![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
rate-determining step
|
in a multistep mechanism, the step that requires the largest activation energy
|
|
|
What affects the rate of the reaction?
|
1. the larger the Ea, the slower the rxn
2. the higher the concentration of starting material, the faster the rxn 3. the higher the temp. the faster the rate |
|
|
RATE EQUATION OF RXN
|
rate = K [reactants]
K = rate constant [concentration of reactants] |
|
|
How do catalysts work?
|
- lower Ea
-does not effect product |
|
|
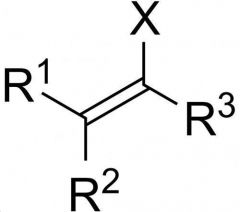
VINYL HALIDE
do not under SN or E reactions because sp² hybridized |
|
|
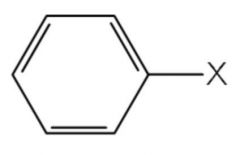
ARYL HALIDE
do not under SN or E reactions because sp² hybridized |
|
|
best leaving group for halogens?
|
iodine
|
|
|
perfect electron deficient group?
|
carbocations
|
|
|
alkyl halides and Brønstead bases
|
elimination rxn
|
|
|
alkyl halides and nucleophiles
|
substitution reactions
|
|
|
as the size of the leaving group increases ( F < Cl < Br < I).....
|
basicity decreases
(size increases down the column, basicity increases up the column) |
|
|
What makes a better leaving group?
|
A weaker base (which is a stronger acid)
|
|
|
Nucleophilicity increases with...
|
basicity
(from right to left on the periodic table) |
|
|
What determines whether a nucleophile or a base?
|
steric hinderance
|
|
|
A molecule that has less steric hinderance
|
is a stronger nucleophile and a weaker base
ex: ethoxide |
|
|
A molecule with more steric hinderance
|
is a weaker nucleophile and a stronger base
ex: tert-butoxide |
|
|
e2 / sn2 rate equation
|
rate eq = K [RX] [B/NU:]
|
|
|
all sn2 reactions proceed with.....
|
a back attack of the nucleophile, resulting in an inversion of configuration (inversion only when carbon being attacked is already a stereogenic center)
|
|
|
rate determining step in sn2 mechanism
|
formation of the carbonation (which is sp2 hybridized)
|
|
|
what stabilizes a carbocation
|
-INDUCTIVE EFFECT (alkyl chains donate e- via hyperconjugation)
-RESONANCE |
|
|
in an endothermic rxn, what product is formed faster?
|
the most stable product forms faster
(in exothermic, either or may form faster) |
|
|
e1 / sn1 rate equation
|
rate = K [RX]
|
|
|
in an exothermic reaction, what is formed?
|
the most stable product may or may not be formed faster (b/c the Ea in both cases is similar)
|
|
|
polar protic solvents favor...
|
SN1 & E1
|
|
|
polar aprotic solvents favor...
|
SN2 & E2
|
|
|
What generally has a negative charge?
|
bases and good nucleophiles
|
|
|
Regioselective
|
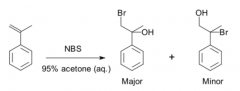
the rxn yields a CONSTITUTIONAL isomer predominantly or exclusively
|
|
|
Stereoselective
|
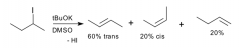
The rxn yields a STEREOISOMER predominantly or exclusively
|
|
|
syn periplanar
|
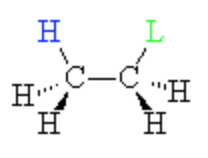
H & X on same side
|
|
|
anti periplanar
|
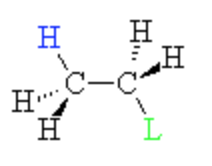
H & X on opposite sides
- E2 occurs via anti-periplanar elimination |
|
|
How are alkynes prepared?
|
Two successive elimination rxns
(geminal and vicinal dihalides) |
|
|
geminal dihalide
|
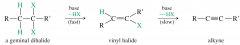
both halogens are on the same carbon
|
|
|
vicinal dihalide
|
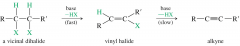
the halogens are on opposite carbons
|

