![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
An Act to reform the law relating to thehealth & safety of employees and other people at work or affected by thework of other people’ |
Health & Safety (H&S) inEmployment Act 1992 , Amendment 2002 |
|
|
What are the duties of the employers? |
1. Safe & healthy working environment 2. Health & Safety Inductions to newemployees 3. Safe machinery, facilities, equipment 4. Supervision, training and instruction towork safely 5. Safe access to & egress fromworkplaces 6. Systematic process to identify andcontrol hazards 7. Supervisor responsible to investigate incidents /accidents |
|
|
What are the duties of employees? |
1. Their own safety whileat work, including using suitable protective clothing & equipment providedby the employer 2. No action or inaction ofthe employee while at work causes harm to any other person |
|
|
What is Harm? |
Means illness, injury or both; and includes physical or mental harm caused by work-related stress |
|
|
What is Serious Harm? |
Any condition that results in permanent loss of bodily function /temporary severe loss Example: Amputation of body part Serious Burns Loss of consciousness Any harm that causes the person harmed to be hospitalised for a period of 48 hours or more commencing within 7 days of the harms occurrence |
|
|
What is Hazard? |
Anysource of potential damage, harm or adverse health effects on something orsomeone under certain conditions at work. It cancause harm or adverse effects (to individuals as health effects or toorganizations as property or equipment losses). |
|
|
Give some examples of Actual or Potential source of harm? |
1. activity,arrangement, event circumstance, occurrence, phenomenon, process, situation or substance 2. person’sbehaviour |
|
|
What is Risk? |
Thelikelihood of an incident and the consequence of the incident |
|
|
How do we manage hazards? |
By doing a RISK ASSESSMENT |
|
|
What is the most effective way of control? |
Hierarchy of Controls (how we control risks) |
|
|
What does Hierarchy of Controls consists of? |
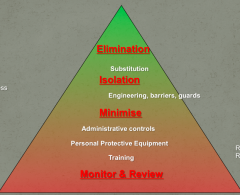
|
|
|
How do we manage accidents and near misses? |
1. Notifysupervisor ASAP 2. Recording& notification of incidents documents and process 3. Investigationinto cause of accident 4. Worksafe NZ:notification of Serious Harm 5. Employeesmay (are permitted to) refuse to perform work likely to cause serious harm |
|
|
What are the type of Hazards? |
1. Biological 2. Chemical 3. Physical 4. Ergonomic 5.Psycho-social |
|
|
How do we reduce the risk of bio hazards? |
Wearing PPE Infection control Sterilisation |
|
|
What is a Material Safety Data Sheet implemented by the Hazardous Substances & New OrganismsAct – HSNO? |
Explainswhat the hazards are for the product and the appropriate controls |
|
|
•How do we handle chemical hazardous substances? |
1. Wearcorrect PPE 2. Handlematerials with care 2. Correctstorage 3. Followsafety & use instructions 4. Ensurethat first aid provision is made 5. Reportincidents immediately |
|
|
Examples of Physical Hazards? |
1. Premises(flooring, lighting, etc.) 2. SecurityEquipmentand plant (testing and maintenance) 3. StorageFireor emergency egress 4. Sourcesof radiation and electricity |
|
|
Examples of Chemical Hazards? |
•Explosives •Gases (combustible, toxic & flammable) •Liquids (combustible, toxic & flammable) •Oxidising substance •Toxic substance •Corrosive substances |
|
|
Examples of Biological Hazards? |
Bacterial Viral Fungal Parasites |
|
|
Examples of Ergonomic Hazards? |
Bad working habits |
|
|
What are the steps to prevent harm related to ergonomic hazards? |
1.Take a break 2. good working posture 3. good working station |
|
|
Examples of Psycho-socio Hazards? |
1. Workloads 2. Excessivestress 3. Workingalone/together 4. Drugs/alcohol 5. Home& family 6. Parentalpressure 7. Studypressure |
|
|
How to avoid strain on your back when sitting on your work chair? |
1. set chair height first – feetflat on floor 2. now draw up to workstation 3.comfort is when shoulders are lowand elbows hang comfortably at the side 4. adjust the backrest height so that yourbottom fits into the space between the backrest and the seat pan 5. the backrest should support thehollow of your back |
|
|
hasultimate responsibility for providing a healthy and safe environment for all ofits staff, students, visitors, contractors and members of the public who maytake part in, or be affected by, the University's activities. |
The University Council |
|
|
executiveresponsible of Health and Safety at AUT |
VC and senior leadership |
|
|
operationalresponsible of Health and Safety at AUT |
Managers and supervisors |
|
|
healthand safety of students in their class |
Academic Supervisor |
|
|
Supportingand facilitating role in promoting the highest practicable standard ofoccupational health, safety and wellbeing within AUT that is in compliance withthe national standards. |
The(AUT) Occupational Health and SafetyTeam: |

