![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ions are formed when... |
...electrons are transferred from one atom to another. |
|
|
The simplest ions are single atoms which have either lost or gained electrons so as to have a... |

...full outer shell. |
|
|
There are lots of ions that are made up of a group of atoms with an overall charge. What are these called? |
Molecular ions. |
|
State the formula for the following ions. |
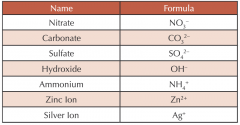
|
|
|
Charges in ionic compounds always... |
...balance out to 0. |
|
|
How are ionic compounds formed and what type of bonding to they use? |
|
|

|

|
|
|
What is formed when an acid and a base react? |
They form water and a salt. |
|
|
What is a salt? Describe the structure. |
|
|
|
What is the name of water in a lattice? What is the name of a solid salt containing water and a solid salt that doesn't? |
|
|
|
How is water held inside the lattice in a salt? |
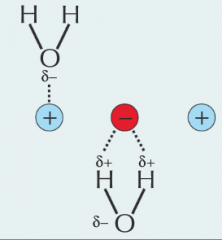
Due to the lattice and waters polarity, they are able to form bonds due to the opposite charges. |
|
|
.......... mole of a particularly hydrated salt always has the same number of ......... of ............ of ............. . |
1. one 2. moles 3. water 4. crystallisation |
|

|

|

