![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Signs of chorioamnionitis
|
1) Maternal fever
2) Uterine tenderness 3) Fetal tachycardia 4) Elevated WBC |
|
|
|
What is definition of late pregnancy bleeding?
|
Bleeding after 20 weeks
|
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of late-trimester bleeding?
|
Placental abruption
|
|
|
|
Risk factors for placental abruption
|
1) Previous abruption
2) Maternal trauma 3) Hypertension 4) Maternal cocaine abuse 5) Premature membrane rupture |
|
|
|
Signs of mild abruption
|
Moderate vaginal bleeding with no fetal monitor abnormality. Localized uterine pain and tenderness.
|
|
|
|
Signs of moderate abruption
|
Pain and bleeding can be gradual or abrupt in onset.
FHT may show tachycardia, decreased variability or mild late decels |
|
|
|
Signs of severe abruption
|
Abrupt pain that is continuous and knifelike. Greater than 50% separation.
FHT shows severe late decels, bradycardia or death. DIC may occur |
|
|
|
Why does DIC occur with abruption?
|
Release of tissue thromboplastin from placenta into maternal circulation.
|
|
|
|
What is couvelaire uterus?
|
Blood extravasating between myometrial fibers. Bruises appear on serosal surface.
|
|
|
|
What are complications of severe abruption?
|
Acute tubular necrosis from severe hypotension.
DIC from release of tissue thromboplastin. |
|
|
|
What is characteristic of bleeding with abruption?
|
Painful bleeding
|
|
|
|
What is characteristic of bleeding with previa?
|
Painless bleeding
|
|
|
|
Which single dose oral regimens for gonorrhea should be avoided in pregnancy?
|
Ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin.
|
|
|
|
Single dose treatment for gonorrhea
|
Intramuscular ceftriaxone
|
|
|
|
Treatments for chlamydia
|
Single dose azithromycin
1 week regimen of doxycyline or erythromycin |
|
|
|
Who should be routinely screened for gonorrhea and chlamydia?
|
All sexually active women who are young or have other risk factors.
|
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of septic arthritis in sexually active young adults?
|
Neisseria gonorrhea
|
|
|
|
What is the hormone imbalance in polycystic ovarian syndrome?
|
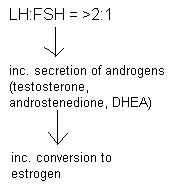
Too much LH
|
|
|
|
What are the origins of ovarian cancers?
|
Epithelial, germ cell and stromal
|
|
|
|
What is the most common type of ovarian cancer?
|
Serous cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
|
|
What is the most common type of ovarian cancer?
|
Serous cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
|
|
What is the most common type of ovarian cancer?
|
Serous cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
|
|
What do women over 35 with abnormal bleeding need to rule out?
|
Endometrial carcinoma
|
|
|
|
What prevents gonadal malignancy in Turner's syndrome?
|
Prophylactic removal of gonads.
|
|
|
|
What congenital anomalies are associated with Turner's syndrome?
|
1) Coarctation of the aorta
2) Cystic hygroma 3) Renal anomalies |
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of primary amenorrhea?
|
Turner's syndrome (45, X0)
|
|
|
|
What happens if a Turner patient is given progesterone?
|
Nothing, no bleeding because there was no estrogen to begin with.
|
|
|
|
What conditions has bacterial vaginosis been linked with?
|
Postpartum endometritis, pelvic infections, preterm labor.
|
|
|
|
What are three classical presentations of endometriosis?
|
Pain, abnormal bleeding and infertility
|
|
|
|
At what ages do most women present with endometreosis?
|
Between 20 and 35
|
|
|
|
What is medical therapy for endometriosis?
|
NSAIDS for pain; OCPs, danazol and GnRH agonists to induce "medical menopause" for relief of symptoms
|
|
|
|
What is normal pH of the vagina in a premenopausal woman?
|
Acidic (<4.5)
|
|
|
|
What is characteristic of the discharge produced by bacterial vaginosis?
|
Profuse, thin, foul smelling, "dirty-grey"
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment for BV?
|
Metronidazole for 7 days
|
|
|
|
What is the alternative treatment for BV?
|
Clindamycin
|
|
|
|
What time period during pregnancy should Metronidazole be avoided?
|
First trimester
|
|
|
|
Classic findings for endometriosis on physical exam
|
Fixed, retroverted uterus
Nodularity of uterosacral ligaments Fixed ovaries |
|
|
|
T or F: High parity is a risk factor for cervical cancer
|
True
|
|
|
|
What can vaginal discharge of cervical cancer look like?
|
Malodorous, purulent or clear
|
|
|
|
HPV serotypes that cause cancer
|
16, 18, 33, 36 and others
|
|
|
|
Type of herpes that mostly causes genital warts
|
HSV Type II (90% of cases)
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment for herpes genitalis?
|
Acyclovir, valacyclovir or famcicyclovir for 7-10 days
|
|
|
|
In which eating disorder are severe electrolyte abnormalities and cardiac arrythmias seen?
|
Bulemia
|
|
|
|
What should be the antibiotic coverage for treatment of PID?
|
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, gram negative rods and anaerobes
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment for PID?
|
Cefotetan or cefoxitin and doxycyline
|
|
|
|
How long do you watch a tubo-ovarian abscess on antibiotics before resorting to surgery?
|
72 hours
|
|
|
|
In what type of patient is and IUD a bad idea?
|
Women under 35, promiscuous women, those desiring future fertility
|
Questionable correctness of this answer. Doctor dependent
|
|
|
T or F: Patients with adenomyosis tend to present at a later age than patients with endometriosis
|
True (35-45 years)
|
|
|
|
Smooth symmetrically enlarged, boggy uterus that may be tender to palpation probably describes....
|
Adenomyosis
|
|
|
|
What is condyloma accuminata assiciated with?
|
Genital warts or HPV
|
|
|
|
Which conditions can cause genital warts to grow rapidly and larger?
|
Pregnancy, diabetes, immunosuppresion and taking OCPs.
|
|
|
|
What has to be included in the investigation of vaginal bleeding in postmenopausal woman?
|
Pap smear, endocervical curettage, endometrial biopsy
|
|
|
|
What is benign cystic teratoma known as?
|
Mature teratoma or dermoid cyst
|
|
|
|
What are the most common ovarian neoplasms?
|
Benign cystic teratoma
|
|
|
|
What is struma ovarii?
|
Fuctioning thyroid tissue in a benign teratoma causing hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
|
What are the screening tests for syphilis?
|
VDRL and RPR
Nonspecific, false positives, become negative after treatment |
|
|
|
What are confirmatory tests for syphilis?
|
FTA-Abs, MHT-TP
More specific, stay positive for life |
|
|
|
What is Jarish-Herxheimer?
|
It is a reaction that occurs in patients with syphilis on the first day of treatment.
Fever, sweating, malaise. Not an allergic reaction! |
|
|
|
What might a false positive syphilis screening test mean?
|
Lupus or some collagen vascular disorder (anti-phospholipid syndrome)
|
|
|
|
How early can pregnancy be detected by transvaginal ultrasound?
|
5 weeks
|
|
|
|
T or F: Mild glucosruia and proteinuria is normal in pregnancy
|
True
|
|
|
|
What LFT value is normally elevated in pregnancy?
|
Alkaline phosphatase
|
|
|
|
When in pregnancy is the "triple screen" done?
|
16-20 weeks
|
|
|
|
When in pregnancy is diabetes screening done?
|
24-28 weeks
|
|
|
|
What are normal pregnancy levels of beta-HCG?
|
<100,000
|
|
|
|
What is another name for molar pregnancy?
|
Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN)
|
|
|
|
What is the next step in a molar pregnancy if beta-HCG levels continue to rise after a D&C?
|
Chemotherapy with methotrexate or actinomycin D
|
|
|
|
Describe complete molar pregnancy
|
46, XX; no fetal tissue present
|
|
|
|
Describe incomplete molar pregnancy
|
47, XXY; some fetal tissue present
|
|
|
|
Date of delivery based on LMP
|
subtract 3 months and add 7 days
|
|
|
|
What is the definition of spontaneous abortion?
|
Expulsion of fetus at <20 weeks or <500 grams
|
|
|
|
In which trimester does Pregnancy Induced Hypertension classically occur?
|
Third trimester
|
|
|
|
Second trimester + signs of pre-eclampsia = ?
|
Possible molar pregnancy
|
|
|
|
What are classic complaints of PIH?
|
Dec. urine output, headache, visual changes, altered mental status, RUQ pain, face, hand or leg swelling
|
|
|
|
What defines pre-eclampsia?
|
Hypertension + PROTEINURIA + edema
|
|
|
|
What distinguishes pre-eclampsia from eclampsia?
|
SEIZURES
|
|
|
|
What is in the HELLP syndrome?
|
Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets +/- RUQ pain
|
|
|
|
What can occur with magnesium sulfate toxicity?
|
Dec. deep tendon reflexes
Hypotension Respiratory depression |
|
|
|
Which PIH is okay to treat with BP control and observation?
|
Those with mild disease:
BP < 160/110, 1-2+ proteinuria and no symptoms besides edema |
|
|
|
What is symmetric IUGR a result of?
|
Fetal anomalies and infections
|
|
|
|
What is asymmetric IUGR a result of?
|
Maternal or placental factors
More common |
|
|
|
What are the three most common presenting complaints for an ectopic pregnancy?
|
Amenorrhea, abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding.
|
|
|
|
24 year old, RLQ pain, spotting, LMP 5 weeks ago: first test?
|
beta-HCG
|
|
|
|
Name three initial lab values to check in a pre-menopausal woman presenting with amenorrhea.
|
beta-HCG, TSH, prolactin
|
|
|
|
Which metabolic disorders are women with PCOS at risk for?
|
Diabetes mellitus type 2 and dyslipidemia
|
|

