![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Learning by
|
Experience and association
|
|
|
|
Experience
|
-predict events we like/don't like
-noticing events and sensations -consequences of our actions -watching other people |
|
|
|
Association
|
-When two stimuli tend to occur together or in sequence
-when actions become associated with pleasant or aversion results -when two pieces of information are linked |
|
|
|
Higher-order conditioning
|
Turning a neutral stimulus into a Conditioned Stimulus by associating it with other Conditioned Stimulus.
|
|
|
|
Acquisition
|
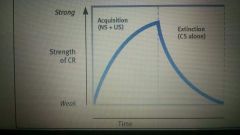
Refers to when the strength of a Conditioned Response grows with conditioning
|
|
|
|
Extinction
|

Refers to the diminishing of a Conditioned Response. If the Unconditional Stimulus (food) stops appearing with the Conditioned Stimulus (bell), the the Conditioned Response decreases
|
|
|
|
Generalization
|
Refers to the tendency to have Conditioned responses triggered by related stimuli.
|
More stuff makes you drool.
|
|
|
Discrimination
|
The learned ability to only respond to a specific stimuli, preventing generalization.
|
Less stuff makes you drool.
|
|
|
Pavlov's Legacy
|
*Insights about conditioning - occurs in all creatures. -Related to biological drives and responses.
*Insights about Science - learning can be studies objectively, by quantifying actions and isolating elements of behavior *Insights to specific applications - substance abuse involves Conditioned triggers, and these triggers can be avoided or associated with new responses. |
|
|
|
John B. Watson
|
Classical Conditioning
Fear Little Albert Experiment |
|
|
|
Operant Conditioning
|
Involves adjusting to the consequences of our behaviors, so we can easily learn to do more of what works, and less of v.v.
|
|
|
|
Respondent Behavior
|
Reflexive, automatic reactions such as fear or craving
-these reactions to US become associated with neutral (then - > conditioned) stimuli |
The experimental (Neutral) stimulus repeatedly PRECEDES the respondent behavior, and eventually riggers that behavior.
|
|
|
Operant Behavior
|
Chosen behaviors that "operate" on the environment.
-these behaviors become associated with consequences which PUNISH (decrease) or REINFORCE (increase) the operant behavior. |
The experimental (consequence) stimulus repeatedly FOLLOWS the operant behavior, and eventually pushes or reinforces that behavior.
|
|
|
Thorndike' Law of Effect
|
Behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely.
|
Cat in the puzzle box.
|
|
|
B.F. Skinner
|
-more carefully measure the effect of chosen behavior?
-what else can creatures be taught to to by controlling consequences? -what happens when we change the timing of R? |
The operant chamber aka "the Skinner box"
|
|
|
Reinfocement
|
Any feedback from the environment that makes a behavior more likely to recur.
|
|
|
|
Positive reinforcement
|
ADDING something desirable to the environment that makes a behavior more likely to recur.
|
|
|
|
Negative reinforcement
|
ENDING something unpleasant to make a behavior more likely to recur.
|
|
|
|
Shaping Behavior
|
Reinforcing succession approximation.
-when a creature in not like to randomly preform exactly the behavior you are trying to teach, you can reward any behavior that comes close the the desired behavior. |
Rewarding a dog for squatting instead of sitting all the way.
|
|
|
Discrimination
|
The ability to become more and more specific in what situations trigger a response.
-Shaping can increase discrimination, if reinforcement only comes for certain discrimination stimuli. |
|
|
|
Primary reinforcer
|
A stimulus that meets a basic need or otherwise is intrinsically desirable.
Ex. Food, money, fun, attention, power |
|
|
|
Secondary/Conditioned Reinforcer
|
A stimulus which has become associated with a primary.
Ex. Money (buys food, builds power) |
|
|
|
Delayed Reinforcement
|
The ability to link a consequence to a behavior even if they aren't linked sequentially in time.
|
|
|
|
Delayed gratification
|
A skill related to impulse control that enables longer-term goal setting.
|
|
|
|
Continuous reinfocement
|
(reward every time) the subject acquires the desired behavior quickly.
|
|
|
|
Partial/intermittent reinforcement
|
(rewards part of the time) the target behavior takes longer to be acquired/established but persists longer without reward.
|
|
|
|
INTERVAL OF TIME that has gone by
|
FIXED INTERVAL SCHEDULE: reward every time a certain amount of time is reached regardless of the amount of work performed.
VARIABLE INTERVAL SCHEDULE: reward after a changing/random amount of time passes. |
FI: Getting Paid weekly no matter how much work is done
VI: Checking your phone all day; sometimes getting a text |
|
|
RATIO of rewards/# of instances of desired behavior
|
FIXED RATIO SCHEDULE: reward every certain number of targeted behaviors.
VARIABLE RATIO SCHEDULE: reward after randomly chosen instances of the target behavior. |
FR: Rat gets food every third time it presses the lever
VR: Hitting a jackpot sometimes on the slot machine |
|
|
Which reinforcements produce more "responding" (target) behavior?
|
FI: slow UNSUSTAINED responding
VI: slow CONSISTENT responding FR: high rate of responding VR: high CONSISTENT responding, even if reinforcement stops (resisting extinction) |
FI: If I'm only paid for my Saturday work, I'm not going to work as hard other days.
VI: Don't know when my lucky lottery number will pay off, I better play it every day FR: Buy 2 get 1 free? Buy much! VR: Slot machine sometimes pays. Pull as much as I can cuz it may pay this time! |
|
|
Punishment
|
Have the opposite effects of reinforcement. These consequences make the target behavior less likely to occur in the future.
SEVERITY of punishments in Not as helpful as making the punishments IMMEDIATE and CERTAIN. |
|
|
|
Positive Punishment
|
You ADDING something unpleasant/aversion.
|
Spank the child
|
|
|
Negative Punishment
|
You TAKE AWAY something pleasant/desired.
|
No TV Tim, no attention
|
|
|
Problems with Physical Punishment
|
-may restart when punishment is over (learning is not lasting)
-instead of learning BEHAVIORS, the child may learn to discriminate among situ. -child might learn an attitude of fear or anger which can generalize to a fear/hated of all adults or many settings -it models aggression and control as a method of dealing with problems |
|
|
|
Summary: Types of Consequences
|
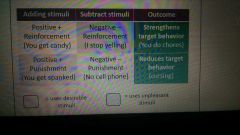
|
|
|
|
Operant vs Classical Conditioning
|
OC: Response > Consequence > Response Strengthened
-if the organism is learning associations b/w it's behavior and the resulting event CC: Conditioned Stimulus (spash) > Unconditioned Stimulus (shock) -the organism is learning associations b/w events that it does not control. |
|
|
|
Cognitive Processes CC/OC
|

|
|
|
|
Latent Learning
|
Skills or knowledge gained from experience, but not apparent in behavior until rewards are given.
|
Rats tin a maze.
|
|
|
Cognitive maps
|
Rats can learn a maze just by wandering, with no cheese to reinforce their learning.
|
|
|
|
Intrinsic motivation
|
The desire to perform a behavior well for its own sake.
-reward is internalized as feeling of satisfaction. -can sometimes be reduced by external rewards, and can be prevented by using continuous reinforcement. |
|
|
|
Extrinsic motivation
|
Doing a behavior to receive rewards from others.
|
|

