![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the AUA |
Average ultrasound age is the average of BPD, HC, AC and Fl |
|
|
If the patient does not have a prior sono, how can you determine dates? |
Compare the AUA to LMP dates |
|
|
What do you do if the AUA and LMP are not within the measurements of ultrasound error (no prior sono) |
you change the EDC |
|
|
What is the error of ultrasound in the first trimester? ( up to 12 wks) |
+/- 4 days |
|
|
what is the error of ultrasound between 13-24 weeks? |
+/- 1 week |
|
|
Error of ultrasound after 24 weeks up to 32 weeks? |
+/- 2 weeks |
|
|
Error of ultrasound after 32 weeks |
+/- 3 weeks |
|
|
Ratio of cerebellum to gestational age before 22 weeks |
one to one |
|
|
What are some measurements that can help identify gestational age |
clavicle measurement, foot length, the epiphyses presence, and the cerebellar measurements |
|
|
Parameters for BPP |
8/8 & 8/10 is wnl 6/8 physician will order NST 6/10 Doctor will moniter pregnancy 4/10 delivery indication 2/10 Happy Birthday |
|
|
After how many weeks are they more willing to let a pt. get induced for labor |
36 weeks |
|
|
PROM |
Premature Rupture of Membrane |
|
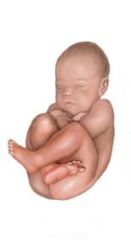
What kind of breeched position is this baby in?
|
Complete breech |
|
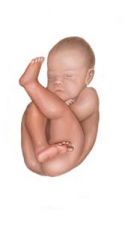
What kind of breeched position is this baby in? |
Incomplete breech |
|
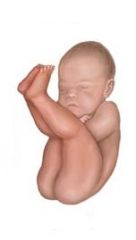
What kind of breeched position is this baby in? |
Frank breech |
|
|
36 week patient by prior sono. The BPP is 8/10. AFI 2cm.... |
The BPP is fine. Since the AFI is 2cm and patient is 36 weeks it is in an indication of delivery |
|
|
Why is it safer to induce patient (after 36 weeks) when AFI is less than 2x2 cm |
Oligohydramnios can lead to heart decelerations on the fetus during labor. The cord gets constricted with contractions when the fluid is too low. |
|
|
24 week pt by prior sono. The BPP is 8/10. AFI 2cm. |
check for kidneys, growth restriction, or suspect PROM. Will not induce, only follow. The pt is too early and babies lungs are at risk. Fluid necessary for lung maturity |
|
|
26 week twins. One baby has oligo, the other AFI wnl |
Watch pregnancy and hope it reaches 34 weeks. Before 34 weeks they should not intervene since the healthy baby will be put at risk for prematurity. |
|
|
Patient arrives at 32 weeks by dates and prior sono. Measurement averages out to be about 35 weeks by every parameter. What is your interpretation about this case? |
Growth accelerated baby. |
|
|
The patient is 32 weeks by her dates, no prior sono. Biometrics are BPD=33 wks, HC=34 wks, AC=33wks, FL=31wks. What is the gestational age, why? |
Note, her dates have not yet been established. When establishing dates for the first time average all the measurements. They are within the range of error for 32 weeks, so you keep her at 32 weeks. |
|
|
If you are not sure of dates, what can help you identify dates better? |
Cerebellum is the best. |
|
|
Which parameter best estimates dates, BPD, AC or FL? |
BPD & HC &Fl. The AC has more to do with weight. |
|
|
Symmetrical IUGR |
All parameters are small. More common with chromosomal and genetic problems |
|
|
Assymmetrical growth restriction |
the AC is small and the rest are okay. More common and usually do to placental insufficiency. |
|
|
When do we use MCA doppler? |
Systolic velocity is used to evaluate for fetal anemia when a mom is RH sensitized. S/D ratios are used to evaluated in IUGR babies. |
|
|
There is high resistance flow in normal ______ doppler and low resistance flow in normal _______ artery |
MCA (middle cerebral artery); umbilical |
|
|
Macrosomia |
Big baby. Greater than 4000 grams |
|
|
Cidex |
Used to clean tx |
|
|
Indigo Carmine |
dye used in twins. the first twin amnio is done and the dye is injected. if the dr gets blue dye on the next needle insertion then he is in the same sac and has to re tap to make sure in correct sac |
|
|
Genetic amnios |
to see chromosomes |
|
|
Delta amnios |
to evaluate bilirubin |
|
|
L/S amnios |
to evaluate lung maturity |
|
|
Most common reason for polyhydramnios |
ideopathic (no reason) |
|
|
CVS removes ___ for genetic testing. Amniocentesis removes _____. |
Chorionic villus (tissue); amniotic fluid |
|
|
T or F: CVS needles enter the sac. |
False; they are behind the placenta |
|
|
Why are corticosteroids given to pregnant mom? |
To advance baby's lung maturity |
|
|
When using doppler, which is the one used in OB US, continuous or pulsed? |
pulsed |
|
|
What is the new recommendation given by ACOG about amniocentesis? |
Risk of amnios is low so everyone can have one
|
|
|
Why do we look above the fundus and at kidneys? |
To make sure there are no other masses or something compressing the ureters and causing hydronephrosis |
|
|
Is transvaginal transducer sterilized? |
No, its a High-level disinfection. Destruction/removal of all microorganisms except bacterial spores |
|
|
What are measurements and images included in GYN report. |
LG and Trv of uterus, AP diameter of the endometrium and lg and tr of each ovary. |
|
|
In what modality should f/u measurements be reported |
They should be reported in same modality previously used. If mass was measure transvag, use the transvag measurement to compare |
|
|
What is on the report |
LMP, meds, gravida, surgeries |
|
|
AFI |
Amniotic Fluid index-sum of the four quadrants |
|
|
Normal AFI |
8-20 cm |
|
|
Oligohydramnios |
less than 5cm of fluid |
|
|
polyhydramnios |
greater than 20 cm |
|
|
How far away should placenta be from 0ss |
5cm |
|
|
Placenta accreta risk factors |
c-section and myomectomy |
|
|
BPP |
a. fetal breathing(30 seconds sustained breathing in 30 minutes) b. Fetal tone ( episode extremity extension and flexion) c. Body movement(three episodes of body movements over 30 minutes) d. Amniotic fluid( more than 1 pocket amniotic fluid greater than 2cm in depth e. Non-stress test (reactive) |
|
|
What should the CM measure. What does it tell us? |
CM measures less than 10mm always. Tells about structure |
|
|
NF should be measure before ___ weeks and should measure less than _____ mm. Measure for...? |
24 weeks; less than 6mm; for risk of chromosomal problems |
|
|
Usually which long bones are measure |
Only humerus and femur, but if they are short, measure all to rule out skeletal dysplasia. |
|
|
Cervix should measure more than |
2.5cm |
|
|
Lateral ventricles should always measure less than |
10 mm |
|
|
Renal pelvis in second trimester should measure less than ______. In third trimester, less than _______. |
3mm; 10mm |
|
|
A cephalic index of less than 71% |
Dolichocephalic |
|
|
A cephalic index greater than 87% |
Brachycephalic |
|
|
When is distal femoral, proximal humeral, proximal tibial visible? |
Distal femoral 31 weeks proximal tibial 35 weeks proximal humeral 37 weeks |
|
|
Labeling twins |
Twins are labeled baby A and baby B. Baby A is the baby closest to cervix |
|
|
Brain Sparing. |
Brain is spared by the blood flow resistance changing. Growth restricted babies, the MCA doppler will change from high resistance to low resistance |
|
|
High level Disinfection |
Destruction/removal of all microorganisms except bacterial spores |
|
|
Mid-level disinfection |
inactivation of myobacterium Tuberculosis, bacteria, most viruses and most fungi, and some bacterial spores. |
|
|
Low- Level disinfection |
Destruction of most bacteria, some viruses, and some fungi. Low level disinfection will not necessarily inactivate myobacterium, tuberculosis, or bacterial spores. |
|
|
What is the grade of a placenta whose chronic plate is straight and well defined, placental substance is homogenous, the basal layer does not have densities |
Placenta Grade 0 |
|
|
placental grade with anterior surface subtle undulations. Placental substance:few scattered echogenic areas. Basal layer no densities |
Grade 1 |
|
|
Placenta grade anterior surface will have indentations extending into placenta but not to basal layer. The substance of placenta will have linear echogenic densities ("comma like"). The basal part will have linear arrangement of small echogenic areas ("basal stippling") |
Grade II |
|
|
Placental grade: The surface will have indentations communicating with basal layer. The substance has circular densities with echo-spared areas in center; large irregular densities may cast acoustic shadows. Large and somewhat confluent basal echogenic areas. |
Grade III |
|
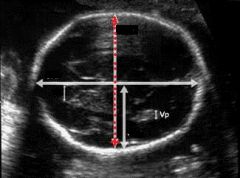
The dotted line shown is measuring... |
BPD |
|
|
How is BPD measured? |
From leading edge to leading edge (outer to inner) |
|
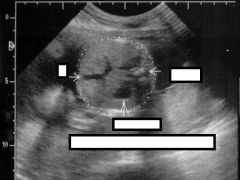
Example of which measurement |
Abdominal circumference |

