![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_______ & _______ are diffuse disease processes of the female pelvic cavity. |
PID and Endometriosis |
|
|
What are the common causes for PID? |
Sexually transmitted diseases including gonorrhea and chlamydia. |
|
|
what are the uncommon cases for PID? |
1. ruptured appendix 2. peritonitis 3. diverticulitis 4. pelvic abscess 5. IUD string 6. post-abortion 7. post-delivery infection |
|
|
PID risk factors include: |
1. early sexual activity 2. multiple sex partners 3. history of STD 4. history of PID 5. IUD |
|
|
_____, ______, & ______ are a few clinical findings for PID. |
Intense pelvic pain, tenderness, constant vaginal discharge |
|
|
PID affects ______ women each year. |
750,000 |
|
|
High _____ is likely to be associated with PID. |
white blood cell count |
|
|
______ & ______ are sonographic findings of PID. |
Free fluid in the cup-de-sac & large palpable bilateral complex mass(es). |
|
|
Thickening or fluid in the endometrium is known as _______. |
Endometritis |
|
|
Enlarged ovaries with multiple cysts, indistinct margins indicate _______ inflammation. |
Periovarian |
|
|
Fluid-filled, irregular fallopian tube with or without echoes is known as ______. |
Pyosalpinx or Hydrosalpinx |
|
|
Endometriosis, Salpingitis, Hydrosalpinx, Pyosalpinx, Periovarian inflammation, Tubo-Ovarian Complex & Tubo-Ovarian abscess are all synonyms for _______. |
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease |
|
|
Infection usually occurs bilaterally and may be found in: ______, ______, ______, ______, ______. |
1. Endometrium 2. Myometrium 3. Uterine Serosa & Broad ligament 4. Ovary 5. Oviducts |
|
|
Where is the most common location for salpingitis to implant? |
Oviducts |
|
|
Right flank pain may be associated with _________. |
Perihepatic Inflammation |
|
|
Perihepatic inflammation pain may mimic _____, _____, or _____ pain. |
Liver, GB or Right Kidney |
|
|
Liver capsule inflammation is known as ______. |
Adhesions |
|
|
What am I describing? - Perihepatic inflammation and adhesions - develop in 1% to 10% of acute PID |
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome |
|
|
What is the medical term for fallopian tube? |
Salpingitis |
|
|
What am I describing? - Inflammation of the fallopian tube - Tortuous, dilated tube |
Salpingitis |
|
|
_____ & _____ are clinical findings for salpingitis. |
1. Asymptomatic to pelvic fullness or discomfort 2. Low grade fever |
|
|
What am I describing? - Walls become thin - Appearance of multi cystic mass - Bilateral - Ampullary portion is more dilated than interstitial part of the tube. |
Hydrosalpinx |
|
What is this image demonstrating? |
Salpingitis |
|
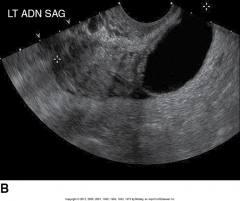
What is this sonographic image showing? |
Salpingitis |
|
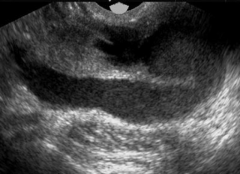
What is this an image of? |
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease of the Fallopian Tube |
|
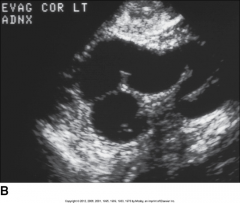
This image is showing ________. |
Hydrosalpinx |
|
|
Is hydrosalpinx (unilateral or bilateral)? |
Bilateral |
|
|
In hydrosalpinx, are the walls thick or thin? |
Thin |
|
|
Free fluid in the cul-de-sac is a sonographic finding for ______. |
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease |
|
|
Previous history of an STD is a risk factor for ______. |
Pelvic inflammatory disease |
|
|
TOA is the abbreviation for what? |
Tubo-Ovarian Abscess |
|
|
As tubo-ovarian abscesses become worse, _____ may form. |
Periovarian adhesions |
|
|
______, ______ & _____ are sonographic findings for tube-ovarian abscess. |
Irregular margins, scattered internal echoes & variable septations |
|
|
_____ usually responds well to antibiotic treatment without the need for surgical drainage. |
Tubo-ovarian abscess |
|
|
Inflammation of the peritoneum is known as: |
Peritonitis |
|
|
_______ can spread to the bladder, ureters, bowel, and adnexal area |
Peritonitis |
|
|
Once peritonitis spreads to the bladder, bowel and adnexal areas; it is known as _____ _____. |
Pelvic Peritonitis |
|
|
Peritonitis is caused by infectious organisms that gain access by was of ______ of the viscera or associated structures through the female genital tract or abdominal wall. |
rupture |
|
|
_____ & _____ are sonographic findings for peritonitis. |
Gas bubbles & loculated fluid in the pelvis |
|
|
Endometriosis is know as _____ cyst. |
Chocolate |
|
|
Infection of the endometrium is known as _____. |
Endometritis
|
|
|
Endometriosis can be found _______. |
Almost anywhere in the pelvis. |
|
|
List the places endometriosis is commonly found: |
Bladder, broad ligament, cul-de-sac, fallopian tubes, ovary, peritoneum, uterus |
|
|
______ can be divided into obstetric and non obstetric cases. |
Endometritis |
|
|
What are the clinical findings for endometriosis? |
1. severe dysmenorrhea 2. chronic pelvic pain 3. bleeding 4. dyspareunia |
|
|
What are the sonographic findings for endometriosis? |
1. endometrium may appear thick, contain fluid, clots, or appear normal. 2. Measurements of >20 mm should raise suspicion. |
|
|
In ________, the uterus may appear bulbous and the boarder between endometrium and myometrium become indistinct. |
Adenomyosis |
|
|
"blurred boarder" appearance is associated with ______ in the posterior aspect of the uterus. |
Adenomyosis |
|
|
______ ultrasound is helpful in obtaining biopsies for benign and malignant solid pelvic masses. |
Interventional |
|
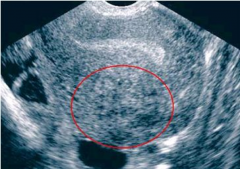
This is an image of? |
Adenomyosis |
|
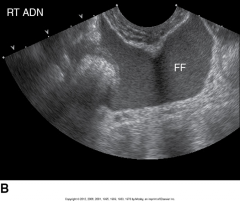
This is an image of? |
Peritonitis |
|
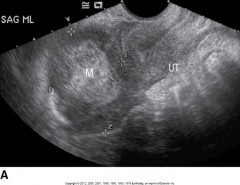
This is an image of? |
Tubo-Ovarian Abscess |
|
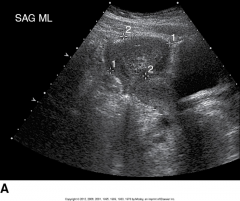
This is an image of? |
Tubo-Ovarian Abscess |
|
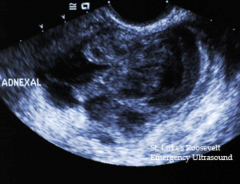
This is an image of? |
Tubo-Ovarian Abscess |
|
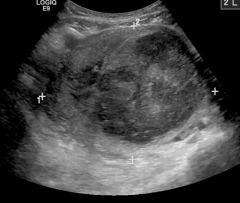
This is an image of? |
Tubo-Ovarian Abscess |

