![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
325 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Most common cause of preterm birth |
Placenta Previa or abruptio |
|
|
|
Birth before 37 weeks from the first day of LMP or 245 days after conception |
Preterm birth |
|
|
|
Contraction with cervical change before 37 weeks |
Pre term labor |
|
|
|
Fetus pregnancy or neonate that is between 20 to 37 weeks |
Preterm |
|
|
|
Underdeveloped organ function |
Premature |
|
|
|
Preterm labor with Intact membranes PPROM preterm cervical effacement or insufficiency and uterine bleeding |
Spontaneous preterm birth |
|
|
|
Medically initiated |
Indicated preterm birth |
|
|
|
Single most powerful predictor of preterm |
TVS |
Best time to screen: 22 to 25 weeks aog |
|
|
Tocolytic of agent of choice in preterm |
Nifedipine |
|
|
|
Premature closure of ductus arteriosus |
Indomethacin |
|
|
|
Antibiotic of choice for preterm |
Ampicillin 2 grams iv q 6 Gentamicin 1.5 mg/kg q 8 |
|
|
|
Corticosteroid for Preterm |
Betamethasone 12 mg im q 24 for 2 days Dexa 6 mg im q12 for 4 doses |
|
|
|
Most catastrophic site of ectopic pregnancy -- madugo! |
Interstitial |
|
|
|
Most common site of ectopic pregnancy |
Ampulla |
|
|
|
Most common symptom of ectopic pregnancy |
Pelvic and abdominal pain |
|
|
|
Gold standard for ectopic pregnancy |
Laparoscopy |
|
|
|
Methotrexate dosage |
50 mg/m2 BSA |
|
|
|
Indication for Methotrexate |
1. Pregnancy is less than 6 weeks 2. Tubal mass of less 3.5 cm 3. NO cardiac activity 4. Serum Beta HCG <10 to 15k miU/ml |
|
|
|
Contraindications for methotrexate |
Active bleeding Breast feeding Immunodeficienxy Alcoholism Blood dyscrasia Liver or renal dse Pulmonary dse
|
|
|
|
Accessory gland infection and perihepatitis |
Gonorrhea |
|
|
|
Treatment for gonorrhea |
Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM single dose Azithromycin 1 gm PO single dose |
|
|
|
Gold standard dx for gonorrhea |
Culture (Thayer Martin) |
|
|
|
Vagina ph >4.7 Clue cells Fishy odor |
Bacterial vaginosis |
|
|
|
Tx for Bacterial Vaginosis |
Metronidazole |
Routine screening is not recommended Routine tx of sex partners not recommended |
|
|
Green yellow frothy discharge Strawberry cervix |
Trichomoniasis |
|
|
|
Tx for Trichomoniasis |
Metronidazole Partner should be treated Breastfeeding must be withheld to 12 to 24 hours after last dose |
|
|
|
Vulvar pruritus External dysuria and dyspareunia White curdy vaginal wall |
Vulvovaginal candidiasis |
|
|
|
Diagnosis for vulvovaginal candidiasis |
KOH or saline wet prep |
|
|
|
Best diagnostic tool for thyroid dse? |
TSH |
|
|
|
Goal of 3rd stage of labor |
Delivery of intact placenta Avoidance of uterine inversion Avoidance of post partum hemorrhage |
|
|
|
Signs of placental separation |
1. Globular and firmer fundus
2. Sudden gush of blood
3. Rise of uterus into abdomen
4. Lengthening of umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Unang yakap |
1. Immediate and thorough drying 2. Early skin to skin contact 3. Properly timed cord clamping 4. Non separation for early breastfeeding |
|
|
|
Lacerated extend through skin, mucous membrane, and perineal body and anal sphincter |
3rd |
|
|
|
Extension of laceration through the rectal mucosa to expose lumen of rectum |
4th |
|
|
|
Aside from skin and mucous membrane, the fascia and muscles of the perineal body |
2nd |
|
|
|
Fourchette perineal skin and vaginal mucous membrane but not the underlying fascia and muscle |
1st |
|
|
|
Goal is to bring fetal feet within reach Two fingers will push knee away from midline Spontaneous flexion of extremity follows Foot maybe grasped and brought down |
Breech decomposition |
|
|
|
Both feet grasped through the vagina Ankles held with 2nd finger bet them Feet brought through the introitus with gentle traction |
Complete breech extraction |
|
|
|
Breech spontaneously delivered to the umbilicus Posterior hip will deliver from 6 oclock Anterior hip delivers next Ext rotation to sacrum anterior Fetal bony pelvis grasped with both hands using cloth towel Fingers rest on anterior superior iliac Thumbs on sacrum |
Partial Breech Extraction |
|
|
|
Delivery of entrapped aftercoming head Divides sympheal cartilage to widen pubis symphisis pubis up to 2.5 cm |
Symphysiotomy |
|
|
|
Apply pressure on malar prominence to flex the head |
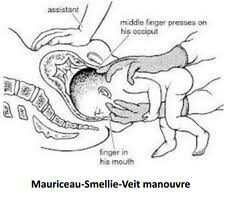
Mauriceau |
|
|
|
Incision on the cervix at 2 oclock and at the 10 oclock position |
Duhrssen Incision |
|
|
|
Puerperium period time |
4 to 6 weeks post delivery |
|
|
|
Prolonged latent phase for nulliparas |
>20 hours |
|
|
|
Prolonged latent phase for Multiparas |
>14 hours |
|
|
|
Protracted active phase dilatation for nulliparas |
At phase of max. slope <1.2 cm/hr |
|
|
|
Protracted active phase dilatation for multiparas |
At phase of max. slope <1.5 cm/hr |
|
|
|
Protracted descent for nulliparas |
At max slope of descent <1 cm/hr |
|
|
|
Protracted descent for multiparas |
<2 cm/hr |
|
|
|
Prolonged deceleration phase for nulliparas |
Arrested at deceleration phase (cx 8 to 9 cm) >3 hours Arrested at deceleration phase (cx 8 to 9 cm) >3 hours |
|
|
|
Prolonged deceleration phae for multiparas |
Arrested at deceleration phase (cx 8 to 9 cm) >1 hour |
|
|
|
Secondary arrest of dilatation for both nulliparas and multiparas |
Stops at phase of max slop for more than 2 hours |
|
|
|
Arrest of descent for both nulli and multiparas |
Stops during pelvic division station +1 >1 hour |
|
|
|
Failure of descent |
Station 0 Lack of descent during decel phase or 2nd stage of labor |
|
|
|
Prolonged 2nd stage for nullipara |
Cervix 10 cm >3 hours with RA >2 hours without RA |
|
|
|
Prolonged 2nd stage for multiparas |
Cx at 10 cm >2 hours with RA >1 hour without RA |
|
|
|
Suprapubic pressure over posterior aspect of anterior shoulder |
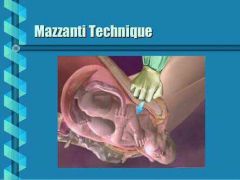
Mazzanti maneuver
|
Anterior shoulder disimpaction |
|
|
Two fingers vaginally pushing the posterior aspect of anterior shoulder towards chest |
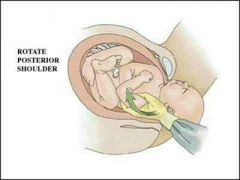
Rubin Maneuver |
Anterior shoulder disimpaction |
|
|
Two fingers on anterior aspect of posterior shoulder to rotate obliquely |
Woodscrew |
Rotation |
|
|
Patient in all 4's maneuver Grasp posterior arm and sweep against chest and deliver |
Gaskins maneuver |
Shoulder dystocia |
|
|
Restore fetal head to an occiput anterior or posterior position |
Zavanelli |
Shoulder dystocia |
|
|
Lateral rot of thigh flex knees |
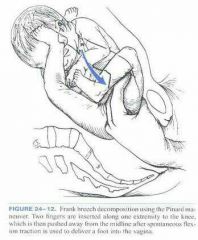
Pinard |
Breech delivery |
|

|
Loveset maneuver |
Breech delivery |
|
|
5 contractions in 10 mins |
Tachysystole |
|
|
|
Contractions lasting more than 2 mins |
Hypertonus |
|
|
|
Antidote for mag sulfate |
Calcium gluconate 10 ml of 10% |
|
|
|
Sonographic signs of preterm birth |
Shortening of cervix at 25 mm at 16 to 24 weeks Dilatation of internal os of more than 5 mm at 30 weeks Prolapse of membrane into cervix Funneling |
|
|
|
Biochemical markers for preterm |
Ffn elevated Mmp 8 elevated Insulin like factor binding protein 1 or actin partus Placental alpha microglobulin 1 or amnisute test |
|
|
|
What is the only reliable indicator of clinical chorioamnionitis in women with preterm rupture of fetal membrane |
Fever |
|
|
|
NEC |
Coamox |
|
|
|
When you proceed to delivery in PROM |
34 weeks and above |
|
|
|
When will you do expectant management in PROM? |
Less than 34 weeks |
|
|
|
Group b strep prophylaxis and corticosteroids are not recommended for this week of aog |
Less than 24 weeks |
|
|
|
Group b strep prophylaxis and corticosteroid use are recommended in this week of aog |
24 to 33 weeks |
|
|
|
Heavy vaginal bleeding Tissue with appearance of placenta Cervix open |
Incomllete abortion Plan for dilatation and curretage |
|
|
|
Minimal bleeding per os Passage of meaty tissue Cervix closed Uterus not enlarged |
Complete abortion Request for TVS |
|
|
|
TVS revealed intrauterine pregnancy No fht Cervix closed Uterus not enlarged |
Missed abortion Ripen the cervix then D&c |
|
|
|
Most Common symptom of ectopic pregnancy |
Pelvic and abdominal pain |
|
|
|
Painless vaginal bleeding |
Placenta previa |
|
|
|
Preterm labor for placenta previa management |
Tocolysis |
|
|
|
Vaginal delivery for placenta previa indicated for weeks aog |
More than 35 weeks |
|
|
|
Placental edge of more than 20 mm (2 cm) away from os |
Vaginal delivery |
|
|
|
Placental edge within 0 to 2 fm from os |
Vaginal delivery |
|
|
|
CS is indicated in previa |
Overlap 0 mm> >37 weeks fot previa >36 weeks for accreta |
|
|
|
Villi attached to myometrium |
Placenta accreta |
|
|
|
Villi actually invade the myometrium |
Placenta increta |
|
|
|
Villi that penetrate through the myometrium and to or through serosa |
Placenta percreta |
|
|
|
DIC intrinsic pathway |
Septic abortion Chorioamnionitis |
|
|
|
DIC extrinsic pathway |
Abruptio placenta, amniotic fluid embolism, retained dead fetus, saline induced abortion |
|
|
|
Most common cause of DIC |
Abruptio Placenta |
|
|
|
Frequent complication of precipitous delivery |
Uterine atony |
|
|
|
Nifedipine when combined to this will cause neuromuscular blockade |
Magnesium |
|
|
|
Gestational HTN criteria |
HTN after 20 to 40 weeks aog Normal BP after 12 weeks post partum No proteinuria |
|
|
|
Pre eclampsia Mild without severe features |
>140/90 after 20 weeks aog With or without proteinuria Platelet less than 100k Increase transaminase levels 2x above normal Serum creatinine >1.1 mg dl in absence of renal dse Pulmonary edema Cerebral or visual disturbances |
|
|
|
Pre ec with severe features |
>160/110 after 20 weeks aog RUQ or epig pain <100k Transaminase level elevated Serum crea more than 1.1> or 1.2 mg/dl in the absence of renal disease Oliguria <400 to 500 ml/day Pulmonary edema Severe headache altered mental status Partial or total loss of vision in normal appearing eyes |
|
|
|
Chronic HTN |
>140/90 prior to pregnancy before 20 weeks and persistent 12 weeks postpartum |
|
|
|
Terminate preg in severe pre eclampsia if weeks aog |
Less than 23 weeks |
|
|
|
Expectant management in severe pre eclampsia |
23 to 34 weeks |
|
|
|
DOC for gestational or chronic htn in pregnancy |
Methyldopa |
|
|
|
DOC for urgent control of severe htn in pregnancy |
Hydralazine |
|
|
|
Fetal growth restricion side effect of drug |
Labetolol |
|
|
|
Neonatal thrombocytopenia side effect of drug |
Hydralazine |
|
|
|
Impair fetal respnse to hypoxic stress side effect of drug |
Beta blocker |
|
|
|
Neonatal hypoglycemia at high doses side effect of this drug |
Beta blocker |
|
|
|
Volume contraction and electrolyte disorders side effect |
Hydrochlorothiazide |
|
|
|
Useful in combination with methyldopa and vasodilator to mitigate compensatory fluid retention |
Hydrocholorothiazide |
|
|
|
Inhibits labor synergistic axn with mgso4 in lowering bp |
Nifedipine |
|
|
|
Do CS if what age of gestion in severe pre eclampsia |
Less than 32 weeks |
|
|
|
Do vaginal delivery in severe pre eclampsia in what weeks aog |
>34 weeks |
|
|
|
Deliver baby if in severe pre eclampsia |
>34 weeks aog |
|
|
|
Dosage of Mgso4 |
4 g sivp 5 g im |
|
|
|
Serum Mgso4 levels |
4 to 7 meq/L (4.8 to 8.4 mg/dl) |
Prevents convulsions |
|
|
Patellar relflex disappears |
8 to 10 meq/l |
|
|
|
Prolonged av conduction |
12 meq /l |
|
|
|
Serum mgso4 level of respiratory depression |
12 to 15 meq/l |
|
|
|
Cardiac arrest |
24 meq/l |
|
|
|
Most common adverse cv event encountered in pregnant women |
Arrythmia |
|
|
|
Intermittent asthma |
<2 day / week daytime <2x /month nocturnal Normal fev1/fvc >80% predicted fev1
|
|
|
|
Mild persistent asthma |
>2 day/week daytime >3-4x /month nocturnal awakening Normal fev1/fvc >80% predicted fev1
|
|
|
|
Moderate persistent |
Daily symptom >1x per week but not nightly Reduced 5% fev /fvc 60 to 80% fev1 |
|
|
|
Severe persistent asthma |
Throughout the day Often 7x/wk <60% predicted fev1 Reduced more than 5% fev1/fvc |
|
|
|
Tx for severe persistent asthma |
High dose ICS LABA |
|
|
|
Tx for moderate persistent asthma |
Low dose ICS LABA |
|
|
|
Mild persistent asthma tx |
Low dose ICS |
|
|
|
Milt intermittent tx |
SABA |
|
|
|
Very severe persisent asthma tx |
Oral corticosteroid |
|
|
|
Most frequent complication of pneumonia in pregnancy |
Premature rupture of membranes |
|
|
|
Effect of chlamydia and gonorrhea to fetus |
Opthalmia neonatorum |
|
|
|
Ocular prophylaxis |
1% silver nitrate 1% tetracycline ointment or 0.5% erythromycin ointment |
|
|
|
Most common transmission of syphilis |
Transplacental |
|
|
|
Screening Diagnostic for Syphilis |
VDRL or RPR (reactive) |
|
|
|
Confirmatory test for syphilis |
FTA ABS TP - A MHA - TP |
|
|
|
Tx for early syphilis |
Benzathine pen G single IM dose |
|
|
|
Appears after penicillin tx of women with primary and secondary syphilis characterized by uterine contractions accompanied by fetal heart decelerations |
Jarisch Herxheimer rxn |
|
|
|
Indication for sx during pregnancy |
Appendicitis Adnexal mass Cholecystitis |
|
|
|
Overt DM |
FBS more than 126 mg/dl RBS more than 209 mg/dl HBA1c more than 6.5 2 hour 75 g ogtt more than 200 mg/dl |
|
|
|
GDM |
Fbs >92 mg/dl 1 hour >180 mg/dl 2 hour >153 mg/dl or >140 mg/dl |
|
|
|
No risk fx dm when is the best screening time |
24 to 28 weeks using 2 g ogtt |
|
|
|
If ogtt at 24 to 28 weeks normal what step will u do |
None |
|
|
|
If ogtt at 24 to 28 weeks normal but present with clinical signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia |
Retested at 32 weeks |
|
|
|
If with risk for dm |
2 hour 75 gram ogtt at 1st consult |
|
|
|
Dm pregnant when is delivery |
39 > weeks |
|
|
|
Elective cs if dm pregnant |
Feus is suspected to be obese Efw of >4500 grams |
|
|
|
Estimated blood loss of NSVD singleton |
500 to 600 ml |
|
|
|
Estimated blood loss of CS |
1000 ml |
|
|
|
Estimated blood loss of NSVD twins |
1000 ml |
|
|
|
Cervical mucus plug acts as a barrier against infection for the fetus because there an increase of this agent |
IgA and IgG IL-1B |
|
|
|
Vaginal mucus |
IL-B |
|
|
|
Results in remission in some of autoimmune disorder |
Supressed th1 response |
|
|
|
Iron rqt for normal pregnancy |
1k mg of iron |
|
|
|
Coagulation and fibrinolysis that increases |
Fibrinogen Factor 7 Factor 10 Flasminogen |
|
|
|
Softening of isthmus |
Hegars sign |
|
|
|
Increases on pulmonary fxn in pregnant |
TV and inspiratory capacity |
|
|
|
Weight of uterus at term |
1100 grans |
|
|
|
Term weight of uterus |
1100 grams |
|
|
|
Bluish tint of the cervix |
Goodells sign |
|
|
|
Soft in consistency of cervix due to |
Increased cervical edema |
|
|
|
Corpus luteum fxns maximally at |
First 6 to 7 weeks |
|
|
|
Total urine blood flow |
450 to 600 ml per min |
|
|
|
Increased vascularity vagina violet discoloration |
Chadwicks |
|
|
|
Metabolic demand in 1st tri |
85 kcal per day |
|
|
|
Metabolic demand in 2nd tri |
285 kcal per day |
|
|
|
Metabolic demand in 3rd tri |
475 kcal /day |
|
|
|
Leptin deficiency is associated with |
Anovulation Infertility |
|
|
|
Secreted primarily by stomach in response to hunger Cooperates with leptin in energy homeostasis modulation |
Grhelin |
|
|
|
Abnormally elevated leptin have been associated with |
Pre eclampsia and gestational dm |
|
|
|
Primarily secreted by adipose tse and some by placenta plays a role in body fat and energey expenditure regulation |
Leptin |
|
|
|
Increased electrolytes and minerals |
Iodine Iron |
|
|
|
Decreased in adrenal hormone |
DHEAS |
|
|
|
Chadwick sign is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Montgomery tubercle is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Chloasma is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Thermal changes is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Striae gravidarum is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Linea nigra is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Spider telangiectasia is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptivs |
|
|
|
Perception of fetal movement by patient is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Nausea and vomiting is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Breast tenderness is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptivw |
|
|
|
Positive preg test is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Probable |
|
|
|
Outlining of fetal parts is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Probable |
|
|
|
Abdominal enlargement is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Probable |
|
|
|
Goodelss sign is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Probable |
|
|
|
Hegars sign is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Probable |
|
|
|
Ballotment is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Probable |
|
|
|
FHT is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Positive |
|
|
|
Ballotment happen at |
20 weeks |
|
|
|
Fht via ultrasound |
5 to 8 weeks |
|
|
|
Fht via doppler |
10 to 12 weeks |
|
|
|
Fht via stet |
16 to 19 weeks |
|
|
|
Fetus via utz see gestational sac |
4 to 5 weeks |
|
|
|
Fetus via utz see fetal heartbeat |
6 weeks |
|
|
|
Fetus via ultz see crown rump length |
12 weeks |
|
|
|
Embro or fetus by utz is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Positive |
|
|
|
Fetal movement perceived by examiner is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Positive |
|
|
|
Fetal movement will be perceived by examiner by |
20 weeks aog |
|
|
|
Secondary ammenorrhea is presumptive/probable or positive sign and symptom? |
Presumptive |
|
|
|
Ductus venosus will become |
Ligamentum venosum Falciform ligament |
|
|
|
Umbilical artery will become |
Umbilical ligament |
|
|
|
Umbilical vein will become |
Ligamentum teres |
|
|
|
Umbilical artery and vei will close at |
3 to 4 days |
|
|
|
Ductus arteriosus and venosus closes |
2 to 3 weeks |
|
|
|
Foramen ovale closes |
1 yr |
|
|
|
Functionally closes venosus at |
10 to 96 hours |
|
|
|
Fxnally closes ductus arteriosus |
10 to 12 hours |
|
|
|
Presence of terminal sac |
26 weeks |
|
|
|
Bronchial branching |
16 to 26 weeks |
|
|
|
Surfactant detectable in the amniotic fluid |
24 weeks |
|
|
|
Secondary septation |
32 weeks |
|
|
|
Formation of major airways Birth of acinus |
6 to 16 weeks |
|
|
|
Pulmonary surfactant mature |
34 weeks |
|
|
|
Amniotic fluid by 12 weeks |
60 ml |
|
|
|
Amniotic fluid by 34 to 36 weeks |
1 L |
|
|
|
Amniotic fluid by term |
840 ml |
|
|
|
Amniotic fluid by 42 weeks |
540 ml |
|
|
|
Removal and regulation of amniotic is done by |
Fetal swallowing Fetal aspiration Exchange through skin and fetal membranes |
|
|
|
Source of amniotic fluid by early preg |
Maternal plasma as ultrafiltrate |
|
|
|
Source of amniotic fluid by 2nd trimester |
ECF that diffuses through fetal skin |
|
|
|
Source of Amniotic in more than 20 weeks |
Fetal urine |
|
|
|
Nephrotoxicity and otoxicity side effect in preterm infants |
Aminoglycosides (gentamicin or strep) |
|
|
|
Gray baby syndrome in neonates |
Chloramphenicol |
|
|
|
1st trimester hypoplastic left heart syndrome Microphthalmia Anophthalmia Clefts and asd |
Nitrofurantoin |
|
|
|
1st tri: anencephaly, left ventricular outflow obstruction, choanal atresua and diaphragmatic hernia |
Sulfonamides |
|
|
|
More than 25 weeks yellowish brown discoloration of deciduous teeth |
Tetracycline |
|
|
|
Cleft |
Corticosteroid |
|
|
|
Miscarriage and ear defects |
Mycophenolic acid |
|
|
|
Hypopladtic t shaped uterine cavity Cervical colars and breast ca Epididymal cysts Hypospadia Cryptorchidism |
Diethlystilbesterol |
|
|
|
Embryopathy at 6 to 9th week Stippling of vertebrae Nasal hypoplasia Choanal atresia |
Warfarin |
|
|
|
Clover leaf skull Wide nasal bridge Low set ears Micronathia Limb abnormalities |
Methotrexate |
|
|
|
Irreversible hypothyroidism Risk of thyroid cancer |
Radioiodine |
|
|
|
Ebsteim anomaly Displacement of tricuspid valve |
Lithium |
|
|
|
Cranial neural defects |
Retinoid - most potent teratogen |
|
|
|
Retinol of how many iu per day causes defect |
More than 10,000 |
|
|
|
Most common non lethal trisomy |
Downs syndrome |
|
|
|
Strawberry shaped cranium trisomy 18 |
Edwards |
|
|
|
Holoprosencephy |
Patau |
Trisomy 13 |
|
|
Only monosomy compatible with life |
Turners |
45 x |
|
|
Most common sex chromosome abnormality |
Klinefelters |
47xxy |
|
|
Microdeletion Cat like cry |
Cri du chat |
|
|
|
Fetal movement in primigravid |
18 weeks to 20 weeks |
|
|
|
Fetal movement in miltigravid |
16 to 18 weeks |
|
|
|
Crown rump length be detected at |
10 to 12 weeks |
Most accurate tool for gestational assignment |
|
|
Yolk sac |
5 to 6 weeks |
|
|
|
Embryonic pole with cardiac motion |
6 weeks |
|
|
|
Fh is at pubic symphysis |
12 weeks aog |
|
|
|
Fh is at umbilicus |
20 weeks |
|
|
|
Fh is at xiphoid process |
36 weeks |
|
|
|
Iron sup for anemic twin and late intake and large women |
60 to 100 mg per day |
|
|
|
Iodine |
220/day |
|
|
|
Iron low risk |
27 mg day |
|
|
|
0.4 to 0.8 mg day folate |
For all women |
|
|
|
4 mg per day folate |
With previous NTD |
|
|
|
Contraindicated vaccines for preg |
Mmr Varicella HPV |
|
|
|
Fetal activity normal |
10 fetal movement in up to 2 hours |
|
|
|
NST |
Fetal health |
|
|
|
CST |
Uteroplacental fxn |
|
|
|
Component of BPS |
Non stress test Fetal breathing Fetal movement or tone Amniotic fluid volume |
|
|
|
No late or significant variable decel |
Negative |
|
|
|
Late decel following 50 percent or more contraftions |
Positive cst |
|
|
|
Intermittent late decel or significant variable decel |
Equivocal suspicious |
|
|
|
Fetal heart rate decel that occur in the presence of contractions more frequent than every 2 mins or lasting longer than 90 seconds |
Equivocal hyperstimulatory |
|
|
|
Fewer than 2 contractions in 10 mins or an uninterpretable tracing |
Unsatisfactory |
|
|
|
0 to 2 bps |
Almost certain fetal asphyxia Deliver |
|
|
|
4 bps |
Probable fetal asphyxia Repeat testing the same day If still less than 6, deliver |
|
|
|
6 bps |
Possible fetal asphyxia If amniotic fluid abn deliver If normal amniotic fluid with favorable cervix and >36 weeks deliver If repeat test less than 6 delicer If more than 6 observe |
|
|
|
8/10 bps with normal afv |
Normal non asphyxiayed fetus No intervention Repeat test or protocol |
|
|
|
10 bps |
Normal non asphyxiated fetus No intervention Repeat test weekly except in
Dm and post term preg twice weekly |
|
|
|
8/10 bps with decreased afv |
Chronic renal Asphxia suspected Deliver |
|
|
|
Aceleration for >32 weeks |
Acceleration for >15 bpm from baseline last for more than 15 secs but less than 2 minutes from onset to return |
|
|
|
Onset nadir and recovery of deceleration are conincident with beg peak and ending of contractions |
Early decel Fetal head compression |
|
|
|
Mostly the onset nadir and recovery of decel occur after beg peak and ending of a contraction |
Late decel Decreased uteroplacenta o2 transfer |
Hydrate the patient |
|
|
Most commonc decel pattern due to |
Umbilical cord occlusion |
Mobilization Amnioinfusion |
|
|
Brady or tachy Minimal baseline Mark baseline Absent baseline with no recurrent deceleration |
Fht 2 indeterminate |
|
|
|
Brady Absent variability Recurrent late and variable decel Sinusoidal pattern |
Fhr cat 3 abnormal |
|
|
|
Contractile unresponsiveness cervicsl softening |
Phase 1 |
|
|
|
Uterine preparedness for labor snf cervicsl ripening |
Phase 2 |
|
|
|
Uterine contraction cervical dilation Fetal and placenta expulsion |
Phase 3 |
|
|
|
Uterine involution Cervicsl repair or remodelling Breastfeeding |
Phase 4 |
|
|
|
Stripping of fetal membranes increase blood levels of prostagladin f2 metabolite |
1st stage of labor Ferguson reflex |
|
|
|
Maternal surface appears first Seperates first at the periphery |
Duncan |
|
|
|
Criteria for labor |
1 in 10 mins contraction with atleast 200 mvu Cervical dilation >3 cm Cervical effacement of >70 to 80% |
|
|
|
Favorable cervix bishop score |
9 |
|
|
|
Unfavorable cervix bishop score |
Less than 4 |
|
|
|
Effacement 30 to 50% |
1 |
|
|
|
Effacement 60 to 70% |
2 |
|
|
|
Station -2 |
1 |
|
|
|
Station -1 |
2 |
|
|
|
Medium consistency |
1 |
|
|
|
Soft consistency |
2 |
|
|
|
Mid position |
1 |
|
|
|
Mid position |
1 |
|
|
|
Anterior position |
2 |
|
|
|
1-2 cm dilated |
1 |
|
|
|
3 to 4 cm dilated |
2 |
|
|
|
Relation of long axis of the fetus to that of mother |
Fetal lie |
|
|
|
Presenting part foremost in the birth canal or in closest proximity |
Fetal presentation |
|
|
|
Relationship of an arbitrarily chosen presenting part to the right or left of the maternal birth canal |
Fetal position |
|
|
|
Acceleration at what cm |
3 to 4 cm |
|
|
|
Maximum slope |
5 to 7 cm |
|
|
|
Decel phase at what cm |
8 cm and above |
|
|
|
Mechanism by which the bpd the greatest transverse diameter in occiput presentation passes through the pelvic inlet |
Engagement |
|
|
|
Promontory to upper margin of symphysis |
True or anatomic conjugate |
11 cm |
|
|
Promontory to posterior symphysis |
Obstetric conjugate |
More than 10 cm |
|
|
Promontory to lower margin of symphysis |
Diagonal conjugate |
>11.5 cm |
|
|
First requisite for birth of the newborn |
Descent |
|
|
|
Occurs as the descending head meets resistance Chin is brought into more intimate contact with fetal thorax and shorter suboccipitobregmatic dm is substituted for longer occipitobregmatic dm |
Flexion |
|
|
|
Largest transverse diameter of fetal head |
Baparietal diameter |
|
|
|
Greatest circumference of fetal head |
Occipitofrontal |
|
|
|
Smallest head circumference |
Sub occipitobregmatic |
|
|
|
Largest length of fetal head |
Occipitomental |
|
|
|
Turning the head in such a manner that the occiput gradually moves towards the symphysis pubis anteriorly |
Internal rotation |
|
|
|
Base of the occiput is in direct contact with the inferior margin of the symphysis |
Extension |
|
|
|
Restitution followed by rotation to the transverse position Corresponds to rotation of the fetal body and serves to bring its bisacromial dm into relation with the ap dm of the pelvic outlet |
External rotation |
|
|
|
Anterior shoulder appears under the symphysis pubis |
Expulsion |
|
|
|
Saggital suture approaches the sacral promintory more of the anterior parietal bone |
Anterior asynclitism |
|
|
|
Sagittal suture lies close to the symphysis more of the posterior parietal bone will present |
Posterior asynclitism |
|
|
|
Goals of 3rd stage lab0r |
Intact placenta Avoid uterine inversion Avoid post partum hgw |
|
|
|
Signs of placental separation |
Sudden gush of blood Globular and firmer fundus Lengthening of cord Rise of uterus into the abdomen |
|
|
|
Outlet forceps criteria |
Scalp is visible at introitus without separation of labia Fetal skull has reached the pelvic floor Sagittal suture is on ap diameter or roa or loa or rop lop Fetal head is at or on perineum Rotation doesnt exceed 45 degrees |
|
|
|
Most common cause of ectopic pregnancy |
Tubal pathology |
|
|
|
Gender be identified by experienced observer? |
14 weeks |
|
|
|
Between umbilicus and symphysis pubis |
16 cm |
|
|
|
6 bps |
Possible fetal asphyxia If amniotic fluid abn deliver If normal amniotic fluid with favorable cervix and >36 weeks deliver If repeat test less than 6 delicer If more than 6 observe |
|
|
|
8/8 bps |
Nst not done |
|
|
|
Onset nadir and recovery of deceleration are conincident with beg peak and ending of contractions |
Early decel Fetal head compression |
|

