![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
233 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Secondary medication causes of hypertension
|
midodrine
sirolimus cyclosporine/tacrolimus sibutramine |
|
|
hydrochlorothiazide brand
|
hydroDIURIL
Esidrix |
|
|
chlorothiazide sodium brand
|
Diuril
|
|
|
indapamide brand
|
Lozol (thiazide diuretic)
|
|
|
metolazone brand
|
Zaroxolyn (thiazide related)
|
|
|
torsemide brand
|
Demedex (loop diuretic)
|
|
|
triamterene brand
|
Dyrenium
|
|
|
eplerenone brand
|
Inspra
|
|
|
methyldopa brand
|
Aldomet
|
|
|
terazosin brand
|
Hytrin
|
|
|
prazosin brand
|
Minipress
|
|
|
doxazosin brand
|
Cardura
|
|
|
hydralazine brand
|
Apresoline
|
|
|
propanolol brand
|
Inderal
|
|
|
labetalol brand
|
Normodyne
|
|
|
carvedilol brand
|
Coreg
|
|
|
amlodipine brand
|
Norvasc
|
|
|
felodipine brand
|
Plendil
|
|
|
nisoldipine brand
|
Sular
|
|
|
nicardipine brand
|
Cardene
|
|
|
nifedipine brand
|
Procardia
Adalat |
|
|
verapamil brand
|
Calan
Isoptin |
|
|
verapamil SR
|
Calan SR
Isoptin SR Verelan |
|
|
verapamil ER
|
Verelen PM
Covera HS |
|
|
diltiazem CD
|
Cardizem CD
Dilacor XR Tiazac Cartia XT |
|
|
losartan brand
|
Cozaar
|
|
|
valsartan brand
|
Diovan
|
|
|
irbesartin brand
|
Avapro
|
|
|
candesartan brand
|
Atacand
|
|
|
telmisartan brand
|
Micardis
|
|
|
eprosartan brand
|
Teveten
|
|
|
olmesartan brand
|
Benicar
|
|
|
benazepril brand
|
Lotensin
|
|
|
captopril brand
|
Capoten
|
|
|
enalapril brand
|
Vasotec
|
|
|
fosinopril brand
|
Monopril
|
|
|
lisinopril brand
|
Zestril
Prinivil |
|
|
ramipril brand
|
Altace
|
|
|
quinapril brand
|
Accupril
|
|
|
trandolapril brand
|
Mavik
|
|
|
perindopril brand
|
Aceon
|
|
|
amiloride/HCTZ combination brand
|
Moduretic
|
|
|
triamterne/HCTZ combination brand
|
dyazide (capsules)
maxzide (tablets) |
|
|
benazepril/amlodipine combination brand
|
Lotrel
|
|
|
enalapril/feldopine combination brand
|
Lexxel
|
|
|
enalapril/diltiazem combination brand
|
Teczem
|
|
|
trandolapril/verapamil combination brand
|
Tarka
|
|
|
pulmonary hypertension medication cause
|
fenfluramine
|
|
|
pulmonary hypertension treatment
|
CCB
epoprostenol/trepostinil/iloprost bosentin (endothelial blocker) sildenafil ambrisentin (endothelial blocker?) |
|
|
Shown reduced mortality in hypertensive patients
|
thiazide diuretics
|
|
|
Thiazide location
|
cortical diluting segment
|
|
|
Thiazide effect on electrolytes
|
dec:
K, Mg Inc: Ca, GLC, Lipid, Uric acid |
|
|
Thiazide effect on lithium concentrations
|
increases
|
|
|
thiazide or thiazide like that has vasodilation properties
|
indapamide
|
|
|
Loop diuretics location
|
thick ascending loop of Henle
|
|
|
Loop diuretics effects on electrolytes
|
dec:
K, Mg, Ca |
|
|
Short-acting, very ototoxic loop diuretic with no sulfonamide moeity
|
ethacrynic acid
|
|
|
longest acting loop diuretic
|
torsemide
|
|
|
IV use of loop diuretics induces _
|
venous vasodilation
|
|
|
beta-blockers with ISA
|
pindolol
acebutolol penbutolol |
|
|
beta blockers with alpha blocking properties
|
labetalol
carvedilol |
|
|
IV beta blocker with short half life
|
esmolol
|
|
|
renally eliminated beta blockers
|
atenolol
bisoprolol nadolol sotalol |
|
|
ACE inhibitors adverse effects
|
dysgeusia
first-dose hypotension renal failure hyperkalemia nonproductive cough angioedema |
|
|
ACE inhibitors and ARBs effects on lithium
|
increase lithium conc
|
|
|
ACE inhibitor that may be consideration in pts w/ renal disease
|
fosinopril
|
|
|
Food effects absoprtion of what beta blockers
|
captopril
moexipril |
|
|
Central alpha2 agonists adverse effects
|
dry mouth
bradycardia CNS Rebound hypertension |
|
|
Sometimes causes positive Coomb's test
|
methyldopa
|
|
|
Drug-induced SLE
|
hydralazine
|
|
|
hirsutism and pericarditis
|
minoxidil
|
|
|
depression
|
reserpine
|
|
|
Elderly population choice
|
diuretic
|
|
|
African-americans
|
CCB
diuretic |
|
|
CAD
|
beta-blocker
|
|
|
HF
|
ACE (ARB)
|
|
|
Diabetes
|
ACE(ARB)
|
|
|
pregnancy
|
central alpha2 agonists
Avoid ACE and ARB |
|
|
Definition of hypertensive emergency
|
severe HTN (diastolic >120) w/ concurrent end-organ damage:
AMS papilledema proteinuria chest pain |
|
|
DOC for hypertensive emergencies
|
nitroprusside
|
|
|
drawbacks of nitroprusside
|
coronary steal (dilate healthy vessels as opposed to ischemic ones)
increase ICP cyanide toxiicty liver dz (need rhodanase enzyme to convert cyanide to thiocyanate) |
|
|
DOC if patient has HTN and chest pain
|
nitroglycerin
labetalol |
|
|
how is thiocyanate eliminated
|
renally
|
|
|
risk factors for NTP to cause cyanide toxicity
|
>10mcg/kg/min
liver dz rhodanase deficiency |
|
|
thiazide and loop diuretic patient information
|
upset GI system (may take c food)
may cause photosensitiviy elevate GLC in DM patients precipitate gout attack |
|
|
central alpha agonist patient information
|
patches may take 2-3 d for onset of effect
drowsiness don't abruptly d/c |
|
|
beta blockers patient information
|
drowsiness, fatigue, nightmares
alter GLC conc mask hypoglycemia take sotalol on empty stomach |
|
|
hydralazine pt information
|
notify of pericardial, pleural, or joint pain
|
|
|
CCB pt information
|
may cause constipation, swelling of hands or feet, slow heart rate
|
|
|
ACE inhibitor pt information
|
seek emergent attention if lips, throat, or tongue swell
may cause extreme orthostasis after initial dose may alter taste perception avoid high intake of foods rich in K |
|
|
bosentan pt info
|
notify of darkened urine, light-colored stools, or abdominal discomfort
do not use if pregnant |
|
|
Calculating LDL
|
LDL= TC - (HDL + TG/5)
TG<400 |
|
|
secondary medication causes of hyperlipidemia
|
ticlopidine
cyclosporin atypical antipsychotics (pines) propofol progesterone beta blockers thiazide diuretics |
|
|
NCEP ATP III guidelines
LDL cholesterol a)pts w/o CAD and minimal risk b)pts w/ CAD and modest risk patients w/ CAD,DM, or at high risk |
a)<160
b)<130 c)<100 TG<150 HDL>40 |
|
|
Elevated triglycerides treatment
|
fibrate
niacin omega esters primary target if TG>500 |
|
|
reduced HDL treatment
|
fibrate
niacin |
|
|
bile acid sequestrants dosage administration
|
before meals
take w/ 120mL chiiled noncarbonated beverages allow mixture to stand for 1-2 mins before stirring |
|
|
bile acid sequestrants adverse effects
|
GI-diarrhea, constipation, belching, bloating
raised TG and VLDL |
|
|
nicotinic acid dosage administration
|
75-325mg aspirin 30 min prior to niacin dose
take w/meals or after eating avoid taking with warm beverages |
|
|
nicotinic acid adverse effects
|
facial flushing
inrease uric acid, glucose gastric irritation hepatitis (SR dosage forms) pruritis |
|
|
gemfibrozil dosage administration
|
take 30 min prior to meals
|
|
|
fibric acid adverse effects
|
gallstones
GI may elevate LDL |
|
|
less risk for rhabdo when this is used with statins
|
fenofibrate
|
|
|
statin that should be taken with meals
|
lovastatin
|
|
|
don't have to take these statins in evening
|
atorvastatin
rosuvastatin due to long half life |
|
|
statin adverse effects
|
myalgias
GI hepatitis sleep disturbances |
|
|
increased risk of rhabdomyolysis when used with statins
|
nicontini acid
fibrates erythromycin cyclosporin |
|
|
Statins that are metabolized by CYP3A4
|
lovastatin
simvastatin atorvastatin |
|
|
statins that are metabolized by CYP2C9
|
fluvastatin
|
|
|
ezetimibe adverse effects
|
arthalgia
headache diarrhea infection |
|
|
ezetimibe should not be used concurrently with
|
bile acid sequestrant
|
|
|
omega-3-acid esters indication
|
TGS>500
reduce hepatic synthesis of triglycerides |
|
|
omega-3-acid esters adverse effects
|
GI
enhanced bleeding? |
|
|
niacin/lovastatin combination brand
|
Advicor
|
|
|
cholestyramine brand
|
Questran
|
|
|
colesevelam
|
Welchol
|
|
|
colestipol
|
Colestid
|
|
|
fenofibrate
|
Tricor
|
|
|
fluvastatin
|
Lescol
|
|
|
gemfibrozil
|
Lopid
|
|
|
omega-3-acid
|
Omacor
|
|
|
0= rapid sodium influx
1= slow potassium efflux 2= slow calcium influx w/ potassium efflux 3= potassium efflux 4= sodium efflux and potassium influx |
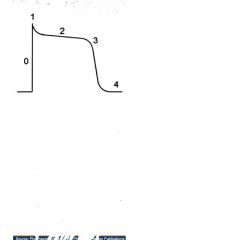
Identify phases of action potential
|
|
|
Class 1A
|
slows phase 0
prolongs APD |
|
|
Class IB
|
slows phase 0
shortens APD |
|
|
Class 1C
|
markedly prolongs phase 0
no effect on APD |
|
|
Class II
|
slows phase 4 rise
|
|
|
Class III
|
prolongs APD
|
|
|
Class IV
|
slows phase 4 rise
|
|
|
PHenothiazines
|
"quinidine" like effects
|
|
|
TCAs
|
"quinidine-like effects"
|
|
|
phenytoin
|
"lidocaine-like effects)
|
|
|
Classes that prolong QT interval
|
Class 1A
Class III |
|
|
Class 1A agents
|
quinidine
procainamide disopyramide |
|
|
Class 1B agents
|
lidocaine
mexiletine |
|
|
Class 1C agents
|
flecainide
propafenone |
|
|
Class II agents
|
beta-blockers
|
|
|
Class III agents
|
amiodarone
sotalol dofetilide ibutilide |
|
|
Class IV agents
|
CCBs
|
|
|
quinidine adverse effects
|
GI (NVD)
cinchonism (tinnitus, headache, dizziness, blurred vision) thrombocytopenia hepatitis |
|
|
quinidine sulfate and quinidine gluconate percent of base
|
quinidine sulfate = 83%
quinidine gluconate = 62% |
|
|
quinidine drug interactions
|
elevates digoxin conc
enhance warfarin effect conc elevated by amiodarone |
|
|
quinidine elimination
|
liver
|
|
|
procainamidE adverse effects
|
drug induced SLE
neutropenia GI |
|
|
procainamide metabolite
|
50% metabolized to NAPA in liver (rapid production= fast acetylators) then NAPA is renally excreted
|
|
|
test that is commonly positive with use of procainamide
|
ANA
|
|
|
Classification of antiarrhythmic agents based on roman numerals 1-4
|
I. Sodium channel blockers
II. Beta blockers III. Potassium blockers IV. Calcium channel blockers |
|
|
Can be used to reverse digitalis-induced arrhythmias
|
Phenytoin (1B activity)
|
|
|
Commonly used in arrhythmias during the acute phase of myocardial infarction
|
Procainamide
|
|
|
Quinidine and digoxin interaction
|
quinidine reduces clearance of digoxin and may increase the serum concentration markedly
|
|
|
Exacerbates cardiac toxicity of class 1 drugs
|
hyperkalemia
|
|
|
Treatment of overdose with class I agents
|
sodium lactate (reverse drug-induced arrhtyhmias)
pressor sympathomimetics (reverse drug-induced hypotension) |
|
|
Disopyramide notes
|
antimuscarinic effects and may precipitate heart failure
negative inotrope |
|
|
Why is lidocaine never given orally?
|
very high first past effect and its metabolites are potentially cardiotoxic
|
|
|
Useful in acute ventricular arrhtyhmias especially those involving ischemia (following MI)
|
lidocaine
|
|
|
lidocaine adverse effects
|
CNS stimulation (convulsions)
allergy (rash to anaphylaxis) |
|
|
Approved only for refractory ventricular tachycardias that tend to progress to VF at unpredictable times, resulting in "sudden death" and for certain intractable supraventricular arrhyhtmias
|
flecainide
|
|
|
Flecainide notes
|
Very proarrhythmic
Negative inotrope CNS and GI toxicity |
|
|
Class II drugs (beta-blockers) mechanism of action
|
cardiac beta blockade and reduction in cAMP, which results in reduction of both sodium and calcium currents and suppression of abnormal pacemakers
|
|
|
Class III agents sotalol, ibutilide, dofetilide toxicities
|
proarrhthymic (sotalol, ibutilide)
torsades de pointes |
|
|
antiarrhythmic agents that are renally eliminated
|
sotalol, dofetilide, digoxin, NAPA
flecainide, disopyramide (partially) |
|
|
predominately used to convert atrial fibrillation/flutter to normal sinus rhythm
|
ibutilide, dofetilide
|
|
|
Considered the most effective antiarrhythmic for ventricular arrhythmias
|
amiodarone
|
|
|
Amiodarone half life
|
35-110days
|
|
|
Amiodarone adverse effects
|
pulmonary fibrosis
thyroid dysfunction corneal deposits optic neuritis hepatotoxicity blue-gray skin photosensitivity CNS GI |
|
|
Amiodarone drug interactions
|
elevates concentrations of:
warfarin digoxin phenytoin quinidine |
|
|
Advantage of amiodarone against other antiarrhythmics
|
minimal proarrhythmic effects
|
|
|
Amiodarone is metabolized by the
|
liver
|
|
|
Amiodarone and Warfarin interaction
|
empiric dosage reduction in warfarin of 30-50% when amiodarone is added
|
|
|
Cause state or use-dependent actions
|
class I and class IV
|
|
|
Type IV antiarrhythmic prototype
|
verapamil (can be given parentally)
|
|
|
Drug of choice for abolishing AV nodal arrhythmias
|
adenosine
|
|
|
adenosine MOA
|
blocks conduction in AV node by hyperpolarizing this tissue (through increased Ik) and by reducing calcium current
|
|
|
adenosine adverse effects
|
facial flushing
dyspnea chest pressure hypotension short term asystole (<1min) |
|
|
Potentiates adenosines effects
|
dipyridamole
carbamazepine |
|
|
Antagonizes adenosine's effects
|
methylxanthines (theophylline, caffeine)
|
|
|
adenosine should not be used in patients with...
|
heart transplants
|
|
|
digoxin notes
|
renally eliminated
36h t1/2 and long distribution phase (wait 6-12 hours after administration before measuring conc) |
|
|
factors enhancing digoxin tocicity
|
hypokalemia
hypomagnesemia hypercalcemia hypothyroidism |
|
|
Elevated digoxin concentrations can cause...
|
hyperkalemia
|
|
|
concurrent use of these may enhance digoxin absorption
|
macrolide antibiotics
tetracyclines PPIs |
|
|
rapid injection of digoxin may cause...
|
peripheral vasoconstriction
|
|
|
Effect of sodium lactage in Class I overdose
|
increase sodium current by increasing the ionic gradient
reduce drug-receptor binding by alkalinizing the tissue |
|
|
Propofenone notes
|
combined type 1C and b-blocker antiarrhythmic
non-linear first pass effect and non-linear elimination metabolized to active cmpds GI and CNS toxicity |
|
|
Adenosine brand
|
Adenocard
|
|
|
amiodarone brand
|
Cordarone
Pacerone |
|
|
disopyramide brand
|
Norpace
|
|
|
dofetilide brand
|
Tikosyn
|
|
|
esmolol brand
|
Brevibloc
|
|
|
flecainide brand
|
Tambocor
|
|
|
ibutilide brand
|
Corvert
|
|
|
lidocaine brand
|
Xylocaine
|
|
|
procainamide brand
|
Procanbid
|
|
|
sotalol brand
|
Betapace
|
|
|
Medications which may cause heart failure
-negative inotropes |
CCBs
BBs disopyramide flecainide propafenone sotalol |
|
|
medications which may cause heart failure
-exogenous sodium administration |
sodium polystyrene sulfonate
antibiotics (PCNS, CEPH) antacids cough syrups |
|
|
medications which may caused heart faiilure
-sodium retaining products |
NSAIDs
glucocorticoids androgens/estrogens |
|
|
medications which may cause heart failure
-cardiotoxins |
doxorubicin
ethanol |
|
|
medications which may cause heart failure
-other |
glitazones
infliximab trastuzamab |
|
|
digoxin MOA
|
inhibition of Na/K ATPase
reduction of calcium expulsion from cell by Na/Ca exchanger caused by increase in intracellular sodium |
|
|
Oral bioavailability of furosemide
|
50%
|
|
|
demonstrated to improve survival in CHF patients
|
ACE-I, ARB, hydralazine/ISDN
|
|
|
This benefited african american patients with heart failure
|
Hydralazine/ISDN 75/40 TID added to ACE-I or ARB
|
|
|
beta blockers approved for heart failure
|
bisoprolol
metoprolol carvedilol |
|
|
considered for patients with decompensated CHF and in acute heart failure
|
dobutamine
milrinone |
|
|
can help prevent dysrhythmias in patients w/ CHF w/o worsening surival
|
amiodarone
dofetilide |
|
|
digoxin bioavailability
-IV -Caps -Soln -Tabs |
IV=100%
Caps=90-100% Soln=75-85% Tabs=70-80% |
|
|
predisposing factors to digoxin toxicity
|
hypokalemia
hypomagnesemia hypercalcemia hypothyroidimsm alkalosis |
|
|
digoxin therapeutic range
|
1-2ng/mL
|
|
|
digoxin distributive phase
|
6-12h
|
|
|
renal failure and effect on digoxin
|
require smaller doses due to decreased Vd
|
|
|
drugs enhancing digoxin absorption
|
macrolides
PPIs "conazoles" ranolazine |
|
|
one vial of digibind binds how much digoxin
|
0.5mg of digoxin
|
|
|
digoxin elimination
|
predominately renal
|
|
|
loading dose of digoxin in pts wihth renal insufficiency
|
reduced due to alterations in tissue protein binding
|
|
|
avoid obtaining blood to measure digoxins concentrations during this period
|
6-12h
|
|
|
half life of digoxin in patients with normal renal function
|
1.5days
|
|
|
Use IBW in obese patients when calculating loading dose
|
True; since digoxin distributes mostly into muscle tissue
|
|
|
therapeutic range considered optimal in treating CHF
|
0.6-1ng/mL
|
|
|
Administer potassium in a chronic digoxin patient or in acute overdose
|
chronic
|
|
|
digoxin toxicity
|
arrhtyhmias
GI/anorexia visual disturbances mental confusion |
|
|
More predictable absorption with digoxin caps or tabs
|
caps
|
|
|
nesiritide
|
human brain natriuretic hormone
reduces preload and afterload stimulates diuresis half-life 20min |
|
|
dopamine doses that exhibit renal perfusion
|
<5mcg/kg/min
|
|
|
dopamine doses that exhibit mostly vasoconstrictive activity
|
>15mcg/kg/min
|
|
|
digoxin immune Fab brand
|
Digibind
|
|
|
hydralazine/ISDN brand
|
BiDil
|
|
|
infliximab brand
|
Remicade
|
|
|
inamrinone brand
|
Inocor
|
|
|
milrinone brand
|
Primacor
|
|
|
nesiritide brand
|
Natrecor
|
|
|
dobutamine effect on CO and preload and afterload
|
increases CO
decreases preload and afterload |
|
|
dopamine effect on CO and preload and afterload
|
increases CO
increases preload and afterload |
|
|
hormones released by the posterior pituitary
|
vasopressin
oxytocin (uterine contractions, lactation) |

