![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Water - H2O - Delta Charges - Hydrogen Bond |
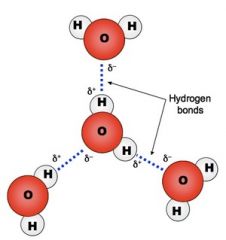
|
|
|
Ice Floats as Less Dense Than Water |
- Molecule spread out and form a crystal lattice structure. Due to the hydrogen bond fixing lightly further apart than in the liquid state. - Forms an insulating layer so water and organism do not freeze underneath. - Organisms can still move; Nutrients circulate. - Provides habitat for animals such as polar bears |
|
|
Polar Solvent |
- Charged polar ions interact with water as its a polar molecule - Forms most of the cytosol where reactions occur in cells, allows substances to interact and react. - Organisms can take up minerals such as nitrates for amino acids. |
|
|
Temperature Stability |
- Many hydrogen bonds between molecules so high specific heat capacity. - Only small variation in temperature - Minimises effect of temperature on enzymes (narrow range, denatured) - Important in cells and aquatic environments. |
|
|
Surface Tension |
- Due to hydrogen bond - Provides habitat for organisms such as pond skaters |
|
|
Transport Medium |
- Polar Molecule - Solvent - Helps transport dissolved substances into and out of cells as well as around organisms |
|
|
Coolant |
- High latent heat of vaporisation - much energy required to turn water into a gaseous state - Sweating and panting used to cool organisms to maintain body temperature. |
|
|
Cohesive |
- Molecules of water are attracted to each each other - Water moves as one mass |
|
|
Adhesive |
- Molecules of water are attracted to other polar surfaces molecules/surfaces - Water can rise up a tube such as the xylem of a plant. |
|
|
Transparent |
- Light can pass through cells or bodies of water for photosynthesis |

