![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common ultrasonographic finding in ectopic pregnancy?
|
Free fluid in the pouch of douglas and an empty uterus.
|
|
|
What are risk factors for ectopic pregnancy?
|
Previous STDs and PID, previous ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, previous instrumentation. IUD is NOT a risk factor.
|
|
|
A pregnant woman is in the ED and you obtain a urinalysis. She has bacteria on microscopic analysis, but no WBCs, nit, or leuk est. What should you do?
|
Treat asymptomatic bacteriuria in all pregnant patients.
|
|
|
A woman is 5 weeks pregnant and on her wet mount she has pear-shaped motile organisms with flagella at one end. How do you treat her?
|
Flagyl 2gms in a one time dose.
|
|
|
True or false: If a woman has a PE during pregnancy, she should be anticoagulated with coumadin.
|
False: she should receive heparin or lovenox
|
|
|
What defines a UTI as pyelonephritis?
|
CVA tenderness or white cell casts on urinalysis or fever with UTI
|
|
|
When is cystitis or a UTI complicated?
|
In any man, pregnant woman, anatomic abnormalities, presence of foley catheter, recent antibiotics, recurrent UTIs, kidney stones, or with any post-void residual.
|
|
|
What are the 2 most common pathogens in UTIs?
|
E. coli (85%)
Staph saprophyticus (10%) |
|
|
What is the most common cause of priapism in children?
|
Sickle cell disease
|
|
|
A woman is 2 months post-partum and presents with a fever of 103 and unilateral breast pain and swelling. What is the organism responsible, and how is this disease treated?
|
The patient has mastitis, usually caused by S. aureus. It is treated with warm compresses, anti-staph antibiotics, breast support, pain control, and continued nursing of the infant. if frank purulent drainage is noted, breast-feeding is discontinued until it resolves.
|
|
|
An 80 year old woman presents with vaginal bleeding. After assuring she is not anemic and has normal platelets and coagulation studies, what are the top two likely diagnoses and what should you do with the patient?
|
The top two causes of post-menopausal bleeding are vaginal atrophy and endometrial cancer, in that order. The patient should be referred urgently for outpatient biopsy of her endometrium.
|
|
|
By what mechanism does obesity cause dysfunctional uterine bleeding?
|
Fat produces estrogens, which interfere with the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
|
|
|
A 2 week old girl presents with vaginal bleeding. Her exam is otherwise normal. What is the likely cause?
|
Newborn girls often have vaginal bleeding as they withdraw from the high estrogen mileau of the mother after birth.
|
|
|
A 3 year old presents with malodorous vaginal discharge. What are 3 diagnoses you should consider?
|
Chemical irritation, child abuse, and foreign body (most common cause)
|
|
|
A woman presents with painless third trimester bleeding. How should you evaluate her?
|
Ultrasound and sterile speculum exam. Do NOT do a bimanual exam. If the patient has a placenta previa, you could cause increased bleeding and placental disruption.
|
|
|
A woman presents in labor. On pelvic exam, you see the cord in the vagina. What should you do?
|
Use your hand to manually displace the baby's head from the pelvic brim to prevent compromise of blood flow in the cord. Have someone else call to get a surgeon and an OR for emergency C-section. Do not remove your hand until you are in the OR.
|
|
|
What is the best way to diagnose abruption?
|
KB test, or fetal hemaglobin in maternal circulation. ultrasound does not detect abruptions involving less than 30% of the area of the placenta.
|
|
|
What are the traditional limits of ultrasound for detection of IUP based on hCG quantitative levels?
|
1000 to 1500 for transvaginal, 6000 to 6500 for transabdominal.
|
|
|
A 15 year old boy complains of unilateral testicular swelling and pain. He has no cremasteric reflex on the involved side, and the testicle is swollen and tender. He has no hernia palpable at the inguinal canal. What is your differential, and what should you do?
|
You should think about epididymitis and testicular torsion. you should get an emergent ultrasound, and should attempt to detorse the testicle by rotating externally, or open book rotation.
|
|
|
What are medications that can be used to reduce priapism?
|
phenylephrine, terbutaline
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of fetal demise with maternal survival in trauma?
|
abruption
|
|
|
what is supine hypotensive syndrome in the setting of pregnancy?
|
women who are greater than 20 weeks pregnant have compression of the IVC by the fetus while lying supine. they will become hypotensive secondary to decreased venous return if they are not tilted 15 degrees to the left.
|
|
|
what is the incidence of abruption in trauma?
|
5% for minor trauma, 50% for major.
|
|
|
Why are fetal heart tones part of the PRIMARY SURVEY for trauma?
|
because maternal hemodynamics are preserved at the cost of the fetus, so the earliest indicator of maternal compromise is fetal compromise
|
|
|
When should you consider a crash C section in a trauma patient?
|
fetal age greater than 24 weeks, maternal arrest less than 5 minutes, or maternal instability or shock with vaginal bleeding.
|
|
|
What are Amsel's criteria for diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis?
|
positive whiff test
clue cells on microscopy pH greater than 4.5 thin, homogeneous discharge requires 3 of 4 |
|
|
what is the most common etiology of vaginitis in children?
|
non-specific vaginitis, from tight clothing, soaps, irritants, and allergens
|
|
|
what is the most common etiology of vaginitis in adults?
|
infectious, with most being bacterial vaginosis, then candida, then trichomonas
|
|
|
Candida, which is treated with oral fluconazole or miconazole suppository.
|
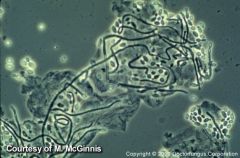
What organism is this, and how is it treated?
|
|
|
Candidal vaginitis
|
What is the likely diagnosis?
|
|
|
The upper image is abnormal, and it shows clue cells. The likely diagnosis is bacterial vaginosis, and it is treated with flagyl.
|
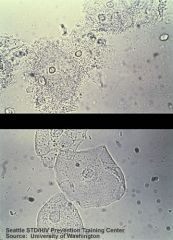
Which of these wet mounts is abnormal, and what is the likely diagnosis and appropriate therapy?
|
|
|
Bacterial vaginosis
|
The patient has a vaginal pH of 7 and a thin watery discharge. What is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
A week
|
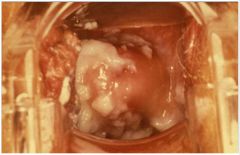
This patient is pregnant. How long should you treat her for?
|
|
|
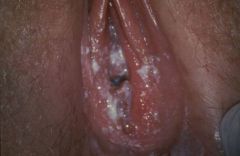
This is a strawberry cervix, and it is pathognomonic for trichomonas infection
|
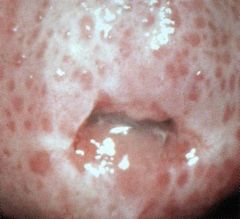
What is this pathognomonic for?
|
|
|
Intravaginal or oral flagyl
|
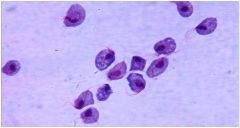
How do you treat this infection?
|
|
|
Trichomonas
|
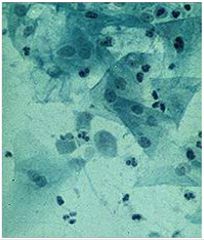
What is the diagnosis?
|
|
|
You should treat this. This is trichomonas, and it can be treated with clindamycin or flagyl.
|
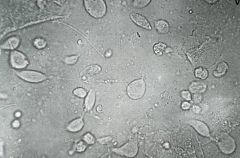
This patient is pregnant. Should you treat this infection, and if so, with what?
|
|
|
Trichomonas
|
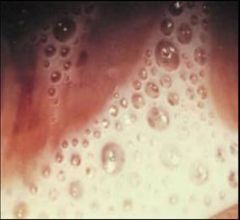
This patient has itching and a positive whiff test. What is the likely diagnosis?
|
|
|
This patient has candidiasis. You only need to give her a single dose of fluconazole
|
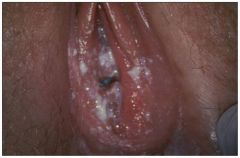
This woman is not pregnant, and complains of itching and external dysuria. How long should you treat her?
|
|
|
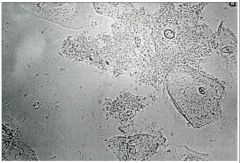
Pseudohyphae from candida
|
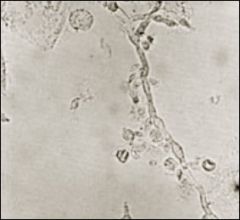
What does this wet mount show?
|
|
|
Why are pregnant women at increased risk for aspiration?
|
They have increased intraabdominal pressure, delayed gastric emptying, and relaxation of their lower esophageal sphincters.
|
|
|
Why are pregnant women at increased risk for bladder injury in trauma cases?
|
Because during pregnancy, the bladder becomes an abdominal rather than a pelvic organ.
|
|
|
During the 1st half of pregnancy, list 4 reasons for vaginal bleeding.
|
ectopic, implantation bleeding, cervicitis, subchorionic hemorrhage, gestational trophoblastic disease, abortion
|
|
|
List the types of abortion
|
Spontaneous
Threatened: Bloody vaginal discharge or frank bleeding during the 1st half of pregnancy without cervical dilatation Inevitable: Vaginal bleeding and cervical dilatation Incomplete: Passage of parts of POC More common between 6 and 14 weeks Complete: Passage of all fetal tissue before 20 weeks Missed Septic: Infection during any stage of abortion |
|
|
When discharging a patient with a diagnosis of threatened abortion, what 2 things are important to discuss with the patient?
|
Close follow up
and avoidance of infection by avoiding tampons and intercourse. low level activity and bedrest have no proven efficacy |
|
|
A 32 multiparous female at 32 weeks gestational age presents to the ED with RUQ pain. Laboratory studies reveal a normal alkaline phosphatase, normal lipase, platelets of 68,000, AST 250, ALT 280. What diagnosis should you suspect?
|
HELLP Syndrome, which is a clinical variant of pre-eclampsia. It includes hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets.
May see schistocytes, abnormal coagulation profile and elevated BUN and creatinine in addition to above. |
|
|
List 3 causes of vaginal bleeding during the second half of pregnancy.
|
abruption, previa, PROM, lesions of the cervix or lower genital tract, preterm labor
|
|
|
A 16 year old female presents to the ED with abdominal bloating. She states that she has noticed that over the last few months, she has felt bloated. She states her periods have always been irregular and she can’t remember her last menstrual period. She is sexually active, G2P0020. On physical exam, you palpate a gravid uterus to the level of the umbilicus. What gestational age would you estimate for this patient?
|
20 weeks
|
|
|
A 24 year old female presents to the ED with RUQ pain. She states she was recently treated for PID and can’t remember what medication she is taking; however, she has about 10 pills left. She has a history of multiple gonorrhea and chlamydial infections in the past. What diagnosis should you suspect?
|
FitzHugh-Curtis syndrome:
Hepatic capsule infection with acute perihepatitis and focal peritonitis. Can occur from direct or lymphatic spread. Risk factors include multiple sexual partners, history of STDs, frequent vaginal douching, history of sexual abuse and IUD use. |
|
|
A 60 year old female presents to the ED with abdominal pain, bloating, weight loss and constipation. On physical exam, you notice a large amount of ascites with no signs of a hepatic etiology. She is diagnosed with a gynecological malignancy. What type would you suspect?
|
Ovarian cancer.
Usually presents after spread of disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, ascites, early satiety, weight loss, and respiratory distress secondary to effusion. Usually presents in the advanced stage secondary to lack of symptoms until metastasis. |
|
|
A 58 year old female presents to the ED with vaginal bleeding. Although not the most common cause, you should consider this at the top of your differential diagnosis.
|
Uterine cancer:
Most common gynecological malignancy. Risk factors include early menses, late menopause, nulliparity, obesity, DM, HTN, unopposed estrogen use, and tamoxifen use. |
|
|
a 75 year old woman presents with vaginal bleeding. What are the number 1 and number 2 diagnostic entities on your differential?
|
The most common cause of post-menopausal bleeding is atrophy. Decreased estrogen results in tissue thinning. The second most common cause of post-menopausal bleeding is endometrial cancer. the diagnosis can be made by biopsy.
|
|
|
a woman has a positive pregnancy test. on her ultrasound, you see a yolk sac implanted in the inferior 1/3 of the uterus. what should you tell her?
|
fetal implantation should be in the top 1/3 or fundus of the uterus. low fetuses either miscarry or are considered ectopic (cervical ectopic). then need urgent followup with OB/GYN.
|
|
|
A pregnant woman presents in active labor. You take a look and see umbilical cord in the vagina. What should you do immediately?
|
put the patient in trendelenberg (this may in fact be the only indication for trendelenberg), put your hand in the vagina, and manually displace the baby's head superiorly away from the pelvic brim to prevent it impinging on the cord. stay like that until she is in the operating room and they are removing the baby surgically.
|
|
|
a woman with a history of infertility presents to the ED with left lower quadrant pain. she has undergone 3 cycles of clomid and is now on injectable fertility agents. she has a positive pregnancy test and you visualize an IUP on ultrasound. You cannot assess the left adnexa. what do you tell her?
a. congratulations. go home. b. you might still have an ectopic. i should probably get a formal ultrasound and talk to your OB c. you probably are constipated. take some miralax d. that's probably just round ligament pain. |
b. you may still have an ectopic. heterotopic pregnancies are rare birds, and don't generally occur in nature. once science is involved, though, they are a real risk. if a patient has pain, an IUP isn't enough to make you rule it out. now, if the patient had never taken a fertility agent, heterotopic pregnancy is reportable, it's so unusual.
|
|
|
a breast feeding woman has a fever of 104 and severe breast pain. her breast is erythemetous and tender. what is the treatment?
a. stop breast feeding, hot soaks b. stop breast feeding, start antibiotics c. hot soaks, antibiotics, keep breast feeding d. keep breast feeding, antibiotics, gentle massage |
d is probably your best bet. stopping breast feeding never helps. hot packs often worsen pain and engorgement, and are usually not recommended. gentle massage, which hurts, may still help alleviate engorgement. some people now advocate cool packs, as well, even for non-infectious engorgement. antibiotics should cover staph. keep in mind that in babies with thrush and moms with immune system problems, candida is also an unusual but real possibility.
|

