![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
high risk pregnancy
|
**woman/fetus at increased risk of illness or death
risk factors-- • biophysical • psychosocial • socio-demographic • environmental |
|
|
pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH)
|
• 140/90; either systolic OR diastolic value
• 2 readings required, must be 6 hours apart • onset is after 20 weeks gestation OR increase in baseline-- > 30 mmHg systolic > 15 mmHg diastolic |
|
|
preeclampsia
|
**PIH w/ proteinuria; can occur up to 48 hours PP
• major cause of prenatal death • often a/w IUGR triad symptoms-- • HTN • proteinuria; ≥+1 • edema; weight gain can be up to 2 kg/wk >> fluid retention |
|
|
preeclampsia s&s
|
• headaches / visual changes r/t constriction
• epigastric pain; (-) liver perfusion, (+) liver enzymes • elevated BP • sudden excessive weight gain • hand/face edema • proteinuria |
|
|
mild v. severe preeclampsia
|
mild--
• BP 140/90 • 2+ to 3+ protein • moderate puffiness • DTRs are WNL (2+) severe-- • BP 160/110 • 3+ to 4+ protein • generalized edema, noticeable puffiness • hyperreflexive (3/4+) • symptomatic • oliguria; < 500 cc in 24 hours |
|
|
preeclampsia management
|
mild--
• rest in LLP periodically • high protein, high calorie diet • FMC • monitor BP q 2x/day • daily urine dip & weight severe-- • hospital & bed rest • (-) environmental stimulation • seizure precautions r/t increased pressure • I&O • fetal assessment- NST/BPP • magnesium sulfate |
|
|
magnesium sulfate (MgSO4)
|
• (-) BP and contractions
• normal levels are 4-7/8 • depressant >> LOC, (-) RR, (-) DTRs initial loading dose-- • IVPB • 4-6 g in 100-250 cc over 15-30 mins maintenance dose-- • 40g/1000cc of LR via pump @ 2 g/hr |
|
|
What is the antidote for magnesium sulfate?
|
calcium gluconate
|
|
|
What is the only cure for preeclampsia?
|
Birth!
|
|
|
eclampsia
|
**preeclampsia w/ convulsions
**treat w/ MgSO4 therapy |
|
|
HELLP syndrome
|
hemolysis
elevated liver enzymes; (+) ALT and AST low platelets; < 100,000 **life threatening; treatment is birth! • 10% pregnant women w/ preeclampsia • low platelet w/ normal co-ag >> abnormal clotting factor |
|
|
What is a normal platelet count
|
150,000 - 415,000
|
|
|
risk factors a/w preeclampsia
|
• chronic renal disease
• chronic HTN • family h/o PIH • primigravidity • maternal age < 14 y/o or > 40 y/o • DM • Rh incompatibility • obesity • twin gestation |
|
|
early pregnancy bleeding
|
• spontaneous abortion
• molar pregnancy • incompetent cervix • ectopic pregnancy • implantation spotting |
|
|
spontaneous abortion (SAB)
|
**pregnancy that ends before 20 weeks
• early SAB- before 12 weeks • late SAB- 12 to 20 weeks • 10-15% of pregnancies end in SAB • 75% occur within 8-13 weeks • 50% are due to chromosomal abnormalities |
|
|
SAB types
|
• complete v. incomplete
• threatened • inevitable • missed • recurrent |
|
|
complete v. incomplete SAB
|
complete--
• all products of conception are expelled • cervix is closed incomplete-- • some but not all products expelled >> some bleeding and tissues may remain • cervix is open |
|
|
threatened SAB
|
• vaginal bleeding
• poc not expelled • cramping • cervix closed treatment-- • bed rest • NPV |
|
|
inevitable SAB
|
**ROM & cervix dilation >> SAB cannot be stopped
|
|
|
missed SAB
|
• fetus dies but poc are retained
• cervix closed |
|
|
recurrent SAB
|
**3 or more consecutive SAB
|
|
|
SAB risk factors
|
• drug use
• infection • maternal structural problems • immunological factors • systemic disorders • inadequate nutrition • endocrine imbalance |
|
|
incompetent cervix
|
**passive, painless dilation in 2nd trimester
risks-- • h/o cervical lacerations • excessive cervical dilation • congenitally short cervix • cervical uterine abnormalities |
|
|
incompetent cervix management
|
**cerclage- tie cervix to prevent preterm birth
• not placed before 25 weeks • can be placed prophylactically if patient has h/o refrain from-- • sex • standing > 90 mins see provider if-- • bleeding, spotting • ROM |
|
|
ectopic pregnancy
|
**fertilized ovum implanted outside uterine cavity
• 95% occur in ampulla • painful lower quadrant pain • referred shoulder pain • vaginal spotting/bleeding • non viable fetus >> abortion clinical findings-- • HCG and ultrasound to confirm diagnosis; HCG low or slowly rising • adnexal tenderness/fullness |
|
|
molar pregnancy
|
causes--
• hydatidiform mole • getational trophoblastic disease (GTD)- abnormal proliferation of trophoblasts >> fill uterus w/ vesicles |
|
|
complete v. partial molar pregnancy
|
complete--
• no genetic material partial-- • fetal tissue/membranes present • chromosomal contribution present • nonviable fetus |
|
|
molar pregnancy s&s
|
• vaginal bledding
• n/v • uterus is large for dates • no fetal heart tones or activy • high hCG and rising rapidly |
|
|
molar pregnancy management & follow-up
|
management--
• immediate vacuum • identify tissues to determine malignant or benign cytology follow-up-- • weekly measurement of hCG; should be declining & undetectable @ 3 weeks • continued monitoring for up to 1 year to detect malignant changes or remaining trophoblastic tissue • avoid pregnancy for 1 year |
|
|
late pregnancy bleeding
|
placenta previa--
• placenta partially/completely covers internal cervical os • painless placenta abruption-- • premature separation of placenta from uterine wall • painful |
|
|
previa risk factors
|
• h/o previa, C-section
• elective TOP • multiple gestation • closely spaced pregnancies • AMA • smoking- larger placenta to compensate for decreased perfusion • cocaine use |
|
|
previa management
|
• bed rest
• NPV • evaluate fetal activity • NO vaginal exam >> C-section |
|
|
placental abruption
|
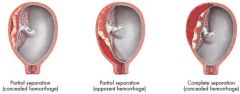
s&s--
• vaginal bleeding can be concealed in partial separation >> will eventually see bleeding in late stage • abdomen pain for contractions are greater than expected and may be localized “classic” s&s-- • uterine tenderness • board-like abdomen |
|
|
T/F. A board-like abdomen is usually a sign of internal hemorrhage.
|
True
|
|
|
placental abruption risk factors
|
• PIH- due to blood vessel constriction
• cocaine use • trauma • smoking • poor nutrition |
|
|
gestational diabetes (GDM)
|
**physiological glucose intolerance in pregnancy
• 4% of all pregnancies • 50% will develop glucose intolerance later on in life |
|
|
GDM risk factors
|
• maternal age > 30 y/o
• obesity • maternal family h/o DMI • previous baby >4000g • polyhydramnios • previous unexplained stillbirth • SAB • congenital anomalies • DM s&s • recurrent glucosuria on dip stick |
|
|
When does GDM normally appear?
|
Insulin requirement increases between weeks 18-24; GDM usually appear after week 24.
|
|
|
glucose testing
|
glucose challenge test (GCT)
• screen b/w 24-28 weeks • NPO, draw blood glucose tolerance test (GTT) • diagnostic; follow-up to (+) GCT • NPO, draw blood >> give glucose >> draw blood again to see if patient is able to tolerate |
|
|
What are normal glucose levels?
|
70-100 mg/dL
|
|
|
diagnosing GDM
|
**GCT value > 200 mg/dL
OR **two abnormal GTT values • fasting ≥ 105 mg/dL • 1 hour ≥ 190 mg/dL • 2 hours ≥ 165 mg/dL • 3 hours ≥ 145 mg/dL |
|
|
GDM treatment
|
**goal is to control glucose; 60-100 mg/dl
• fasting levels < 105 mg/dl • 2 hour postprandial < 120 mg/dl • diet and exercise • educate family |
|
|
GDM dietary guidelines
|
• standard diabetic diet
• small frequent meals • high fiber foods • lower fat intake • avoid sugar & concentrated sweets |
|
|
size less than dates
|
• intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
• small for gestational age (SGA) • oligohydramnios |
|
|
IUGR
|
**pathological; (-) O2 and nutrition available to fetus
symmetric-- • chronic “insult” • small in all parameters, i.e. head development asymmetric-- • late occurring/acute deprivation • head sparing >> small body w/ large head |
|
|
IUGR risk factors
|
• poor nutrition and maternal weight gain
• maternal vascular disease • preeclampsia • multiple gestations • smoking • genetic disease • drug & alcohol abuse • anemia |
|
|
SGA
|
• nonpathological
• constitutionally small fetus |
|
|
amniotic fluid index (AFI) v. amniotic fluid volume (AFV)
|
AFI normal value is 5-20 cm
AFV normal value is 800-1200 cc |
|
|
oligohydramnios
|
**abnormally small amount of fluid
• AFI < 5 cm • associated w/ marked perinatal mortality factors-- • congenital anomalies • IUGR • early rupture of membranes • post-maturity |
|
|
oligohydramnios management
|
• bed rest
• hydration • encourage good nutrition • assess fetal well-being, e.g. FMC, AFV, BPP • induction & delivery if severe and fetus is mature |
|
|
size greater than dates
|
• macrosomia
• large for gestational age • multifetal pregnancy • fibroid uterus • polyhydramnios |
|
|
polyhydramnios
|
**excessive amount of amniotic fluid; rule out GDM and ABO/Rh disease
• AFI > 20 cm • difficulty auscultating fetal heart tones & palpating fetus • unstable fetal lie |
|
|
polyhydramnios risk factors
|
• multiple gestations
• uncontrolled GDM • fetal malformations • chromosomal abnormalities |
|
|
polyhydramnios complications
|
• fetal malpresentation
• placental abruption due to excessive fluid weight • uterine dysfunction during labor- have to push harder • cord prolapse • preterm labor- body thinks it’s further along |
|
|
post-term pregnancy
|
**extends >42nd week gestation
• unknown cause • h/o previous incidents increases risk for future incidents by 30-40% |
|
|
post-term clinical manifestations
|
• maternal weight loss
• decreased uterine size • meconium in fluid b/c fetus is mature • advanced bone maturation of fetal skeleton w/ hard skull |
|
|
post-term risks
|
maternal risks--
• dysfunctional labor • perineal trauma • PPH • infection • interventions may be necessary, e.g. forceps, vacuum, c-section • emotional stress fetal risks-- • macrosomia • birth trauma • distress • hypoxia/asphyxia |
|
|
post-term management
|
• BPP, NST, FMC
• cervical assessment for ripeness • induction |

