![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
200 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Assess the height, position, and consistency of these.
|
Uterus/fundus
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment; m311
|
|
|
The stage of labor during the 1st hr after delivery is a critical period; PP hemorrhage is most likely to occur during this time eg, bleeding from the birth canal > 500cc during 1st 24 hrs
|
The fourth stage of labor; Bleeding 300-400cc is normal
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period Ch 21 m309
|
|
|
During this time monitor anesthesia recovery score eg, activity, V/S, LOC, Color
|
Assessment
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period Ch 21 m309
|
|
|
Mom>35yr→loss of mus tone, uterus does not contract well; Multipara→loss of uterine mus tone; Rapid labor < 3hrs → ↑chance of lacerations/trama; Full bladder→uterine atony; Prolonged labor→ fatigued uterine mus
|
Postpartum Hemorrhage Predisposing factors
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period Ch 21 r139 m310
|
|
|
Overdistended uterus eg, poly-hydramnios, multiple preg → macrosomic infant; Previous uterine atony - often recurs; Induced→uterus↓sensitive to oxytocin, mus fatigue; Gen anesthesia→↓uterus contratn; Placental frags →uterine atony
|
Postpartum Hemorrhage Predisposing factors
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period Ch 21 r139 m310
|
|
|
The BP and HR should stablize to this within one hour after birth
|
Pre-labor values
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment; Audio Lec Ch 21 r531
|
|
|
BP, P, & RR; q15min x1hr; q30min x1hr; q1hr x2hrs
|
V/S
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m310 r531
|
|
|
H&H; WBC; Coagulation factors (for ↑bleeding) are indicated values during postpartumm period
|
Lab Values
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m310 r638
|
|
|
Document status of this possible complication and this disease
|
Rh and Rubella
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m310 Audio Lec
|
|
|
Mom lying w head ↑slightly and knees flexed
|
Uterus/fundus assessment
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m311 r712
|
|
|
Support this while doing a fundal assessment
|
Lower uterine segment over her pubic bone or you can prolapse it
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec r758
|
|
|
Do not massage this constantly bc mus fatigue → uterus relaxes
|
Uterus
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m311 r841
|
|
|
Can give oxitoxyn IV or breast feeding to help uterus __
|
contract
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec r900
|
|
|
Monitor for bladder distention which displaces the uterus __ and causes uterine __
|
↑→; atony
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m311 r928
|
|
|
Mom should do this spontaniously within the first 6-8hrs
|
void
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec
|
|
|
May see bladder as a rounded superpubic buldge esp if you have a __ mom
|
thin
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec
|
|
|
Tepid water, po fluids, and ambulation encourage this
|
NI to encourage natural voiding
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec
|
|
|
Palpate these to make sure mom is emptying
|
bladder and uterus
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec
|
|
|
If mom has an epidural she may need to have this
|
cath
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec
|
|
|
To assess this turn mom to side. She should have a moderate amt of moderate ruba during 4th stage
|
Lochia
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m311 r1113
|
|
|
Lochia ruba should not come out in spirts because it indicates this
|
Arterial bleeding; Notify Dr and assess for vaginal or cervical lacerations
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec
|
|
|
If the uterus is filling with clots (may c/o severe bck ache) uterus will ↑ and deviate to what side? If uterus deviates to the opposite side it a distended bladder
|
Left; Right
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 Audio Lec
|
|
|
Chart scant, light,moderate, heavy for this
|
Lochia
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 p540 m311
|
|
|
When assessing mom's perineum place her on side lying position. Assess REEDA
|
Redness; Edema; Eccymosis; Discharge; Approximation
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 p541 Box 21-4 r1310
|
|
|
Cleansing; Ice Pack; Squeeze Bottle; Sitz Bath (Built-In or Disposable Type); Surgi-Gator; Topical Applications
|
Interventions for Episiotomy, Lacerations, and Hemorrhoids
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 p541 Box 21-4
|
|
|
The nurse always checks under the mother's __ as well as on the perineal pad. Blood may flow __, although the amt on the perineal pad is slight; thus excessive bleeding goes undetected.
|
buttocks; b/t the buttocks onto the linens under the mom
|
Nursing Alert p541
|
|
|
Assess for this if mom c/o pain/pressure in vagina, perineum not relieved by pain meds. If ↑large may hv urge to bear down. If ↑in vagina may not see. Can lose >500cc of blood. Surg may be indicated. Assess for hemorrids also
|
Hematoma
|
Nursing Care During the Postpartum Period; Assessment Ch 21 m311 r1416 Audio Lec
|
|
|
Persistent significant bleeding-Perineal pad is soaked ≤15 min; may not be accompanied by change in VS or mom's color/behavior. Mom c/o feeling weak, light-headed, funny, sick to stomach, or sees stars...
|
S/s of Hypovolemic Shock
|
Emergency Box p542
|
|
|
Mom acts anxious or exhibits air hunger; skin turns ashen or grayish; skin feels cool and clammy; ↑P ↓BP...
|
S/s of Hypovolemic Shock
|
Emergency Box p542
|
|
|
Call HCP; If uterus is atonic, massage gently & expel clots to cause uterus to contract; compress uterus manually prn using 2 hands. Add oxytocic agent IV drip as ordered; Adm O2 nonrebreather face mask or nasal prongs @ 10 L/min...
|
NI for Hypovolemic Shock
|
Emergency Box p542
|
|
|
Tilt mom to side or ↑right hip; ↑legs 30° angle; IV (LR or NS) to restore vol; Adm blood as ordered; Monitor V/S; Insert cath to monitor perfusion of kidneys; Adm emergency drugs as ordered...
|
NI for Hypovolemic Shock
|
Emergency Box p542
|
|
|
Prepare for possible surgery or other emergency tx or precedures; chart incident, medical and NI instituted, and results of tx
|
NI for Hypovolemic Shock
|
Emergency Box p542
|
|
|
Can last ≥2; Reassure pt & fam it's normal/uncontrolable, relaxation techniques may↓ it;
|
Postpartum tremors
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Assessment m311 r1600
|
|
|
Assess any __ that is not relieved by analgesics.
|
pain
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Assessment; Audio Lec m311 r1600
|
|
|
These include warmth, relaxation tech, distraction, ice packs, sitz bath; topical anesthetics
|
Non-pharmacologic interventions
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Assessment m312
|
|
|
Narcotics; non-noncartics eg, NSAIDS; PCA; safety with breastfeeding; assess pain not relieved by analgesics
|
Pharmacologic interventions
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Assessment m312
|
|
|
Do this early and often. Prevents thromboembolism; Homan's sign; Consider med usage bf eg, anesthesia, analgesia, MgSO4
|
Ambulation
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Assessment
|
|
|
Can do prn when anesthesia has worn off; If having ↑pain med bf; Prevent falls
|
Ambulation
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Assessment
|
|
|
R/t crying baby, hospitalization, discomfort, anxiety
|
Lack of Rest
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Assessment
|
|
|
NI include: ROM; Amublation; Support hose if varicosities; Homan's sign eg, warmth, redness, tenderness in the calf; TED or SCD's if required to stay in bed
|
Thromboembolism
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Thromboembolism; m313 r1912
|
|
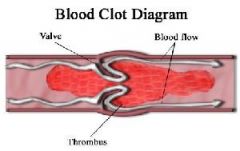
First strict bedrest is required. pt movement should be restricted, but when necessary, it should be performed gently. ↑limb then call the Dr (Most important); Do not massage
|
Indicated if thrombus is suspected
|
Nursing Care during the Pospartum Period ch 21; Thromboembolism; m313 r1950
|
|
|
Watch for this type of engorgement → pooling of blood in viscera and orthostatic hypotension
|
Splanchnic
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period; Safety r2106 m313
|
|
|
Start w sml amts whn stable; maintain IV if N/V or ↑bleeding; encourage ↑protein, fiber; may continue prenatal vit & iron, esp if breast feeding; Cultural preferences may be included eg, no cold or hot foods/drinks
|
Fluid Balance and Nutrition
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period r2152 m313
|
|
|
Indicated ≤ 2hr after delivery; Helps uterus contract
|
Breastfeeding
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period; Breast Care r2236 m314
|
|
|
If inverted difficult for baby to latch on; everted desired
|
Nipples
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period; Breast Care r2236 m314
|
|
|
If the breasts are hard the pt is probably this
|
Engorgement
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period; Breast Care r2236 m314
|
|
|
Indicated if mom has ↑engorgement or not breast feeding any of these may be indicated
|
Breast binder; Ice packs; Cold cabbage leaves
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period; Breast Care r2236 m314
|
|
|
If non-immune should receive this; immunization made from eggs, check for allergy; edu to avoid preg for 3mo after sq inj
|
Rubella (causes birth defects)
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period r2457 m314
|
|
|
Adm ≤ 72hrs if mom is Rh(-), coomb's antibody negative, and baby is Rh(+); If given to Rh(+) mom, may promote lysis of RBC's; Given IM to mom, NEVER to baby
|
Rhogam
|
Nursing care During the Psotpartum Period; Medication guide p547 r2542 m314
|
|
|
Life or health of mom and/or infant is jeopardized by a disorder coincidental or unique to pregnancy
|
High-risk pregnancy
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Definition and Scope of Problem r618 m325
|
|
|
Pregnancy is a maturational crisis; Diagnosis of high-risk adds situational crisis
|
Having a mom who is high risk and adding to her stress by telling her she's high risk tends to make even worse
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Definition and Scope of Problem r618 m325
|
|
|
HTN disorders; Infection; Hemorrhage
|
3 major causes
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
HTN; Pulmonary embolus; Hemorrhage
|
3 leading causes
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death r733 m325
|
|
|
Genetic factors may interfere w normal fetal or neonatal dev, result in congenital anomalies, or create difficulties for mom
|
Genetic considerations
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Defective genes, transmittable inherited disorders, chromosome anommalies, multiple preg, large fetal size, and ABO incompatibility
|
Genetic factors - a genetic risk assessment should be done to determine the family's heritable risk
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
The availability/quality of prenatal care vary greatly with geography. Mom's in metro areas have more prenatal visits than those in rual areas who have fewer opportunities for specialized care & consequently a ↑ incidence of maternal mortality.
|
Geographic location
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Health care in an inner city, where residents are usually poorer and begin childbearing earlier and continue for longer, may be of lower quality than in a more affluent neighborhood
|
Geographic location - there may be unsafe soil and water conditions and environmental exposure to pollutants
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Poverty →many other risk factors →inadequate financial resources for food/prenatal care; ↓general health; ↑risk for medical complications of preg, ↑prevalence of adverse environmental influences eg, substandard living conditions, ↓hygiene/inadequate nutrition
|
Socioeconomic status
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Risk for adverse perinatal outcomes ↓ as educational level ↑
|
Educational attainment
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
The ↑mortality/morbidity rates for unmarried women, including a ↑risk for preeclampsia, are often r/t inadequate prenatal care and a younger childbearing age
|
Marital status
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Demographic Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Mothers < __ and >__ y.o. have a slight ↑ in adverse perinatal outcomes
|
Maternal age
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Demographic Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Although race/ethnicity by themselves are not major risks, race is an indicator of other sociodemographic risk factors.
|
Racial and ethnic origins
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Demographic Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Non-Caucasian women are more than x__ as likely as Causasian women to die of preg-related causes.
|
3
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Demographic Characteristics; Racial and ethnic origins m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
African-American babies have the highest rates of prematurity and LBW, with the infant mortality rates among African-Americans being > x__ that among Caucasians
|
2
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Demographic Characteristics; Racial and ethnic origins m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Can be grouped into chemical, physical, biologic, and psychologic hazards. The risk to the fetus depends on the timing of exporsure, the dose, and fetal and maternal susceptibility
|
Occupational hazards
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Demographic Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Smoking is associated w IGR and LBW; alcohol exerts adverse efffects on the fetus, resulting in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, which include fetal alcohol syndrome, alcohol-related neurodevelopmenntal disorder, and alcohol-related birth defects
|
Substance abuse
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Druge can be teratogenic, cause metabolic disturbances, produce chemical effects, or cause depression or alteration of CNS function
|
Substance abuse
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Failure to diagnose and tx complications early is a major risk factor arising from financial barriers or lack of access to care
|
Failure to seek prenatal care
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Depersonalization of the sys, resulting in long waits, routine visits, variability in health care personnel, unpleasant physical surroundings; lack of undersatanding of need for early/continued care; cultural beliefs that do not support the need; fear of the health care system and its providers
|
Failure to seek prenatal care
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Adequate nutrition, w/o which fetal growth and dev cannon preceed normally, is one of the most important determinants of preg outcome
|
Nutritional status
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Young age; 3 pregnancies in the previous 2 yrs; tobacco alcohol, or drug use; inadequate dietary intake bc of chronic illness or food fads; inadequate or excessive wt. gain; hematocrit value < 32%
|
Conditions that influence nutritional status
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics; Nutritional Statue m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Periodontal disease ↑risk for preterm birth and LBW
|
Dental hygiene
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Childbearing triggers profound and complex physiologic, psychologic, and social changes, w evidence to suggest a relationship between emotional distress and birth complications
|
Psychosocial stressors
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Intrapsychic disturbances and addictive lifestyles; a history of child or spouse abuse; inadequate suppport systems; family disruption or dissoultion; meaternal role changes or conflicts
|
Psychosocial stressors
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Noncompliance with cultural norrms; unsafe cultural, ethnic, or religious practices; and situational crises
|
Psychosocial stressors
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Domestic violence is a serious problem; the risk of violence ↑ during pregnancy
|
Abuse and violence
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Abuse during pregnancy ↑ the risk for abruptio placenta, preterm birth, and LBW infants and infections from forced sex
|
Abuse and violence
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Major Causes of Maternal Death; Behavioral Characteristics m325 Box 9-1 p191
|
|
|
Congenital anomalies; disorders r/t short gestation and LBW; SIDS; Resp distress syndrome; Affects of maternal complications eg, abruptio plancenta
|
Leading Causes of Neonatal
|
Leading Causes of Neonatal Death m326 r820
|
|
|
Mgmt of normal preg, labor and childbirth; earliest possible ID of high-risk preg and high-risk neonate; provisional of stabilization of care in even of unanticipated obstetric/neonatal emergency
|
Level 1
|
Regionalizztion of Health Care Levels of Care m326 r901
|
|
|
Provide care for specified types of maternal and neonatal complications eg, if mom comes in ≥ 34 wks gestation; Babies on vent, c-pap, or extra short term care
|
Level 2
|
Regionalizztion of Health Care Levels of Care m326 r956
|
|
|
Capacity to manage most complex disorder, both maternal and neonatal; Mothers often transported to centers prior to birth to optimize fetal outcome
|
Level 3 - cavate if mom is in immanent danger of delivering, then mom delivers w level 2 and ships baby to level 3 hospt
|
Regionalizztion of Health Care Levels of Care m326 r1130
|
|
|
Done at hm; is non-invasive and no expense involved; research shows tht maternal awareness of movement is 90% accurate; low amt of movement <3/hr warrants NST, contraction stress test CST, or biophysical profile BPP testing
|
(Daily Fetal Movement Counts) DFMC or kick count
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Daily Fetal Movement Counts m327 r1318
|
|
|
Fetal movement ceases for 12 hrs
|
Fetal alarm signal
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Daily Fetal Movement Counts m327 r1420
|
|
|
Uses sound waves at 2-10 megahertz; can be done transvaginally or abd; Level 1 - basic screen eg, how many babies, & aminotic fluid; Level 2 - pts suspected of carrying anatomically or physiologically abnormal fetus
|
Ultrasound
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Ultrasound m327 r1505
|
|
|
Early diagnosis makes choices possible for families; FHR can be seen as early as 6-7 wks (echo); 10-12 wks (doppler); Confirmation of fetal death
|
Findings of Ultrasonography
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Findings of Ultrasonography m327 r1619
|
|
|
Absence of HR, fetal scalp edema, overlap of crainal bones, maceration
|
Confirmation of fetal death
|
Assessment of Risk Factors; Daily Fetal Movement Counts m327 r1707
|
|
|
Indications for checking this: Unsure LMP; discontinuation of oral contraceptives before preg; 1st trimester bleeding; size/date discrepancy; other high risk factors
|
Gestational ages c Ultrasonography
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m328 r1840
|
|
|
Assessment accurate in 1st 18 wks of preg; 8wks-sac dimensions; 7-14 wks - crown-rump; 12 wks- biparietal diameter (sides of head) and femur length
|
Determinants of gestational age
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m328 r2048
|
|
|
Serial measurements are done 2-3 wks apart, between 24 and 32 wks are accurate +/- 10 days; Determines if the fetus is growing the way it should be
|
Findings of Ultrasonography
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m328 r2140
|
|
|
Indicated c poor maternal wt. gain; previous IUGR; chronic infections; drug use; diabetes; HTN disorders; multiple gestation; other med/surg complications
|
US to watch fetal growth
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m330 r2354
|
|
|
Findings of US: Caused by a chronic or longstanding insult
|
Symmetric IUGR
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2447
|
|
|
Caused by acute or late occurring deprivation eg, fetus grows in length but not in wt.
|
Asymmetric IUGR
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2447
|
|
|
Can help diagnose macrosomia (big fetus)
|
Ultrasonography
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2537
|
|
|
Adjunct to amniocentesis, PUBS purcutainous umbilical blood sampling, CVS chorionic villa sampling
|
Ultrasonography
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2606
|
|
|
Amniocentesis, PUBS, & CVS
|
Establishes position of fetus, placenta, fluid pockets (amniotic fluid) ,and umbilical cord position
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2647
|
|
|
≥36 wks 85% of major anomalies can be detected; can see the # of fetuses & presentation to decide mode of delivery eg, vaginally or c-section
|
Fetal Anatomy
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2700
|
|
|
Determines placental position and function eg, placenta previa;
|
Ultrasonography
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2738
|
|
|
Can look at age of placenta and how well its functioning - graded in 3rd trimester (the ↑grade the ↓functioning)
|
Ultrasonography
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2754
|
|
|
With regard to placental position and function, can see Ca deposits eg, as Ca deposits↑ surface area↓, so baby will not be getting blood supply eg, ↓nutrients/O2 supply
|
Ultrasonography
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m331 r2818
|
|
|
Amniotic fluid vol - look for fluid pockets eg, <5 cm (total) - oligohydramnios; 5-8 cm - normal; >8 cm - polyhydramnios; Doppler blood flow analysis (follow blood flow through the heart); fetal echocardiogram; Biophysical profile (BPP)
|
Ways to determine fetal well being using ultrasound
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m332 r2846
|
|
|
A composite assessment of fetal well being; shows function of CNS; provides accurate estimate for risk of fetal death in immediate future; indicate fetal infection esp r/t premature rupture of membranes (fetus will act hypoxic)
|
BPP
|
Findings of Ultrasonography m332 r2959 p199
|
|
|
Can in some hospt
|
Nursing Role
|
Ultrasound r3133
|
|
|
With regard to safety, no conclusive evidence in humans as to if the benefits outweight the risks; Some places have 3D ultrasound
|
Ultrasound
|
|
|
|
A photomicrograph of the chromosomes of a single cell, taken during metaphase, when each chromosome is still a pair of chromatids. The chromosomes are then arranged in numerical order, in descending order of size. Used to determine congenital anomalies
|
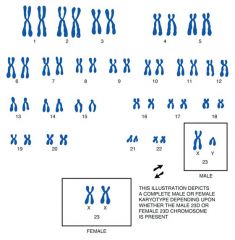
Karyotype
|
|
|
|
Evaluates: fetal structure and growth; placenta, amniotic fluid vol; maternal structures; biochemical status of tissue, organs; can ID soft tissue anomalies; mom may need to be sedated to ↓fetal movement
|
MRI
|
MRI m333 r3303
|
|
|
Needle inserted transabdominally under ultrasound guidance; Done >14 wks for karyotyping to check for fetal anomalies; Done later in preg to check fetal lung maturity
|
Amniocentesis
|
m333 r3400
|
|
|
Hemorrhage; labor; abruption of placenta; amniotic fluid embolism; fetal death; infection; maternal isoimmunization eg, Rh- mom; Rh- mom should receive Rhogam
|
Complications of amniocentesis
|
m333 r3451
|
|
|
Anything (eg, amniocentesis) that irritates the uterus can lead to this
|
Labor (preterm or term)
|
r3500 audio lec
|
|
|
Genetic problems: any disorder with marker genes; cells cultured for Karyotyping and/or sex of fetus (only 100% accurate determination)
|
Indications for amniocentesis
|
m334 r3606
|
|
|
AFP: If mom's ↑AFP, helps confirm diagnosis of open neural tube defect eg, spina bifida
|
Indications for amniocentesis; Alpha Fetal Protein
|
m334 r3657
|
|
|
Fetal Maturity: L/S ratio, 2:1 indicates lung maturity; PG: present = ↓resp distress syndrome (almost 0%) indicates mature lungs or absent = immature lungs
|
Amniocentesis Indications
|
m334 r3727
|
|
|
Fetal Lung Maturity test (FLM): Needs a clean specimen. Not as accurate if blood in it
|
Amniocentesis Indications
|
m334 r3830
|
|
|
Not done until maternal antibody titer reaches 1.8 and is ↑; PUBS is procedure of choice for this now;
|
Amniocentesis Indications to dx fetal hemolytic disease associated with Rh- incompatablity
|
m334 r3905
|
|
|
APT test differentiates fetal from maternal blood; Kleihauer-Betke test done for confirmation
|
Amniocentesis Indications; If blood in the amniotic fluid can test if fetal or maternal blood as in abruptio placenta
|
|
|
|
Not associated with a poor outcome; can be from old insult; physiologic; may need antepartum evaluation if birth is not imminent;
|
Antenatal period
|
Meconium in Amniotic Fluid m335 r4030
|
|
|
Bright green = fresh; Brown = old
|
Meconium
|
m335 r4050 audio lec
|
|
|
EFM; Fetal scalp blood sampling;
|
Intrapartum period evaluation
|
Meconium in Amniotic Fluid m335 r4137
|
|
|
May be normal physiologic function with maturity, or hypoxia induced, or response to cord compression in mature fetus
|
Intrapartum period eval
|
Meconium in Amniotic Fluid m335 r4230
|
|
|
Consistency - thick, more likely d/t fetal stress; timing, color changes with time
|
Meconium in Amniotic Fluid Evaluation
|
Meconium in Amniotic Fluid m335 r4303
|
|
|
Meconium itself is not necessarily a sign of stress; presence of other indicators, decels, poor baseline... is ominous; Suction ithe nasopharynx before newborn's first breath eg, mouth then nose
|
Meconium in Amniotic Fluid Evaluation
|
Meconium in Amniotic Fluid m335
|
|
|
Done in the 2nd or 3rd trimester; a needle is inserted into a fetal umbilical vessel under USG (ultra sound guidance)
|
Percutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling
|
PUBS m336 r4625
|
|
|
Complications: Blood leakage from site; fetal bradycardia; chorioamniontis
|
PUBS
|
PUBS m336 r4732
|
|
|
Indications: Identify inherited blood disorders; detect fetal infection, assess acid-base balance of IUGD fetus; assess/tx isoimmunization (xfuse blood via umbilical vein) and thrombocytopenia
|
PUBS
|
PUBS m336 r4803
|
|
|
Karotyping can be done in 2-3 days; intrauterine xfusion in severely anemic fetus can be done 4-5 wks earlier than intraperitoneal route
|
PUBS
|
PUBS m336 r4925
|
|
|
Continuous FM for up to one hr; repeat ultrasound after one hour to ensure no further bleeding or hematoma
|
Post procedure
|
PUBS m336 r4948
|
|
|
May be done transcervically or abd,↓risk w abd route; Can be done at 10-12 wks of preg; removal of a sml tissue specimen frm fetal portion of placenta; procedure guided by real-time US; indications similar to amniocentesis
|
CVS
|
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) m336 r5003
|
|
|
Developes from zygote. Tissue reflects genetic makeup of fetus
|
Chorionic villus
|
m337 r5115
|
|
|
Complications: Spotting; ROM; chorioamnionitis; if mom is Rh- needs Rhogam; if done between 56 - 66 days, ↑risk of limb abnormalities; tissue reflects genetic makeup of fetus
|
CVS
|
CVS m337 r5129
|
|
|
Most reliable at 15-21 wks; done to screen for neural tube defects
|
Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP)
|
Maternal Assays m337 r5251
|
|
|
An antigen present in the human fetus. Indications: AMA ≥35; multifetal preg; unrecognized demise; severe oligohydramnios; ↓levels indicative of down syndrome, ↑levels are indicative of neural tube defects.
|
Alpha-Fetoprotein
|
Maternal Assays m337 r5321
|
|
|
16-18 wks; AFP, unconjugated estriol, HCG; very sensitive, ↓# of false positives, but if mom's dates are off it will throw off test results, ↓levels indicative of down syndrome, ↑ levels are indicative of neural tube defects
|
Triple Marker Test or Triple screen; Newer forms of AFP; Are not required
|
Maternal Assays m338 r5427
|
|
|
Same as triple acreen + inhibin-A, ↑inhibin-A indicative of Down Syndrome
|
Quad screen; Newer forms of AFP; Are not required
|
Maternal Assays m338 r5540
|
|
|
Rh incomatibility; if maternal titer > 1.8, amniocentesis for bilirubin is indicated
|
Coomb's Test; Newer forms of AFP
|
External Fetal Monitoring m338 r5635
|
|
|
Used to determine whether the intrauterine environment is supportive of the fetus; most often used to determine childbirth timing for mom's at risk for uteroplacental insufficiency
|
External Fetal Monitoring
|
External Fetal Monitoring m338 r5635
|
|
|
Maternal diabetes; HTN, IUGR, sickle cell, maternal heart disease, postmaturity, hist of stillbirth, isoimmunization, meconium stained fluid at amnio, hyperthyroidism, collagen disease, AMA, chronic renal disease
|
Indications for non stress test NST & contraction stress test CST
|
External Fetal Monitoring m338 r5635
|
|
|
None for NST; Absolute for CST: ROM, previous classical incision; preterm labor; placenta previa; abruption: Relative for CST: multifetal preg; previous preterm labor hydramnios; <36 wks gestation; incompetent cervix
|
Contraindications
|
External Fetal Monitoring m338 r5635
|
|
|
↓ as degree of hypoxia and acidosis ↑; presence of normal variability is the most reassuring aspect of FHR monitoring; 98% accuracy for fetal wellbeing
|
Variability
|
External Fetal Monitoring m339
|
|
|
Most widely used type of antepartum eval of fetus; accelerations of FHR in response to fetal movement is desired outcome
|
NST
|
External Fetal Monitoring m339
|
|
|
Ease of testing noninvasive; relatively inexpensive; no known contraindications
|
NST Advantages
|
External Fetal Monitoring m339 r10100
|
|
|
False positive rates for non-reactive finds as a result of fetal sleep cycles; maternal meds eg, narcotics or fetal immaturity; slightly lower sensitivity to fetal compromise than CST or BPP
|
NST disavantages
|
External Fetal Monitoring m339 r10130
|
|
|
≥ 2 accels of 15 bpm lasting ≥ 15 sec over 20 min period; normal baseline FHR (110-160); long term moderate or avg variability amplitude of ≥ 10 bpm
|
NST Interpretation (to be called reactive)
|
External Fetal Monitoring m339 r10313
|
|
|
Procedure: Sit in chair or semifowler's; apply sono (HR) & toco (contractions); may give mom button to push whn fetal movement felt; almost all accels are accompanied by fetal movement; does not require marking by mom to be considered reactive; mom feels approx 75% of movement
|
NST
|
External Fetal Monitoring m340 r10530
|
|
|
Takes 10 min; w fetus monitored 5 min bf stimulation to obtain baseline; Sound source applied to abd ovr fetal head; reactive if accel of 15 bpm for 120 sec ≤5 min of stimulation or 2 accels of 15 bpm for 15 sec each ≤5 min of stimulation
|
Fetal Acoustic Stimulation; May be used to stimulate fetus during NST
|
External Fetal Monitoring m340 r10648
|
|
|
Designed to identify fetus who is stable at rest but compromised w introduction of stress
|
CST
|
External Fetal Monitoring m341 r11045
|
|
|
Earlier warning of fetal compromise than NST; fewer false positives
|
CST Advantages
|
External Fetal Monitoring m341
|
|
|
Observe EFM strip for 10 min for baseline and spontaneous UC's; then produce UC's (3 in 10 min window) by either nipple stimulation or oxytocin
|
CST procedure
|
External Fetal Monitoring m341
|
|
|
Apply warm washrage to breasts; massage nippple for 10 min, x2 min, x4 cycles; if not effective, may massage both nipples; Stop whn there is adaquate contractions or uterus gets hyperstimulated
|
NSCT (nipple stimulation)
|
External Fetal Monitoring m341
|
|
|
Start primary IV, piggyback oxytocin by pump; follow hospital protocol; continue fetal monitoring until preprocedure contractions return bf taking off monitor
|
OCT (oxytocin) CST
|
External Fetal Monitoring m341 r11408
|
|
|
Accels w fetal movement
|
Positive/reactive/reassuring NST
|
audio lec
|
|
|
Contractions w decels
|
Positive CST
|
r11716 audio lec
|
|
|
Following procedure, continue monitoring until preprocedure UC pattern returns
|
CST
|
External Fetal Monitoring
|
|
|
With 3 UC's in 10 min: Negative: no late decels; Positive: persistent and consistent late decels occurring w > 1/2 of UC's; Suspicious: late decels occurring w < 1/2 of UC's
|
CST Interpretation
|
External Fetal Monitoring m342
|
|
|
Educator; support person; assist w precedure; in many settings nurses perform NST's and CST's & begin interventions for non-reassuring patterns
|
Nursing Role In Antenatal Assessment
|
External Fetal Monitoring m342 r11917
|
|
|
3-7% of primiparous women bc preeclamptic; 0.8-5% of multiparous women bc preeclamptic; morbidity and mortality increase whn seizures occur
|
Mortality and Morbidity
|
HTN Disorders in Pregnancy m343 r403
|
|
|
Prematurity IUGR; hypoxia; Maternal:
|
Fetal Perinatal Morbidity
|
HTN Disorders in Pregnancy; Mortality and Morbidity m343
|
|
|
Placental abruption; DIC; renal failure; hepatic failure; ARDS; cerebran hemorhage
|
Maternal Perinatal Morbidity
|
HTN Disorders in Pregnancy; Mortality and Morbidity m343
|
|
|
↑BP w/o proteinuria, after 20 wks gestation; if it happens bf 20 wks it's likely chronic or preexisting conditions; classification of HTN disorders
|
Gestational HTN
|
m344 r604 p335 Table 14-1
|
|
|
BP >140/90 x2, 6 hrs apart; proteinuria 1-2+ on dipstick or >0.3 gm in 24hr differenciates from gestational HTN; possible H/A; reflexes may be normal; ↓placental perfusion→ baby is not getting O2 & nutrients it needs
|
Mild Preeclampsia Characteristics
|
m344 r640
|
|
|
Progression of preeclamsia to seizure activity and/or coma; Seizure risk from preeclampsia→eclampsia: 40% seize antepartum; 20% seize intrapartum; 40% seize postpartum
|
Eclampsia; Can occur up to 14 days after preeclampsia
|
m345 r1100 p347 Emergency Box
|
|
|
HTN before 20th wk; not preganacy related; can develop superimposed preeclampsia with CHTN AEB proteinuria; may need antihypertensives
|
Concurrent HTN
|
m345 r1443
|
|
|
2 to 3 sec: eyes are fixed; twitching of facial muscles
|
Eclampsia; Tonic-Clonic Convulsion Signs; Stage of invasion
|
Eclampsia Emergency Box p347
|
|
|
15 to 20 sec; eyes protrude and are blood shot; all body muscles are in tonic (tension or contraction) contraction
|
Eclampsia; Tonic-Clonic Convulsion Signs; Stage of contraction
|
Eclampsia Emergency Box p347
|
|
|
Muscles relax/contract alternately (clonic); respirations are halted and then begin again w long, deep, stertorous (laborious breathing provoking a snoring sound) inhalation; coma ensues
|
Eclampsia; Tonic-Clonic Convulsion Signs; Stage of convulsion
|
Eclampsia Emergency Box p347
|
|
|
Keep airway patent: turn head to one side, place pillow under one shoulder or back if possible; call for assistance; protect with side rails up; observe and record convulsion activity
|
Eclampsia; Tonic-Clonic Convulsion Intervention
|
Eclampsia Emergency Box p347
|
|
|
Do not leave unattended until fully alert; observe for post- convulsion coma, incontinence; use suction PRN; adm O2 via face mask at 10 L/min; start IV, monitor intake; giv MgSO4 or anti- convulsant drugs prn; support, keep mom/family informed
|
Eclampsia; After convulsion or seizure
|
Eclampsia Emergency Box p347
|
|
|
Insert indwelling urinary cath, monitor output, BP, fetal and uterine status; expedite lab work as ordered to monitor kidney, LFT, coagulation sys, drug levels; provide hygiene and a quiet environment; be prepared to assist w birth whn mom is in stable condition
|
Eclampsia; After convulsion or seizure
|
Eclampsia Emergency Box p347
|
|
|
↑BP detected first time after midpregnance w/o proteinuria (previously known as preg-induced HTN)
|
Gestational HTN
|
p335 Table 14-1 Classification of HTN states of preg
|
|
|
Gestational HTN w no signs of preeclampsia present at the time of birth and HTN resolves by 12 wks after birth; this is a retrospective diagnosis
|
Transient HTN
|
p335 Table 14-1 Classification of HTN states of preg
|
|
|
The occurrence of seizures in a mom w preeclampsia tht cannot be attributed to other causes
|
Eclampsia
|
m354 p335 Table 14-1 Classification of HTN states of preg
|
|
|
HTN tht is present and observable bf preg or tht is diagnosed bf wk 20 of gestation
|
Chronic HTN
|
p335 Table 14-1 Classification of HTN states of preg
|
|
|
Chronic HTN w new proteinuria or an exacerbation of HTN (previously well controlled) or proteinuria, thrombocytopenia, or ↑hepatocellular enzymes
|
Preclampsia superimposed on chronic HTN
|
p335 Table 14-1 Classification of HTN states of preg
|
|
|
Hemolysis; elevated liver enzymes; low platelet count; 2-12% of severe preeclamptics; highest in older, caucasian, multiparous women
|
HELLP Syndrome
|
m348
|
|
|
Platelet count <100,000; ↑liver enzymes (AST, ALT, bilirubin); hemolysis (burr cells); form of coagulopathy; hypoglycemia
|
HELLP Syndrome Diagnosis
|
m349
|
|
|
BP may be normal or only ↑slightly; s/s almost always includes epigastric pain, malaise, and N/V; probable c-section d/t unfavorable cervix and/or aggressive nature of disease
|
HELLP Syndrome Diagnosis (H- hemolysis EL- ↑liver enzymes LP- ↓platelet count)
|
m349
|
|
|
An erythrocyte with 10 to 30 spicules distributed over the surface of the cell, as seen in heart disease, stomach cancer, kidney disease, and dehydration.
|
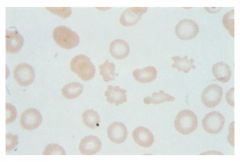
Burr Cell
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
The woman's BP, P, and RR status should be monitored closely while the MgSO4 loading dose is being adm IV and every 15-30 min at other times, depending on the stability of the mom's condition.
|
HELLP
|
Nursing Alert p344
|
|
|
Whn adm antiHTN therapy, the RN must remember that the drug effects depend on intravascular vol. Bc preeclampsia is associated w contracted intravascular vol, initial doses should be given w caution, & maternal response monitored closely
|
NURSING ALERT
|
Severe Preeclampsia or HELLP Syndrome p346
|
|
|
Because a degree of maternal HTN is necessary to maintain uteroplacental perfusion, antiHTN therapy must not ↓arterial pressure too much or too rapidly. Therefore the target range for the DBP <110, SBP<160
|
Control of BP
|
Severe Preeclampsia or HELLP Syndrome p346
|
|
|
Immediately after this, the mom may be very confused and combative. Pat side rails to prevent injury. Maintain a quiet, darkened environment. It may take several hrs for mom to regain her usual LOC. She should not be left alone. Provide emotional support to fam & discuss w them mgmt, its rational, & mom's progress
|
NURSING ALERT; Seizures
|
Eclampsia; Seizure p346
|
|
|
Aspiration is a leading cause of mom's morbidity/mortality after this. So after initial stabilization/airway mgmt, the nurse should anticipate orders for chest x-ray film & possibly ABG's to determine whether aspiration occurred.
|
Eclamptic Seizure
|
Eclampsia; Seizure; NURSING ALERT; p346
|
|
|
The mom is at risk for a boggy uterus and a large lochia flow as a result of the tocolytic effects of this therapy. Uterine tone and lochial flow must be monitored closely
|
NURSING ALERT; MgSO4
|
Eclampsia; Seizure p347
|
|
|
Is this a theraputic MgSO4 level for a preg mom: 4-8 mEq/L
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
Any agent that diminishes uterine contractions by reducing myometrial (the smooth muscle forming the wall of the uterus) excitability
|
Tocolytic
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
A synthetic version of the same peptide. It is used in obstetrics to induce labor, contract the uterus, and control postpartum hemorrhage
|
Oxytocin/Pitocin
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
Pertaining to illnesses whose cause is either uncertain or as yet undetermined
|
Idopathic
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
Risks: Uterine tenderness in the presence of ↑tone may be the earliest finding of this. Idiopathic preterm contractions also may be an early sign.
|
Abruptio placentae
|
NURSING ALERT; HELLP Syndrome; Nursing Care Mgmt p342
|
|
|
Risk for injury r/t signs of preeclampsia; Deficient diversional activity r/t imposed bed rest; Fear/anxiety r/t preeclampsia and its effect on the fetus
|
Mild Preeclampsia Nursing Diagnosis
|
p344
|
|
|
Needs to be observed closely 24-48 hrs; MgSO4 continued 12-48 hrs; Monitor BP, DTR's, urine protein q hr; if epigastric or RUQ pain, massage fundus on L side only and gently bc can rupture liver.
|
Post-Delivery
|
m355
|
|
|
Strict I&O; promote bonding; no ergot meds; pt is improving whn diuresing, improvement of edema, ↓wt.& CNS irritability; improved HTN
|
Post-Delivery
|
m355
|
|
|
Risk for uterine atony if on MgSO4; MgSO4 potentiates narcotics, CNS depressant, and Ca channel blockers
|
Post-Delivery
|
m355
|
|
|
The oval or discoid spongy structure in the uterus of eutherian mammals from which the fetus derives its nourishment and oxygen
|
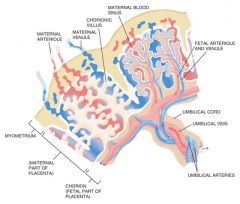
Placenta
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
The innermost fetal membrane; a thin, transparent sac that holds the fetus suspended in the liquor amnii, or amniotic fluid.
This grows rapidly at the expense of the extraembryonic coelom, and by the end of the third month it fuses with the chorion, forming the amniochorionic sac. Commonly called the bag of waters. |
Amnion
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
The shift in frequency produced when an ultrasound wave is echoed from something in motion. The use of the Doppler effect permits measuring the velocity of that which is being studied (e.g., blood flow in a vessel).
|
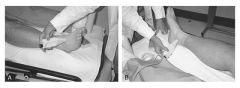
Doppler ultrasonography
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
This identifies the size and position of the fetus, placenta, and umbilical cord enables estimation of gestational age, detects some fetal anomalies and fetal death, and facilitates other diagnostic procedures, such as amniocentesis.
|
Ultrasound
|
Inaudible sound in the frequency range of approx. 20,000 to 10 billion (109) cycles/sec. This has different velocities that differ in density and elasticity from one kind of tissue to the next. This property permits the use of this procedure in outlining the shape of various tissues and organs in the body.
|
|
|
Transabdominal puncture of the amniotic sac under ultasound guidance using a needle and syringe in order to remove amniotic fluid.
This procedure is usually performed no earlier than at 14 weeks' gestation. |
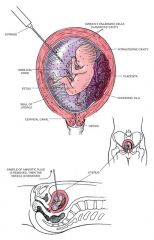
Amniocentesis; The sample obtained is studied chemically and cytologically to detect genetic and biochemical disorders and maternal-fetal blood incompatibility and, later in the pregnancy, to determine fetal maturity. The procedure also allows for transfusion of the fetus with platelets or blood and instillation of drugs for treating the fetus.
|
It is important that the analysis be done by experts in chemistry, cytogenetics, and cell culture. Cell cultures may require 30 days, and if the test has to be repeated, the time required may be insufficient to allow corrective action.
|
|
|
A lab diagnosis of a combo of events signaling a variation of severe pre-eclampsia marked by hemolysis anemia, ↑liver enzymes, & ↓platelet count. This potentially life-threatening condition usually arises in the last trimester of preg.
|
HELLP syndrome; Initially, affected pts may c/o N/V, epigastric pain, H/A, & vision prob. Complications may include acute renal failure, DIC, liver/resp, or multiple organ sys failure.
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
A congenital defect in the walls of the spinal canal caused by a lack of union between the laminae of the vertebrae.
The lumbar portion is the section chiefly affected. The consequences of this defect may include urinary incontinence, saddle or limb anesthesia, gait disturbances, and structural changes in the pelvis. |
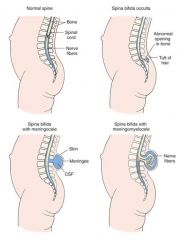
Spina Bifida Cystica
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
1. That state of a body or any of its organs or parts in which the functions are healthy and normal. In a more restricted sense, the resistance of muscles to passive elongation or stretch.
2. Normal tension or responsiveness to stimuli, as of arteries or muscles, seen particularly in involuntary muscle (such as the sphincter of the urinary bladder). |
Tone
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
A system of estimating current fetal status, determined by analyzing five variables via ultrasonography and nonstress testing.
Fetal breathing movements, gross body movement, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal heart rate reactivity are each assigned specific values. |
BPP
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|
|
|
Each expected normal finding is rated as 2; each abnormal finding is rated as 0. Scores of 8-10 with normal amniotic fluid volume and a reactive NST indicate satisfactory fetal status. A score of 6 with normal amniotic fluid vol requires reassessment of a preterm fetus within 24 hr of delivery. Scores of <6 or a nonreactive NST indicate fetal compromise & require prompt delivery.
|
BPP
|
Taber's Medical Dictionary
|

