![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the main nutrients that are needed for RBC production?
|
Iron
Folic acid B12 |
|
|
What's the most common type of acquired anemia?
|
Iron deficiency
|
|
|
Where is the iron stored in the body?
|
Essentially all of it is bound to proteins:
Heme: 70% Ferritin/hemosiderin: 30% The minority is in the plasma, where it's bound to TRANSFERRIN |
|
|
Where does iron intake happen?
|
GI tract
|
|
|
What are some of the other proteins that require iron for synthesis?
|
Cytochromes
Myoglobin |
|
|
What are some of the different ways that iron is absorbed?
|
Heme iron: absorbed as-is
Non-heme iron: -Absorbed as FERROUS (2+) -Inhibited by grain, tea; enhanced by vitamin C |
|
|
Where is ferrous iron absorbed?
|
Duodenum
Proximal jejunum |
|
|
How much of ingested iron is typically absorbed?
|
10%
Adjusted based on how much iron you've got already |
|
|
What is hepcidin?
|
Regulator of iron homeostasis
|
|
|
What is the activity of hepcidin?
|
Limiting GI absorption:
-Inhibiting iron absorption in the GI tract -Inhibiting iron recycling |
|
|
How is iron transported in the blood?
|
Transferrin
|
|
|
How much iron is bound to transferrin?
|
300 ug Fe/dL
|
|
|
What impacts the total iron binding capacity?
|
Increased:
-Iron deficiency -Pregnancy -Estrogen therapy Decreased: -Inflammation -Malignancy -Liver disease -Nephrotic syndrome/malnutrition |
|
|
What is the transferrin saturation?
|
Serum iron/TIBC
|
|
|
How does iron get from transferrin to the RBCs?
|
Endocytosis of the transferring/transferrin receptor complex
Once inside the cell, the iron is released and the transferrin goes back into the plasma |
|
|
What are some of the proteins that store iron?
|
Ferritin
Hemosiderin |
|
|
Which is more useful: ferritin or hemosiderin?
|
Ferritin - more accessible
Hemosiderin: more permanent; can hold more, but it's less accessible |
|
|
How is iron excreted?
|
It's not!
The only way that you can lose cells is when you lose cells that have iron: -Bleeding -Epithelial cells getting sloughed off |
|
|
How is iron regulated?
|
Through absorption, as we can't do anything about excretion
|
|
|
What are some visible symptoms of iron deficiency anemia?
|
Esophageal webs (trouble swallowing)
Blue sclerae Pica: craving for chewing on ice Koilonychia: pitting of nails |
|
|
What labs should you order if you suspect iron deficiency?
|
CBC
Serum iron Transferrin saturation Serum ferritin Bone marrow aspiration |
|
|
Ferritin of what levels is diagnostic of an iron deficiency?
|
< 12 ug/L
|
|
|
What are some things that can cause an inflated serum ferritin level?
|
Inflammation
Infection Malignancy Hemolysis JUST BECAUSE YOU'RE ABOVE 12, DOESN'T MEAN THAT YOU'RE NOT DEFICIENT! |
|
|
What do red cells look like if you're iron deficient?
|
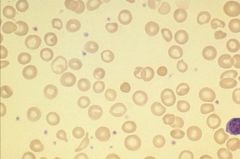
Hypochromic
Central pallor |
|
|
What is responsible for differences in serum levels between men and women?
|
Puberty!
Men have androgenic hormones kicking in, leading to them having MORE serum ferritin |
|
|
What are the first changes that you find in iron depletion? Middle? Last?
|
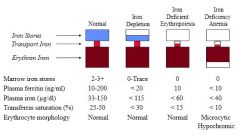
First to change: plasma ferritin levels, marrow iron stores
Second to change: plasma iron Last to change: erythrocyte morphology |
|
|
What stain do you use to look at iron in bone marrow?
|
Prussian blue
This normally isn't done |
|
|
What are some physiologic causes of iron deficiency?
|
Growth
Pregnancy Lactation |
|
|
What are some pathologic causes of iron loss?
|
Blood loss
|
|
|
What are some causes of inadequate iron supply?
|
Low iron containing foods
Impaired iron absorption Transferrin problems |
|
|
What's the normal level for transferrin levels?
|
10%
|
|
|
What's the treatment for iron deficiency?
|
Give them iron!
Oral is best: -Ferrous sulfate -Other salts |
|
|
What's the treatment for people who can't absorb iron?
|
Prenteral iron
|
|
|
What is the cause of the megaloblastic anemias?
|
Defects in DNA synthesis that cause the nucleus to stay big; the nucleus doesn't mature as fast as the rest of the cell
|
|
|
What's the typical appearance of cells with megaloblastic anemia?
|
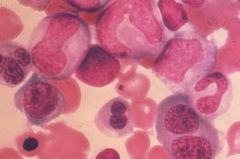
Immature nucleus
Normal cytoplasm Larger than normal cell volume |
|
|
What are the most common causes of megaloblastic anemia?
|
B12
Folic acid |
|
|
When looking at a peripheral blood smear, can you tell the difference between a megablastosis due to B12 vs. folate?
|
NO
|
|
|
What is anisocytosis?
|
A variation in size of RBCs
Elevated RDW |
|
|
What is poikilocytosis?
|
Variation in the shape of the RBCs
|
|
|
What changes happen tot he WBCs with B12/folate deficiency?
|
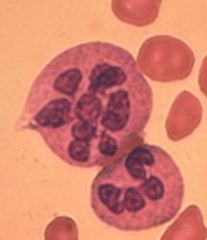
PMNs with more lobes than normal!
5% with 5 lobes 1 with 6 |
|
|
What does the bone marrow look like in megaloblastic anemias?
|
Hypercellular!
The bone marrow can't finish the job...and the cells don't get released until they're finished developing. Bad news. |
|
|
What's on the differential for megaloblastosis?
|
Congenital problems
Erythroleukemia Exposure to drugs Macrocytosis (splenectomy, liver, lung) Artifactural (agglutinination, hyperglycemia) |
|
|
What are some abnormalities that are SPECIFIC (you need to know this!) for B12 deficiency?
|
NEUROLOGIC CHANGES! anywhere.
-Peripheral neuropathies -Dorsal column problems -Spinal degeneration -Psychiatric disorders |
|
|
What is the function of B12 in the body?
|
Homocysteine --> methionine (required for DNA synthesis you need FOLATE!!!)
Methylmalonyl CoA --> succinyl CoA |
|
|
What is regenerated in the reaction of homocysteine to methionine?
|
Tetrahydrofolate
|
|
|
What is the ultimate source of B12?
|
Bacteria and fungi
|
|
|
What are our dietary sources of B12?
|
Animal muscle that has B12 inside of it
Plants (legumes) contaminated with B12 producing bacteria |
|
|
Where are the bacteria that produce B12 located?
|
In the large intestine...which is too far down for us to absorb anything!`
|
|
|
Where is B12 stored in the body?
|
The liver!
|
|
|
What proteins made in the stomach are responsible for the absorption of B12?
|
Intrinsic factor
|
|
|
What receptors are responsible for the uptake of B12 in the intestine?
|
IF receptors
|
|
|
What protein in the saliva binds to B12?
|
R protein
|
|
|
What are causes of B12 deficiency?
|
Inadequate intake: (vegetarian, babies with deficient mothers)
Problems with absorption |
|
|
What are some causes of inadequate absorption of B12?
|
Lack of gastric acid/pepsin
Lack of IF Lack of IF receptors (SURGERY, crohns) Pancreatic insufficiency Zollinger-ellison syndrome NO |
|
|
What are the labs that you do for B12 deficiency?
|
Homocysteine, methylmalonic acid levels
Schilling test IF/Parietal cell Abs |
|
|
What's the treatment for B12 deficiency?
|
Give them B12 (parenterally, typically)
Pancreatic extracts |
|
|
What SHOULDN'T you give someone with B12 deficiency? Why?
|
Folic acid: worsens the neuropsychiatric manifestations of the B12 deificiency
|
|
|
Where is folic acid stored?
|
Liver
We've got a 2-4 month reserve |
|
|
Who needs more folic acid?
|
Women who are pregnant, lactatin
|
|
|
What's the source of folic acid?
|
Leafy greens
Fruits |
|
|
Where is folic acid absorbed?
|
Small intestine
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of distributing folic acid to the body from the liver?
|
Bile.
If you're draining bile because there's a blockage, you can become folic acid deficient |
|
|
What's the function of folate in the body?
|
Tetrahydrofolate is an active coenzyme that donates a methyl group in the conversion of dUMP to dTMP
|
|
|
What are causes of folatedefiency?
|
Intake problems
Increased requirements Intestinal malabsorption Drugs |
|
|
What are labs that you should take for folate deficiency?
|
Measurement of serum foate levels
RBC folic acid levels Homocysteine levels (should be elevated) Methylmalonic acid (normal) |
|
|
What's the treatment for folate deficieny?
|
Give people folate!
|
|
|
Who should we give folate prophylactically to?
|
Women who are pregnant or who are thinking about being pregnant
It prevents neural tube defects |

