![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
145 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What dietary deficiency causes the triad of:
- dermatitis (rash) - diarrhea - dementia |
Pellagra, caused by niacin (vitamin B3) deficiency
|
|
|
What are long-term consequences of lack of dietary fiber?
|
Heart disease
Colorectal cancer Diverticulosis |
|
|
Is breastmilk a good source of iron?
|
No, it has only very meager amounts of iron. Therefore, if baby is solely fed by breastmilk, must give iron supplements.
|
|
|
How do you increase the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin A?
|
Eat the source of the vitamin (carrots for vitamin A) along with a fat source. The fat will increase the absorption.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of vitamin A deficiency?
|
Impaired wound healing
Night vision difficulties Increased risk of respiratory infection |
|
|
Why is vitamin K given to newborns at birth?
|
Placental transfer of K is poor, in contrast to vitamin A, D, and E. Breast milk is also a poor source of K. Vitamin K is needed to clot blood.
|
|
|
How can iron absorption be improved?
|
Eat food rich in vitamin C in the same meal. Helps absorb non-heme iron.
|
|
|
What sort of processes is zinc a cofactor in?
|
- Synthesis of parts of DNA/RNA
- Heme - Release of vitamin A from the liver - EFA, CHO and alcohol metabolism |
|
|
In a child > 2 years old, what is the recommended distribution (in percentages) of calories from macronutrients (CHO, fat, protein)?
|
CHO: 55%
Fat: 30% Protein: 15% |
|
|
What is the order of satiety (from most satiating to the least) between the macronutrients?
|
Fat is the most satiating
Protein is second CHO is the least satiating |
|
|
What are the names of the 2 "families" of essential fatty acids? What is the ideal intake ratio between these two families?
|
Omega-3 (linolenic acid)
- includes EPA and DHA Omega-6 (linoleic acid) Ideal ratio is 1:1 to 4:1 of omega-6 to omega-3 |
|
|
What are the functions of essential fatty acids?
|
- Support cardiovascular, reproductive, immune, musculoskeletal and nervous systems
- Cell membranes manufacture and repair - Prostaglandin production, which regulate heart rate, BP, clotting, fertility, conception, immune function - Neural development in children |
|
|
Is there a way in which omega-3 (linolenic acid) rich foods can not be prepared?
|
Cannot heat them, because heat destroys omega-3.
|
|
|
Functions of vitamin A
|
- Diverse actions in cellular regulation and differentiation
- Essential role in retina - Decreases risk of infection |
|
|
Functions of vitamin E
|
Anti-oxidant for fatty acids in cell membranes
Prevents LDL oxidation Normal immune function |
|
|
Function of pantothenic acid
|
Part of coenzyme A, which is essential for transfer of 2-carbon groups in metabolism of CHO, fatty acids, and synthesis of sterols
|
|
|
Function of vitamin C
|
Collagen synthesis
Promotes activity of aminating enzymes of certain peptides |
|
|
Which vitamins are needed to prevent anemia?
|
• Vitamin B₁₂ and folic acid
• Vitamin B₆ • Vitamin C • Vitamin E |
|
|
Which vitamins have antioxidant properties?
|
A, C, E
|
|
|
Which vitamins help prevent CVD?
|
• Niacin - lowers LDL, raises HDL
• Vitamin C - antioxidative against LDL oxidation, enhance eNOS • Vitamin E - antioxidative • Vitamin B₆, B₁₂ and folic acid reduce homocysteine |
|
|
Which vitamins have been shown to be probably protective against cancers?
|
• Carotenoids (a type of vitamin A) are anti-lung cancer
• Vitamin C is anti-stomach cancer |
|
|
Which vitamins have immune function?
|
• Vitamin A
• B-vitamins • Vitamin C • Vitamin E |
|
|
Which are the lipotropic vitamins?
|
Choline, vitamin B₁₂ and folic acid
- remove fat from liver - reduce liver cancer |
|
|
When does stranger anxiety develop in an infant?
|
9 months
|
|
|
What are the domains of development in infancy and childhood?
|
1. Cognition
2. Language 3. Fine motor 4. Gross motor 5. Adaptive/Activities of Daily Living 6. Socio-emotional |
|
|
List the three constellations of behaviour in infants?
|
1. Easy child (40% of population)
2. Difficult child (20% of population) 3. Slow-to-warm-up child (15% of population) |
|
|
What is Piaget's theoretical framework?
|
SPCA: 4 stages of cognitive development
• Sensorimotor (0-24 months) • Rely on senses and motor reactions to deal with world • Preoperational (2-7 years) • Symbolic thought and play • No logic/deductive thinking • Egocentric • Concrete operations (7-11 years) • Abstract operations (12 years and older) |
|
|
At what age can an infant get into sitting position on their own?
|
8 months
|
|
|
What BMI is considered "at risk of overweight" in children and adolescents?
|
85-95 percentile
|
|
|
Which diseases are more common in Turner's syndrome?
|
CHODOG
Celiac disease Hashimoto's thyroiditis Obesity Diabetes (type 1 and 2) Osteoporosis Gonadal failure |
|
|
Which hormones that normally have a role in growth in infancy and childhood, but have NO ROLE in fetal growth?
Which hormones have a role in fetal growth? |
No role in fetal growth: GH, and TSH/T₄
Have a role in fetal growth: TGF-α, IGF1, IGF2, EGF, Insulin |
|
|
What is the PIT-1 transcription factor needed for?
|
It is needed for pituitary development and hormone expression.
A defect causes deficiency in GH, PRL, and TSH. |
|
|
What causes Laron dwarfism?
|
GH receptor mutation, leading to GH resistance.
|
|
|
If a child has both hypothyroidism and cortisol deficiency, what must you do first?
|
Must replace cortisol before giving T4, to prevent precipitating Addisonian crisis.
|
|
|
If there is concomitant cortisol deficiency along with ADH deficiency, what is the caveat in diagnosis?
|
ADH deficiency will not manifest itself until cortisol deficiency is corrected. This is because cortisol is needed for free water excretion.
|
|
|
Definition of:
Preterm Neonate Infant Child Adolescent Adult |
Preterm 36 weeks and less
Neonate 0-27 days Infant 28 days - 12 months Child 1 - 11 years Adolescent 12 - 17 years Adult > 17 years |
|
|
What is vitamin deficiency risk of eating vegan diet?
|
Vitamin B12 deficiency
|
|
|
What time of food/mineral inhibits iron absorption?
|
Milk and calcium
|
|
|
What causes a disproportionate short stature in infants/children?
|
Skeletal dysplasias, such as achondroplasia (dwarfism)
|
|
|
What causes a proportionate short stature, with loss of height > weight?
|
Endocrine causes (Deficiency in GH, T4, gonadal hormones. Excess in cortisol)
- Exception is deficiency in ACTH/cortisol, and ADH. Patient will be short and thin. Chromosome/genetic causes (Turner, Down) |
|
|
What causes a proportionate short stature, with loss of weight > height?
|
Inadequate calories (malnutrition/malabsorption)
Chronic disease (kidney, cardioresp, hematologic) |
|
|
List the psychoeducational tests used to measure intelligence.
|
Wechsler series
• WPPSI-III (Wechsler preschool and primary scales of intelligence, 3rd ed), for age 2½ - 6 • WISC-III (Wechsler intelligence scales for children, 3rd ed), for age 6-16 • WAIS-III (Wechsler adult intelligence scale, 3rd ed), for age 16-89 SB-V (Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale, 5th ed) Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities DAS - Differential Ability Scales |
|
|
List the psychoeducational tests used to measure adaptive behaviour.
|
1. VABS-II (Vineland Adaptive Behaviour Scales)
2. ABAS (Adaptive Behaviour Assessment System) 3. SIB-R (Scales of Independent Behaviour, Revised) |
|
|
List the psychoeducational tests used to measure academic achievement.
|
1. WIAT-II (Wechsler Intellectual Achievement Test, 2nd ed)
2. WJ-R Tests of Achievement (Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Achievement, Revised) |
|
|
What IQ is considered "intellectual disability"? How about "average"?
|
Intellectual disability is < 69
Average is 90-109 |
|
|
How long do inattentive or hyperactive/impulsive symptoms need to be present for ADHD to be diagnosed? How many symptoms?
What is the other key thing that you need to rule out? |
≥ 6 symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity/impulsivity for ≥ 6 months, to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with developmental level (i.e. their inattentiveness/hyperactivity must be inconsistent with their developmental age)
They need onset before age 7, and impairment of function in 2 or more settings |
|
|
What are some predictors of persistence of ADHD into adulthood?
|
Psychosocial adversity
Psychiatric comorbidity (mood, conduct or anxiety) Familiality |
|
|
In utero, when does the most dramatic brain growth occur?
|
Beginning of fetal stage, especially week 8 - 14
|
|
|
epinephrinum, adrenaline (Tonogen inj.)
|
0.05-0.1-0.2! mg iv
|
|
|
What does the principle of mass action explain in terms of where memory is stored?
|
It says that neurons get grouped together when they fire together.
|
|
|
What are the five steps of neurogenesis?
|
1. Proliferation (in dentate gyrus)
2. Migration (into granule cell layer) 3. Differentiation (into immature neurons) 4. Axonal and dendritic targeting 5. Synaptic integration |
|
|
What are the most significant influences on intelligence?
|
Genetics
Low birth weight Nutrition (but only in developing countries) |
|
|
DSM-IV def of intellectual disability
|
1. Significantly subaverage intellectual functioning
• IQ <= 70 2. Concurrent deficits or impairment in adaptive functioning 3. Onset before age 18 |
|
|
When does a child develop legible printing, and rarely reverses letters?
|
7 years
|
|
|
When does a child have gross motor ability to walk alone?
|
12 months
|
|
|
When does a child have gross motor ability to sit up on their own?
|
8 months
|
|
|
When does a child have gross motor ability to ride a tricycle?
|
3 years
|
|
|
When does a child have gross motor ability to hop or skip?
|
4 years
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to do pincer grasp?
|
10 months
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to scribble?
|
18 months
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to initiate pencil stroke?
|
2 years
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to build tower of 6 cubes?
|
2 years
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to copy a circle?
|
3 years
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to copy a square?
|
4 years
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to copy a triangle?
|
5 years
|
|
|
When does a child have fine motor ability to tie shoes?
|
5 years
|
|
|
When does a child have language ability to coo?
|
2 months
|
|
|
When does a child have language ability to say dada indiscriminately?
|
8 months
|
|
|
When does a child have language ability to have 2 word sentences?
|
2 years
|
|
|
When does a child have language ability to know age and gender?
|
3 years
|
|
|
When does a child have language ability to tell a story, and ask questions?
|
4 years
|
|
|
When does a child have language ability to name 4 colours, and print first name?
|
5 years
|
|
|
When does a child have social development of being able to have social smile?
|
6 weeks
|
|
|
When does a child have social development of being able to wave bye-bye?
|
10 months
|
|
|
When does a child have social development of being able to hug parents?
|
15 months
|
|
|
When does a child have social development of being able to parallel play?
|
2 years
|
|
|
When does a child have social development of being able to participate in associative play?
|
3 years
|
|
|
When does a child have social development of being able to participate in interactive play?
|
4 years
|
|
|
When does a child have social development of being able to play competitive games with rules?
|
5 years
|
|
|
When does a child have adaptive ability to drink from cup?
|
12 months
|
|
|
When does a child have adaptive ability to feed self?
|
18 months
|
|
|
When does a child have adaptive ability to be toilet trained?
|
3 years
|
|
|
When does a child have adaptive ability to undress self, and partially dress?
|
3 years
|
|
|
When does a child have adaptive ability to dress self completely?
|
4 years
|
|
|
What is the definition of a learning disability?
|
Child has significant discrepancy between his/her cognitive ability (IQ) and his/her achievement.
Their IQ profile can be uneven (e.g. bad at verbal IQ, but very good at non-verbal IQ) |
|
|
What is the prevalence of ADHD in North American children?
|
5-15%
|
|
|
What are the most common comorbidities of ADHD?
|
Depressive disorder
Oppositional-defiant disorder Conduct disorder Mania/hypomania Anxiety disorder Learning disabilities Tic disorder |
|
|
What are the first line treatments for ADHD?
|
Ritalin (methylphenidate)
Dexedrine (dextroamphetamine) |
|
|
What are good dietary sources of zinc?
|
Dark red meat
Plain yogurt Cheddar Ricotta cheeses Legumes (also a good source of iron, calcium, fibre) |
|
|
What kind of supplements have shown benefits in children with ADHD?
|
Iron, zinc, magnesium supplements.
|
|
|
What disabilities can FAS cause?
|
ALARMMERS +
- Adaptation - Learning - Attention (limbic system) - Reasoning (frontal lobe) - Memory - Motor (cerebellum) - Executive function (frontal lobe) - Regulation of state (brain stem) - Speech and language (left temporal lobe) + brain and neurological signs |
|
|
At what age is a pregnant woman offered invasive testing without screening?
|
> 40 yr
|
|
|
What is the timing of pubertal stages in girls and boys?
|
Girls
• Thelarche 10 yr • Pubarche 10.5 yr • Menarche 13 yr • Growth velocity peak 11.5 yr • Precocious puberty Thelarche < 8 yr Menarche < 10 yr • Delayed puberty Thelarche > 13 yr Menarche > 16 yr, or absence of menarche within 5 years of pubertal onset Boys • Gonadarche 11.5 yr • Pubarche 12 yr • Growth velocity peak 13.5 yr • Precocious puberty Gonadarche < 9 yr • Delayed puberty Gonadarche > 14 yr |
|
|
What is the first pubertal sign in most girls? boys?
|
Girls: breast development
Boys: testicular enlargement |
|
|
What pubic hair tanner stage is growth velocity peak at for girls?
|
Tanner 3 pubic hair
Approximately 11.5 years old |
|
|
What is the mechanism behind the growth spurt of puberty in adolescents?
|
In both boys and girls, estrogen acts directly on growth plate, and also has permissive effect on GH synthesis and secretion, which promotes growth spurt.
|
|
|
By what bone age is final height of boys and girls established?
|
99% of final height is established at
- bone age 15 in girls - bone age 17 in boys |
|
|
What is one of the most common causes of central precocious puberty?
|
Hypothalamic hamartoma
|
|
|
Causes of peripheral precocious puberty in females and males
|
Females
- McCune Albright syndrome - Adrenal tumour - Primary hypothyroidism (TSH acts on FSH receptor) - Exogenous estrogen (BCPs) - Ovarian tumor/cyst Males - CAH - hCG secreting dysgerminoma/hepatoma - Anabolic steroids - Testicular tumour - Testotoxicosis - Adrenal tumour |
|
|
What is the treatment for central precocious puberty?
|
DepoProvera - for girls
GnRH agonist (Leuprolide) - boys and girls - not recommended in girls who begin puberty at 6-8, with slow progression and/or acceptable predicted adult height |
|
|
What is the management of the delayed puberty in CDGA (constitutional delay of growth and adolescence)?
|
Treatment is never initiated before age 13.
Boys - watchful waiting. Can give 6 mo course of low dose depot testosterone to kick-start puberty. Girls - watchful waiting. Can give ethinyl estradiol. Even more hesitant to treat, because EE is potent at closing growth plate - generally, will not treat girls. |
|
|
What is the most important immediate investigation of anorexia nervosa?
|
Most important investigation for immediate health is ECG, because they often have QT interval prolongation
|
|
|
What is the most common metabolic derangement in bulimia nervosa?
|
Hypochloremic hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
What is involved in an IPS (integrated prenatal screen)?
|
Nuchal translucency
PAPP-A Quad screen - AFP - hCG - uE3 - Inhibin A Note that PAPP-A and NT are done in 1st trimester, and the rest are done in 2nd trimester |
|
|
When is routine prenatal ultrasound usually done?
|
18-20 weeks GA
|
|
|
What is the time window for doing amniocentesis? CVS?
|
Amnio: 15-17 weeks GA
CVS: 10-12 weeks GA |
|
|
What is the background risk of birth defect or mental retardation for each pregnancy?
|
3-5% risk
|
|
|
What is a cystic hygroma?
|
Congenital lymphatic cyst in posterior triangle of neck. If seen on prenatal ultrasound, it is associated with risk of Turner syndrome.
|
|
|
What genes are needed to develop the gonads from the urogenital ridge?
|
WT1, SF-1, DAX1
|
|
|
What is the SRY portion of the Y chromosome required for? What is the long arm of the Y chromosome important for?
|
SRY, on Yp (short arm) - needed for testis formation.
Yq (long arm) - needed for spermatogenesis. |
|
|
What induces formation of Wolffian duct structures?
What induces formation of external genitalia? |
Wolffian duct structures - testosterone
External genitalia - DHT |
|
|
What are the remnants of the Mullerian ducts in male adults?
of the Wolffian duct in female adults? |
Mullerian duct remnants:
- Utriculus prostaticus - Appendix testis Wolffian duct remnants: - Paroophoron - Epoophoron - Gartner's cyst |
|
|
What are derivatives of the Mullerian duct in females?
|
Fallopian tubes
Uterus Upper 2/3 of vagina |
|
|
What is mixed gonadal dysgenesis?
What is pure gonadal dysgenesis? |
Mixed gonadal dysgenesis: 45X / 46,XY mosaicism
Pure gonadal dysgenesis: many variations, but one form is 46,XY with deletion of SRY region |
|
|
What is the clinical picture of a person with pure gonadal dysgenesis?
|
46XY with SRY deletion
• Unambiguous females with streak gonads (therefore no menses) • Have Mullerian duct derivatives (because no MIS) |
|
|
What are the different categories of congenital anomalies?
|
1. Malformations (cleft lip, palate)
2. Disruption (porencephaly) 3. Deformation (plagiocephaly) |
|
|
What symptoms/signs would you see with zinc deficiency?
|
Weak sense of taste and smell
Hypogonadism Immune dysfunction Marked growth reduction Night blindness Dry skin on palms and soles (acrodermatitis) |
|
|
What is marasmus?
|
It is deficiency in energy providing foods
Clinical presentation □ Infant looks wasted, like an old person □ Child is weak, hypotonic, and cold □ Hair loss and loose baggy skin |
|
|
What is phenylketonuria, and what serious effect does it have?
|
Deficiency in phenylalanine hydroxylase in liver.
Phenylalanine accumulation in blood and tissues causes serious effect on brain function (intellectual disability) |
|
|
What are some drugs that are "anti-vitamin"?
|
Trimethoprim affects folic acid
Anti-TB drugs antagonize B6 |
|
|
What are the stages of fetal lung development, and when do they occur?
Which is the stage when postnatal survival becomes a possibility? |
• Pseudoglandular - 5-17 weeks
• Canalicular - 16-25 weeks • Saccular - 24 weeks - term • Alveolar - late pregnancy throughout infancy Saccular stage is when survival is possible. |
|
|
How much fetal lung fluid is formed per day at term?
|
Up to 400 ml / day
|
|
|
What is pulmonary surfactant made of?
|
90% lipid (dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine)
10% protein - SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, SP-D • A and D - immunity -Deficiency causes susceptibility to respiratory infections • B and C - help spread surfactant over the surface -Deficiency causes refractoriness to treatment with exogenous surfactant |
|
|
What are the three most common causes of neonatal respiratory distress?
|
1. Transient tachypnea of the newborn
-FLF still present in lungs -On x-ray, lungs seem overinflated, and there is prominence of cardiac silhouette 2. Respiratory distress syndrome -Lack of pulmonary surfactant production/release -Mostly a problem of pre-term infants -On x-ray, low lung volume, and there is loss of cardiac silhouette 3. Meconium aspiration syndrome -Mostly seen in post-term babies -On x-ray, hyperinflation, areas of emphysema, atelectasis and pleural effusions |
|
|
When can cow's milk be introduced into an infant's diet?
What is the maximum intake of milk at this time? |
After 12 months.
After 1 year, max intake of milk should not exceed 24 oz per day. |
|
|
Name the primitive reflexes, and when they should disappear.
Same with postural reflexes, and when they should appear. |
Primitive reflexes
- Stepping, 2 mo - Moro, 4 mo - Galant, 6 mo - Palmar, 6 mo - Plantar, 7 mo - Rooting/sucking, persist as voluntary feeding Postural reflexes - Protective equilibrium, 4-6 mo - Parachute, 8-9 mo |
|
|
What are the most common infectious agents that cause early onset postnatal sepsis? late onset?
|
Early onset:
-GBS -Listeria -E. coli -Enterovirus Late onset: -Any of the above, PLUS -Staph aureus -Coagulase negative Staph -Anaerobes -Pseudomonas -Candida |
|
|
Postnatally, when is the period of highest susceptibility to extracellular, intracellular and encapsulated pathogens?
|
Extracellular (e.g. E. coli) - first 6 mo
Intracellular (e.g. CMV), and encapsulated (e.g. GBS) - first 2 years |
|
|
What are the most common causes of congenital malformations?
|
1. Multifactorial/unknown 65%
2. Genetic 25% 3. Maternal condition 4% 4. Maternal infection 3% 5. Mechanical deformations 1-2% 6. Drugs and chemicals < 1% |
|
|
What are the 5 FDA classifications for drug safety in pregnant women?
|
A - controlled studies in pregnant women show no risk
B - no evidence of risk in humans C - risk cannot be ruled out D - positive evidence of risk, but benefits may still outweigh risk X - positive evidence of risks, which clearly outweigh the benefits |
|
|
What are the main considerations in neonatal pharmacokinetics?
|
Higher gastric pH (i.e. more basic)
Stratum corneum is thinner More water composition, less fat composition Some liver enzymes are not fully expressed at birth Lower GFR and renal tubular excretion |
|
|
What is the conversion calculation for infant dosages of medications, based on dosages meant for adults?
|
Dose for infant = dose (for adult) * (BSA of infant / BSA of adult)
BSA = body surface area |
|
|
What are characteristics of a drug that cause more of it to be excreted in breast milk?
|
Lipophilic
↓ Ionization Low molecular weight Low protein binding |
|
|
Which drugs may be excreted into breast milk?
|
Benzodiazepines
Barbiturates Narcotics Anticancer drugs Antidepressants and antipsychotics |
|
|
What are the mechanisms by which thyroid hormone contributes to growth?
|
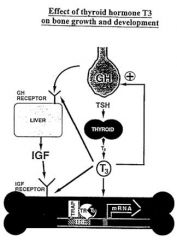
T3 has direct effect on osteoblasts via interaction with thyroid hormone receptor (TR).
Indirect action via permissive effect on GH and IGF synthesis and action |
|
|
How does Cushing syndrome cause growth retardation?
|
Positive feedback on somatostatin, which inhibits GH release
Disrupt GH pulsatility ↓IGF-1 activity ↓Connective tissue synthesis ↓Adrenal gland androgen production |
|
|
How many words should be in the vocabulary of a 2-3 year old?
3-4 year old? |
2-3 yr: 200 words
3-4 yr: 400-1500 words |
|
|
What are the daily iron requirements for age 9-13? 14-18?
|
Age 9-13 years: 8 mg
• Need more if in growth spurt ◊ +2.9 mg for boys ◊ +1.1 mg for girls ◊ +2.5 mg If menstruating Age 14-18 □ Boys need 11 mg □ Girls need 15 mg □ Can take less (11.4 mg) if taking oral contraceptives If vegetarian, multiply by 1.8 to correct for non-heme iron Upper level of iron is 45 mg/day |
|
|
What is the issue with taking too much zinc?
|
It competes with copper.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for the following STIs -
Chlamydia? Neisseria gonorrheae? Treponema pallidum? Trichomonas vaginalis? Scabies? |
Chlamydia - tetracycline
Neisseria gonorrheae - cefixime Treponema pallidum - penicillin G Trichomonas vaginalis - metronidazole Scabies - permethrin |
|
|
What organisms are possible in urethritis?
What is the empiric treatment? |
Chlamydia
Ureaplasma Mycoplasma Gonorrhea Trichomonas Cefixime and doxycycline |
|
|
What organisms are possible in cervicitis?
What is the empiric treatment? |
Gonorrhea
Chlamydia Cefixime and doxycycline |
|
|
What organisms are possible in pelvic inflammatory disease?
|
Gonorrhea
Chlamydia Polymicrobial (anaerobes, gram negatives) |
|
|
What organisms are possible in epididymitis?
What is the empiric treatment? |
Gonorrhea
Chlamydia UTI pathogens (E.coli) Cefixime and doxycycline Ciprofloxacin for UTIs |
|
|
Which opioid is given for long term treatment of addiction?
|
Naltrexone is p.o., and long-acting.
Contrast with naloxone, which is i.v. and short-acting. |

