspareunia Cx motion |
|
|
|
Endometriosis |
Ectopic endometrial tissue outside uterus |
|
|
|
Most common endometriosis ectopic site |
Ovary |
|
|
|
Endometriosis can be |
Asymptomatic Severe pain |
|
|
|
Endometriosis types |
Diffuse-hard to detect on US focal- endometrioma |
|
|
|
Clinical signs of endometriosis |
Infertility Pain - 4D: Dyspareunia Dysmenorrhea Dysuria Dyschezia
|
|
|
|
Dyschezia |
Difficult defecation |
|
|
|
Focal endometriosis |
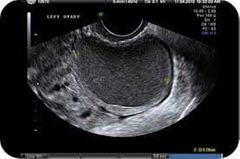
Endometrioma Chocolate cyst |
|
|
|
Stages of endometriosis |
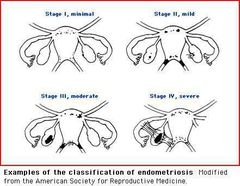
|
|
|
|
Germ cell tumors |
Ovarian tumors |
|
|
|
Germ cell tumors |
Derive from germ cells of embrionic gonads |
|
|
|
Germ cell tumors in adults are mostly |
Benign- cystic teratoma |
|
|
|
Germ cell tumors in kids and adolescents are mostly |
Malignant |
|
|
|
3 Germ cell tumors |
Benign cystic teratoma-dermoid cyst Dysgerminoma- malig Yolk sac tumor-malig
|
|
|
|
Benign cystic teratoma-BCT |
dermoid cyst Usually benign |
|
|
|
Malignant version of teratomas |
Imature teratoma- teratocarcinoma |
|
|
|
Teratoma findings |
Tip of iceberg Dermoid mesh Dermoid plug |
|
|
|
Teratomas can show up differently on us depending on |
Their content : hair, teeth |
|
|
|
Dermoid mesh |
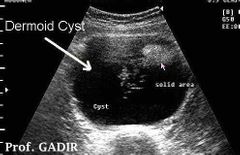
Hair fibers - linear echogenic |
|
|
|
Dermoid plug |
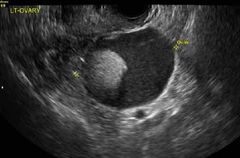
Echogenic mural nodule in cystic mass Shadowing |
|
|
|
Tip of iceberg dermoid |
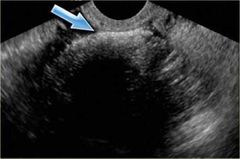
Highly echogenic mass that shadows posteriorly |
|
|
|
Dysgerminoma |
Highly malignant but highly radiosensitive |
|
|
|
Dysgerminoma occur |
Before 30 yrs old |
|
|
|
Equivalent of dysgerminoma in males |
Seminoma |
|
|
|
Marker for dysgerminoma |
High serum lactate dehydrogenase |
|
|
|
Most common germ cell malignancy |
Dysgerminoma |
|
|
|
Second most common germ cell malignancy |
Yolk sac tumors |
|
|
|
Most common germ cell tumor |
Benign cystic Teratoma/ dermoid cyst |
|
|
|
Most common complication of dermoid cyst/BCT |
Ovarian torsion |
|
|
|
Yolk sac tumors |
Endodermal sinus tumors |
|
|
|
Yolk sac tumors |
Malignant |
|
|
|
Yolk sac tumors |
Occur in young adulthood 20-30 |
|
|
|
Yolk sac tumors |
Highly malignant and metastize fast |
|
|
|
Marker for yolk sac tumors |
High AFP High LDH |
|
|
|
Sex cord stromal tumors arise from |
Sex cords or ovarian stroma |
|
|
|
4 Sex cord stomal tumors TheFAG |
Fibroma Thecoma Androblastoma Granulosa cell tumors |
|
|
|
Fibromas |
Benign |
|
|
|
Fibroma is assoc with |
MEIGS SYNDROME |
|
|
|
Meigs syndrome |
Ascites and pleural eff as a result of a benign ovarian tumor |
|
|
|
Thecoma |
Usually benign Post menopausal |
|
|
|
Thecomas produce |
Estrogen Endo changes in post meno |
|
|
|
Thecomas look like |
Fibroma on ultrasound Hypo mass with shadowing |
|
|
|
Fibroma looks like a |
Pedunculated uterine fibroid Hypo with shadowing |
|
|
|
Granulosa cell tumors |
Produce estrogen Same as thecomas Post meno |
|
|
|
Sertoli leydig tumor |
Arrhenoblastoma Androblastoma |
|
|
|
Sertolu leydig cell tumor |
Produce testosterone - virilization Look like granulosa cell tumor 20% malignant Are rare tumors |
|
|
|
Germ cell tumors |
DDY |
|
|
|
Sex cord and stoma tumors -TheFAG |
Produce hormones |
|
|
|
Which ovarian tumor produces estrogen |
Thecoma Granulosa |
|
|
|
Which ovarian tumor produces testosteron |
Sertoli leyding tumor |
|

