![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
which receptors are associated with touch and pressure?
|
Meissner, Merkel
|
|
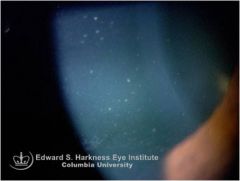
what is this
|
Granulomatous uveitis, Mutton Fat KPs
|
|
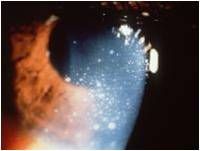
what eye signs are associated with this condition and what is the condition?
|
uveitis
ankylosing spondylitis |
|
what structures are derived from the diencephalon?
|
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus, retina
|
|

what is this picture indicate when it comes to ocular conditions?
|
this picture shows that sports occupation can lead to uveitis
|
|

what does this picture indicate when it comes to ocular conditions?
|
this pic shows how high strung type individuals can get uveitis more often
|
|
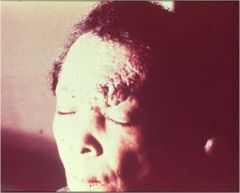
what does this pic represent in relation to ocular dysfunction?
|
sarcoidosis link to anterior uveitis
|
|
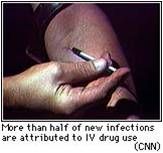
what does this photo predispose a pt to when it comes to ocular dysfunction?
|
high risk for infection leading to predisposition for anterior uveitis
|
|
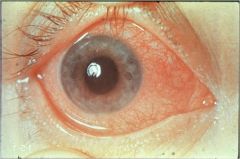
what is this a photo of
|
acute uveitis
|
|
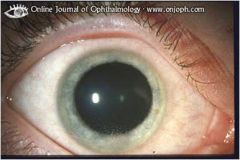
what condition of the eyes does this reveal?
|
this shows how chronic anterior uveitis may be ASYMPTOMATIC
|
|
what is this?
|
uveitis
|
|
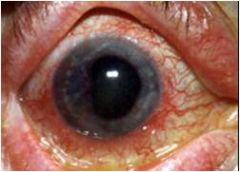
what is this?
|
Circumcorneal (perlimbal) flush --> RED EYE!!! (signs of uveitis)
|
|

what is this
|
acute uveitis
|
|

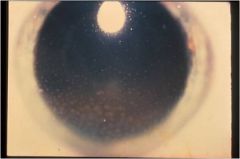
what is this
|
mutton fat KPs called granulomatous KPs
|
|

what is this showing?
|
cells in aqueous (anterior chamber) *CLASSIC!!! LOOK FOR THEM!!!
|
|

go over 4 levels of relative grading of uveitis cells
|
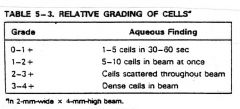
|
|

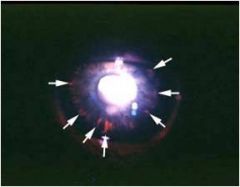
what is this *CLASSIC sign
|
flare in aqueous (anterior chamber sign of uveitis)
|
|
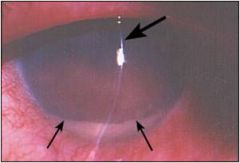
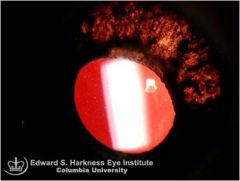
what is this a pic of
|
AC hypopion in anterior uveitis
|
|
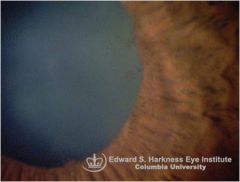
what is this showing and how/why do you prevent it?
|
posterior synechiae in anterior uveitis. want to prevent glaucoma so should CYCLOPLEGE!!
|
|
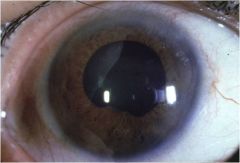
what is this photo showing
|
atrophy of iris in prolonged chronicity and certain specific forms of uveitis
|
|
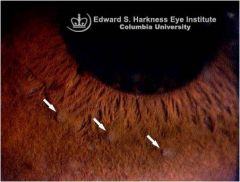
what is this showing
|
iris nodules (busacca) granulomatous uveitis
-whitish-yellow lumps away from pupil border |
|
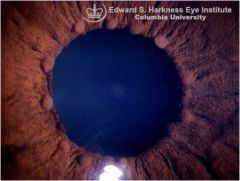
what is this photo showing
|
Koeppe nodule in iris
-round or oval solid tissue located AT pupil border -can be found in nongranulomatous as well as granulomatous uveitis |
|
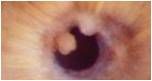
what is this
|
Granuloma
-fleshy, white-pink, slightly vascularized mass |
|
what structures of the brainstem may be involved if a patient has dysphonia
|
nucleus ambiguous, corticobulbar tract
|
|

what is this showing
|
pigment debris (posterior synechiae remnant)
|
|

what is this showing
|
"Candle wax drippings" in sarcoid
|
|
what are the three types of glial cells?
|
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia/macrophages
|
|
|
what is the objective plan/therapy for uveitis (5 points). which one is most important
|
Protect vision
Reduce pain Eliminate inflammation and identify source Prevent the formation of synechiae Manage the IOP ***prevent synechiae formation |
|
|
what are 2 TPAs used to treat uveitis (topical ocular)
|
1. Pred-forte
2. Durezol |
|
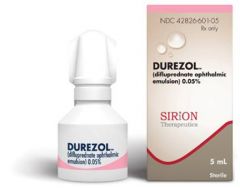
what is this used to treat?
|
uveitis
|
|

what is this used to treat
|
uveitis
|
|
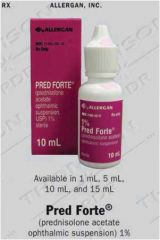
what is the % on this (prednisolone acetate) and how often is it taken
|
1%
qid |
|
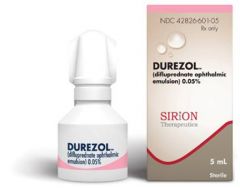
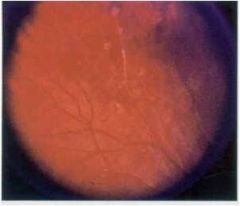
what is the % on difluprednate and how often is it taken?
|
0.05% q4-6h
|
|

what is this used for
|
uveitis
|
|
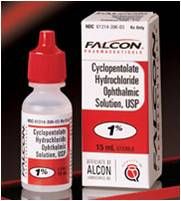
what % and how often is this used?
|
1-2% qid
|
|

for moderately severe cases what % and how often is prednisolone acetate taken
|
1% q2-3h
|
|
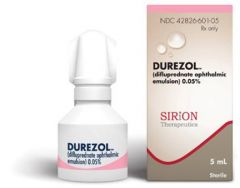
for moderatly severe cases what % and how often is difluprednate taken to treat uveitis
|
0.05% q4-6h
|
|
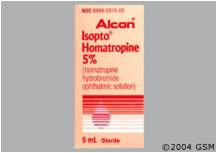
what is this and want is it used to treat
|
homatropine to treat uveitis
|
|
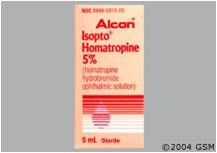
for moderately sever cases what % and how often is homatropine taken
|
5% bid-qid
|
|

for severe cases what % and how often is prednisolone acetate taken
|
1% q1-2h
|
|
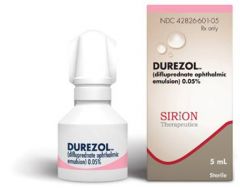
for severe cases how often and want % is difluprednate taken
|
0.05% q2-4h
|
|
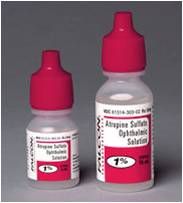
what is atropine used for
|
Atropine used to treat uveitis
|
|

where does the alimentary tract start and end?
|
oral cavity, anus
|
|
|
what comprises the small intestine?
|
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
|
|
|
what is the follow up schedule for topical ocular therapy for uveitis
|
1-7 days depending on severity and complicating factors.
factors to consider: -elevated IOP w/ chronic -posterior segment (if not responsive or inflammation worsens) |
|
|
when can you begin tapering from uveitis therapy?
|
if improvement is noted
|
|
|
what is it important not to do when treating uveitis
|
it is important NOT to discontinue the medication prematurely
|
|
|
how do you take/finish Cycloplegics (while treating uveitis)
|
continue until the cellular rxn is subsiding and flare is absent
|
|
|
how do you take/finish Steroids when treating uveitis
|
continue until cells are minimal or absent.
-taper based on initial potency, frequency, and duration of use -usually over a 1-2 wk period |
|
|
when pt is tapering when/why should they be observed?
|
pt should be observed during and a few weeks after tapering process for signs of rebound inflammation
|
|
|
for chronic cases, requiring use of mild steroids, how much, what % and what should be used
-what are the side effects |
1 drop
0.125% prednisolone acetate qid elevated IOP, PSC |
|
|
steroids
used for? used for? causes? |
uveitis unresponsive to topical
bilateral posterior uveitis significant systemic side effects |
|
|
what non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat uveitis
|
ASA
Ibuprofen |
|
|
what drug therapy for uveitis comes with these indications
-useful in cases of unilateral posterior uveitis -administered close to site of inflammation -may have other complicatioins (IOP elevation needs to be managed) |
Periocular steroids (Injectable steroids)
|
|
|
what treatment/plan for uveitis has these indications about it?
-cytotoxic effects interfere w/ cellular () system -serious potential side effects ()consulation |
Immunosuppressive agents (immunity) (immunologic) consultation
|
|
|
what supportive therapy is provided for uveitis plan/therapy
|
sunglasses
plus for near patching |
|
|
what are the four major complications associated with anterior uveitis
|
1. Glaucoma
2. Cataracts 3. Band Keratopathy 4. CME (cystoid macular edema) |
|
|
what are four conditions associated with anterior uveitis? which isopathy this
|
CME* cystoid macular edema
glaucoma cataracts band keratopathy |
|

what are the four major complications associated w/ anterior uveitis. which is this
|
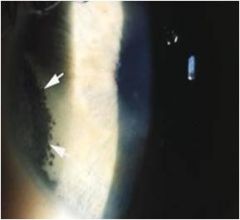
CME cystoid macular edema
cataracts band keratopathy glaucoma |
|
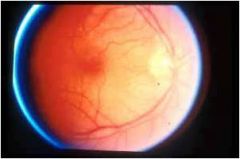
what are the four major complications associated with anterior uveitis?
which is this? |

glaucoma*
cataracts band keratopathy CME (cystoid macular edema) |

