![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the structural differences between bronchi and bronchioles?
|
Bronchi:
Cartilage SM Mucosal glands Bronchioles: No cartilage No glands |
|
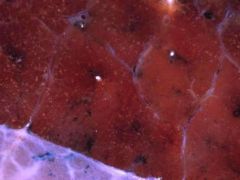
What are the white lines? White dots? What runs through both?
|
White lines: interlobular septae
Dots: bronchovascular bundles - lymphatics, bronchi |
|
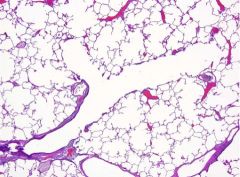
What structures are present here?
|
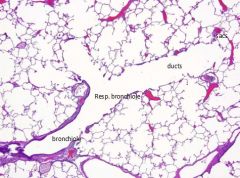
The different components of the normal lung
|
|
|
What are the different conditions under the heading of obstructive pathology?
|
Empysema
Chronic Bronchitis Asthma Bronchiectasis |
|
|
What are the characteristics of centriacinar emphysema?
|
Involves central/proximal parts of the acini
More severe in upper lobes Predominant in heavy smokers |
|
|
What are the characteristics of panacinar emphysema?
|
Acini uniformly involved from resp. bronchiole donw
More severe at bases Associated with alpha-1-antitrypsin problems |
|
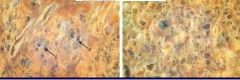
What types of lung pathology is happening in each picture?
|
Left: centraacinar emphysema
Right: paraacinar |
|
|
What are the symptoms of empysema?
|
Dyspnea
Cough, wheezing Weight loss |
|
|
When do patients with emphysema start to show symptoms?
|
When 1/3 of the lung parenchyma is destroyed
|
|
|
What is the cute description of people with emphysema?
|
"Pink puffers"
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of chronic bronchitis?
|
Persistent cough with sputum production
Dyspnea upon exertion |
|
|
What are serious systemic secondary problems to chronic bronchitis?
|
Cor pulmonale
Cardiac failure Recurrent bacterial infections |
|
|
What is the cute description of people with chronic bronchitis?
|
Blue bloaters
|
|
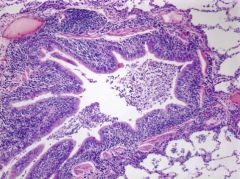
What pathology is present here?
What are some observations that lead you to think this? |
Chronic bronchitis
Inflammation of the bronchial wals Increase in mucus secreting golbet cells |
|
|
What are the different types of asthma?
|
Atopic asthma
Nonatopic asthma Drug-induced asthma Occupational asthma |
|
|
What triggers atopic asthma?
|
Environmental antigens
|
|
|
What type of a hypersensitivity reaction happens in atopic asthma?
|
TypeI hypersensitivity
|
|
|
What is a cause of nonatopic asthma/
|
Virus
Lowers threshold of lung receptors to irritants |
|
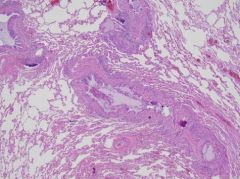
What type of lung pathology is present? What causes you to think this?
|
Asthma
Intact parenchema Thinning of airway; basement membrane thickening Edema and inflammatory infiltrate in wall Mast cells, eosinophils SM hypertrophy |
|
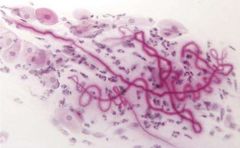
What do you see here? What conditions are these present in?
|
Curschmann spirals: spirally shaped mucus plugs with lots of eosinophils inside of them.
Astma |
|
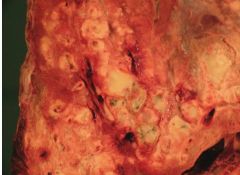
What condition is grossly present? What is the pathophysiology?
|
Widening of the airways causes impeded mucociliary clearance. Causes severe obstructive disease.
|
|
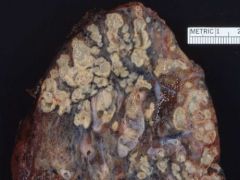
What is a fungal infection of the lungs that we learned about?
|
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Allergic reaction to a common fungus. |
|
|
What is the presentation of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis?
|
Insidious cough
Abundant sputum Impaired surfactant clearance from the lungs |
|
|
What are the three types of PAP?
|
Acquired: most common - autoantibody to GM-CSF
Congenital Secondary |
|
|
What is the treatment for PAP?
|
Lavage
|
|
|
What is goodpasture syndrome?
|
AutoAbs against collagen IV
|
|
|
What problems happen in the lungs due to goodpasture syndrome?
|
Necrotizing hemorrhagic interstitial pneumonia due to destruction of the basement membrane.
|

