![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
orgz. culture
|
the shared values, beliefs, and norms which influence the way employees think, feel and act towards others in and outside of the orgz.
|
|
|
First level culture
|
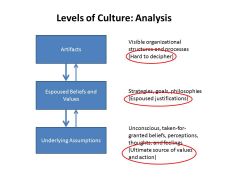
surface manifestation of culture- cultures most accessible form which are visible and audible patterns and objects e.g. rolls Royce artifacts- name badges, work wear (polo shirt)
|
|
|
Second level culture
|
orgz. values- the beliefs held about how work should be done and situations should be dealt with that guide employee behavior e.g. Motorola 1)uncompromising integrity 2)constant respect for people
|
|
|
Edgar Scheins Model 2004
e.g. Google- encouraged to work on whatever they feel is important, easily adaptable environment, university playground, laid back atmosphere |
|
|
|
orgz. socialisation
|
process through which an individuals pattern of behavior and his/her attitudes/motives are influenced to conform with those seen as desirable in a particular organization. Socialisation = important; Edgar Schein-"new orgz. recruits have to be taught to see the orgz. world as their more experienced colleagues do
|
|
|
stages socialisation
|
1)pre-arrival stage- period of learning in the process that occurs before an applicant joins an organization
2)encounter stage- new recruit learns about orgz. expectations 3)metamorphosis- new employee adjusts to the organizations values, norms |
|
|
Socialization case study
|
Inculcating Disney values into employees
-Disneys 40 hour training course -employees speak Disney e.g. customers are guests -company grooming each employee e.g. hair -employers discuss early memories Disney |
|
|
Arguments
|
1. culture has vs culture is-
2. integration vs differentiation 3. culture managed vs culture tolerated 4. symbolic leadership vs management control |
|
|
Strong Culture
|
a culture in which an organizations are widely shared among the employees and intensely held by them and which guiders their behavior e.g. Mcdonalds/Apple strong cultures are slow to develop and difficult to change. e.g. IBM strong culture failed company when competition to Apple in 1990s.
|
|
|
weak culture
|
a culture in which there is little agreement among employees about their organizations core values the way things are supposed to be
|
|
|
advantages strong culture
|
Advan- differentiates organization
Allows employees to identify themselves w/ the organization facilitates behavior desired by management among employees creates stability in orgz. |
|
|
disadvantages strong culture
|
Dis- makes merging more difficult
attracts, retains similar kings employees creates extreme behaviours makes adapting difficult |
|
|
types of organizational culture
Charles Handy |
1) power culture- have single dominant individual who exerts those with a similar viewpoint, little emphasis on discussion e.g. small companies run by founder
2) Role- organizations emphasize the importance of rules, procedures, and job descriptions. they operate by the book e.g. advertising agencies 3) Person- culture organizations are focuses on individuals, exist for benefit of members include star-performer e.g IT start up companies 4) task- job or project orientated working as a team, influence is based on expertise rather than position and personal power e.g. advertising agencies |
|
|
types of organizations culture
Rob Goffee & Gareth Jones (2003) |
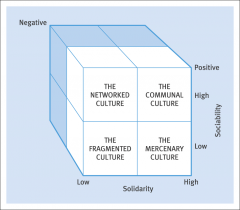
sociability- concerns emotional relationships with each other
solidarity- task orientated co-operation the degree to which members think and act in similar ways |
|
|
Rob Goffee & Gareth Jones (2003)
diagram explained.. |
communal culture- members are friendly to each other, think and act differently. stimulates creativity
networked culture- staff thinks alike, not friendly. rapidly changing highly competitive firms , employees seek to maximize personal gains only co-operate when they see their own benefits and rewards fragmented culture- employees think and act differently, showing little liking each other |
|
|
Can a common organizational culture in a multi-national firm be undermined by the strengths of the national cultures.
|
Yes. e.g. Japanese culture- food brings people together/shared tables and pots. food with bread considered snack vs mcdonalds hamburgers eaten seperately it has become ahngout place younger kids
|
|
|
Hofstedes five dimensions of national culture
|
1. social orientation- relative importance of the interests of the individual versus the interest of the group
2. power orientation- the appropriateness of power/authority within organizations 3. uncertainty orientation- emotional response to uncertainty and change 4. goal orientation- motivation achieve goals, 5. time orientation- time outlook on work and life- value dedication, hard work, short term outlook value traditions social obligations |

