![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the basic history include?
|
1. C/C
2. HPI 3. Review of system related to C/C 4. Alergies and Medication 5. Past Medical History 6. Social History 7. Family history |
|
|
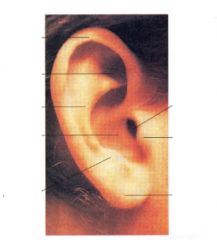
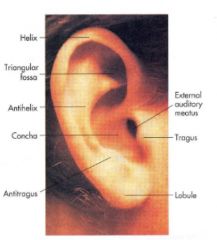
What does the external ear exam include?
|
Auricle
Gently tug- if painful indicated otitis externa Inspect- look for deformities, lumps (gouty tophi), skin lesions (carcinomas "squamous or basal" |
|
|
What does the internal exam of the ear include?
|
Straighten the canal by pulling upward, backward, and away from head
Describe the finding by what time it is positioned - Note Auditory meatus (ear canal) - Dishcharge (color) - Foreign bodies - Erythema - Cerumen (partial or total impaction) |
|
|
|
|
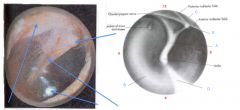
Upon examination of the tympanic membrane what are you looking for?
What are labeled? What is pneumatic otoscope used for? |
should note perforations, bulging, erythema, tympanosclerosis
a. handle of malleus (manubrium) b. pars tensa- major portion of TM c. pars flaccida- superior portion smaller of TM d. light reflex- sharp borders e. short process of malleus- unusually prominent with retracted membrane in eustachian tube dysfunction and serous otitis media pneumatic otoscope- pump that checks mobility of tympanic membrane, could indicate fluid, perforation, or tympanosclerosis |
|
|
What do you inspect with Exam of mouth?
|
1. lips- color, moisture, cracks, ulcers
2. oral mucosa- apthous ulcers-- painful, Cheilitis- B12 or iron deficiency 3. Gums and Teeth- color of gums (pink and moist usually), ulcers, swelling, gum recession,teeth color and position 4. Roof of mouth- color, architecture, torus palatinus (benign lump) 5. Tongue- ask patient to stick tongue out- a. midline- deviation indicates CN XII dysfunction b. movement with sterile gloves (cancer usually hard and at side or base), look for nodule, ulcer, red or white plaque, |
|
|
Describe the examination of the pharynx
|
need tongue blade and ask pt to say "ah"
- not soft palate rise (CN- X) - paralysis will see uvula deviate to opposite side and soft palate not rise - color, swelling - tonsil size and color +4 is only kind that need surgery now. |
|
|
Describe Weber and Rinne findings...
After the patient says that the sound lateralized to the left with the Webber test. |
If lateralizes to the left with Webber, and if
a. heard in air longer than bone (AC > BC) means sensorineural hearing loss of the opposite ear b. heard in bone longer (BC>AC) than air it is conduction loss to the ear being tested (left in this case |
|
|
What is the difference between an adult cranial sinuses child's?
|
Child does not have frontal sinuses (located above eyes)
both need to be palpated for tenderness |
|
|
For external nose examination what needs to be noted (no pun intended)
|
1. Rash, lesion, rhinophyma- acne rosacea
2. tenderness upon palpation- (furuncle) |
|
|
For internal nose examination what needs to be noted (no pun intended)
|
1. Nasal mucosa- (color, bleeding, edema, exudate)
2. Foreign body 3. Nasal septum- deviation 4. Turbinates- superior, middle, and inferior 5. Ulcers- (cocaine users) or polyps (allergy association) |
|
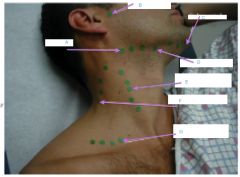
Upon inspection of the neck what might you keep an eye out for?
|
1. Surgical scars
2. Masses- parotid glands, submandibular nodes, lymph nodes a. tonsilar b. preauricular c. submental d. submandibular e. anterior cervical f. posterior cervical g. supraclavicular |
|
|
With the following lymph node problems what pathology might you expect?
a. cervical adenopathy w/o neck infection b. enlarged and firm supra clavicular node c. tender enlarged sub-mandibular lymph nodes |
a. mononucleosus
b. lymphoma (gastro or intra thoracic) c. upper respiratory infection |
|
|
With the following lymph node problems what pathology might you expect?
a. rubbery, non-tender anterior cervical lymph nodes b. enlarged posterior cervical nodes |
a. Tuberculous adenitis (TB?)
b. scalp infections- toxoplasmosis or rubella |
|
|
What three main things may cause tracheal deviation found upon palpation?
|
1. pneumothorax
2. atelectasis 3. mass in neck |
|
|
Name the following pathologies by the description of the palpated thyroid...
a. soft gland b. smooth and free of nodules c. firm gland d. tender gland |
a. Graves disease
b. normal thyroid findings c. Hashimoto's disease or benign/malignant nodule d. thyroiditis |

