![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What will the administration of a parasympathomimetic agent produce? |
Miosis |
|
|
Which agent produces cyloplegia and myhydrosis? |
Atropine |
|
|
What is the first line agent for treatment of glaucoma? |
Latanoprost |
|
|
Hypotrichosis is most appropriately treated with? |
Bimatoprost (PG analog) |
|
|
What is the least appropriate to treat glaucoma in patient who is allergic to sulfonamides? |
Dorzolamide |
|
|
What drug used in treatment of glaucoma does not work by inhibiting aqueous production? |
How can you affect aqueous humor? Change outflow through uveosclearo pathway
DORZOLAMIDE |
|
|
Where in the eye is the aqueous humor produced? |
Ciliary body |
|
|
Which of the following does NOT form part of routine treatment of open-angle glaucoma? |
Surgical iridectomy |
|
|
Pinpoint pupil response to opiate intoxication occurs via drug action upon which component of the autonomic nerves serving the eye? |
Edinger-Westphal nucleus |
|
|
Treated for open angle glaucoma and has altered sense of taste. Which drug? |
Dorzolamide (carbonic anhydrase inhibitor) |
|
|
Atropine Cyclopentolate Homotriptine Scopolamine Tropicamide
What class? |
Muscarinic antagonists |
|
|
Carbachol Pilocarbine Acethylcholine HCl
What class? |
Muscarinic agonists |
|
|
Echothiopate
What class? |
AChE inhibitor
|
|
|
Dipivefrin Phenylephrine Apraclonidine Brimonidine Naphazoline Tetrahydrozoline
What class? |
Sympathomimetics
|
|
|
Latanoprost Travoprost Bimatoprost
What class? |
PG analogs |
|
|
Timolol maleate Levobunolol Metipranolol Carteolol
What class? |
Beta-adrenergic antagonists |
|
|
Dorzolamide Brinzolamide Acetazolamide
What class? |
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors |
|
|
Afibercept Pegaptanib Ranibizumab Bevacizumab Verteporfin
What class? |
Drugs for macular degeneration |
|
|
What are muscarinic receptors responsible for in the eyes? |
Iris sphincter muscle (miosis) M3, ciliary muscle (accommodation) M3, lacrimal gland (secretion) = M2,M3 |
|
|
Where are the alpha receptors in the eye? |
Iris radial muscle (mydiasis) Ciliar epithelium (aqueous production) Lacrimal gland (secretion) Retinal pigment epithelium (H20 transport)
|
|
|
What is the target of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors? |
Ciliary epithelium |
|
|
What is useful for localized activation of pro-drugs with better corneal penetration? |
Esterases Dipivefrin => epinephrine Latanoprost => PGF2 |
|
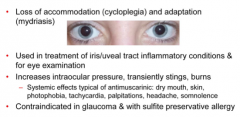
What five drugs cause this? |
Atropine Homotropine Tropicamide Cyclopenolate Scopolamine |
|
|
Which drugs cause blurred vision, burning/stinging, itching acutely
and
slow and permanent brown pigmentation of iris, eyelid skin, and eyelashes; also increasing their growth including length, thickness chronically |
PGF2-alpha analogs |
|
|
What is the effect of beta blockers on aq. humor production and ocular bloodflow?
What "devices" can it damage? |
Decrease aqueous humor production by decreasing cAMP-PKA stimulation Decrease ocular bloodflow and ultrafiltration producing humor.
Benalkonium chlroide preservative can damage soft contact lenses |
|
|
What is the mechanism for how CA inhibitors can decrease IOP?
What are two predominant side effects? |

|
|
|
What are the direct acting miotics?
When are they contraindicated? |

When constriction undesirable, in patients with cholinergic mediated medical conditions, and when used with insecticides, and in CLOSED ANGLE GLAUCOMA |
|
|
What are the ocular side effects of sympathomimetics?
What is the MOA? |
Photosensitivity, conjunctival hyperemia, hypersensitivity
Decrease IOP by increasing outflow of aqueous humor from the eye (caution using with any disease that might be irritated by increased sympathetic effects. |
|
|
What four drugs are used for macular degeneration?
What can VEGF inhibitors be associated with? |
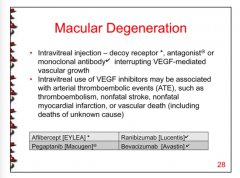
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of verteporfin?
What is the side effect? |

|

