![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The different segments of the gastrointestinal tract are separated by what? A. Valves B. Hemorrhoids C. Sphincters D. Membranes |
C. Sphincters |
|
|
Which enzyme is NOT found in the saliva? A. Lysozyme B. Pingual Lipase C. Pepsin D. Amylase |
C. Pepsin
|
|
|
The accessory organs in the mouth are? A. Gallbladder B. The pancreas C. The liver D. The salivary glands |
D. The salivary glands |
|
|
What is the role of lysozyme?
A. It breaks down fats B. It kills bacteria C. It breaks down proteins D. It breaks down sugars |
B. It kills bacteria |
|
|
Which salivary gland is located next to the ear? A. Parotid B. Sublingual C. Submandibular |
A. Parotid |
|
|
What is bolus? A. A mouthful of chewed food B. Chyme C. Hydrochloric acid mixed with chewed food D. A bowl of food |
A mouthful of chewed food |
|
|
Which one is a correct statement?
A. The trachea is in front of the esophagus B. The esophagus is in front of the trachea C. The esophagus and trachea are sideways next to each other |
A. The trachea is in front of the esophagus |
|
|
If someone is choking what needs to be done? A. Perform mouth to mouth resuscitation B. Perform cardiac difrilation C. Allow the person to recover by himself/herself D. Perform the Heimlich maneuver |
D. Perform the Heimlich maneuver |
|
|
Why food cannot enter the trachea? A. The epiglottis protects the trachea B. The epiglottis protects the esophagus C. The trachea is completely separated from the esophagus |
A. The epiglottis protects the trachea |
|
|
The esophagus connects to the stomach through which sphincter? A. The lower esophageal sphincter B. The ileo-cecal sphincter C. The pyloric sphincter D. The anal sphincter |
A. The lower esophageal sphincter |
|
|
Why giraffes can drink water? How can water flow upwards?
A. Water is absorbed through osmosis B. The peristaltic motion can push liquids upward C. The giraffe stores water in its big head, then lifts it's head to allow water to flow down D. Giraffes can only drink water from waterfalls |
B. The peristaltic motion can push liquids upward |
|
|
If the lower esophageal sphincter does not function properly, what condition develops? A. Diarrhea B. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease C. Food poisoning D. Food allergies |
B. Gastro-esophageal disease |
|
|
What is the main physiological function of the stomach? A. To digest sugars B. To obsorb vitamins C. To disinfect foods D. To obsorb proteins |
C. To disenfect foods |
|
|
The bolus mixed with hydrochloric acid results in what? A. Amylopectin B. Enzymes C. Peptides D. Chyme |
D. Chyme |
|
|
Which enzymes can be found in the stomache? (Choose two) A. Amylase B. Lysozyme C. Trypsin D. Pepsin E. Gastric Lipase |
D. Pepsin E. Gastric lipase |
|
|
What is the main role of the large intestine? A. To obsorb nutrients B. To detox liver C. To obsorb water D. To disenfect food |
C. To obsorb water |
|
|
Where do most nutrients get obsorbed into the body A. Through the micro villi surface B. Through the stomach surface C. Through the rectum surface D. Through the large intestine surface |
A. Through the micro villi surface |
|
|
What is the simplest chemical formula for most carbohydrates? A. CH0 B. CH20 C. CH06 D C2H0 |
B. CH20 |
|
|
What is the average energy content of most sugars? A. 7 kcal/g B. 11 kcal/g C. 9 kcal/g D. 4 kcal/g |
D. 4 kcal/g |
|
|
Glucose is a .... A. Monosaccharide B. Disaccharide C. Polysaccharide |
A. Monosaccharide |
|
|
Galactose is a... A. Monosaccharide B. Disaccharide C. Polysaccharide |
A. Monosaccharide |
|
|
Lactose is a... A. Monosaccharide B. Disaccharide C. Polysaccharide |
B. Disaccharide |
|
|
Table sugar is a... A. Monosaccharide B. Disaccharide C. Polysaccharide |
B. Disaccacharide |
|
|
Sucrose is made of what? A. Glucose + glucose B. Fructose + galactose C. Glucose + galactose D. Glucose + fructose |
D. Glucose + fructose |
|
|
Lactose intolerance is caused by... A. A lack of Maltase B. A lack of pepsin C. A lack of lactase D. An excess of sucrase |
C. A lack of lactase |
|
|
Glycogen is stored where? A. In the kidneys B. In the bones C. In the lungs D. In the adipose tissue E. In the liver and in the muscles |
E. In the liver and in the muscles |
|
|
Glycogen stores will last for how long? A. 7 days B. 24 hours C. 8-12 hours D. 3 days E. A full month |
C. 8-12 hours |
|
|
When glycogen is broken down, it becomes what? A. Starch B. Lipids C. Lactose D. Glucose |
D. Glucose |
|
|
Who is used as a reference point for the glycemic indeces? A. Saturated fatty acids B. Glycogen C. Starches D. Triglycerides C. Glucose |
E. Glucose |
|
|
What is the glycemic index? A. A measure of the sweetness of the food B. A measure of the vitamins content C. A measure of the energy content D. A time measure of absorption into blood |
D. A time measure of absorption into blood |
|
|
Which of these food items contains glycogen? A. Salad B. Cocacola C. Steak D. Baked beans E. Mashed potatoes F. Beer |
C. Steak |
|
|
Which food item contains amylose starch? A. Short grain rice B. Long grain rice C. Waxy potatoes D. Milk E. Foie grass |
B. Long grain rice |
|
|
High glycemic index foods are healthier than low glycemic index foods A. True B. False |
B. False |
|
|
Amylose starches have a lower glycemic index than amylopectin starches do A. True B. False |
A. True |
|
|
If the glucose level in the blood is too high we call this condition... A. Hyperglycemia B. Isoglycemia C. Paraglycemia D. Hypoglycemia |
A. Hyperglycemia |
|
|
If the glucose level in the blood is too low, we call this condition... A. Paraglycemia B. Hyperglycemia C. Isoglycemia D. Hypoglycemia |
D. Hypoglycemia |
|
|
If the blood glucose level is too high, who intervenes to bring it back down to normal levels? A. Amylase B. Pepsin C. Insulin D. Glucagon |
C. Insulin |
|
|
If the blood glucose level is too low, who intervenes to bring it back up into normal range? A. Amylase B. Pepsin C. Insulin D. Glucagon |
D. Glucagon |
|
|
What is the cause of diabetes 1? A. The insulin receptors die B. The pancreatic beta cells die C. The entire glucose metabolism is defective D. The pancreatic alpha cells die |
B. The pancreatic beta cells die |
|
|
What is damaged by high sugar levels in the blood? A. The muscles are damaged B. The capillaries are damaged C. The skin cells are damaged D. The brain is damaged |
B. The capillaries are damaged |
|
|
Which one is a typical pathology in diabetes? A. Brain cancer B. Asthma C. Allergies D. Retinopathy |
D. Retinopathy |
|
|
Generally lipids have how much energy content? A. 4 kcal/g B. 11 kcal/g C. 7 kcal/g D. 9 kcal/g |
D. 9 kcal/g |
|
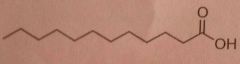
What is shown in this picture?
A. Saturated fatty acid B. Glycerol C. A phospholipid D. Glycogen E. A triglyceride F. An unsaturated fatty acid G. Cholesterol |
Don't know yet lol |
|
|
Phospholipids are used for what? A. Make membranes B. Digest proteins C. Lower the stomachs pH D. Build glycogen stores |
A. Make membranes |
|
|
What is the meaning of an unsaturated fatty acid? A. It lacks glycerol B. It lacks a phosphate group C. It has a maximum number of hydrogens D. Is has double bonds |
D. It has double bonds |
|
|
How are fats transported throughout the body? A. They float easily through the circulation B. Via lipoprotein shuttles C. Via blood cells |
B. Via lipoprotein shuttles |
|
|
How does orlistat/alli/xenical work? A. The drug blocks bile B. The drug blocks amylase C. The drug blocks proteases D. The drug blocks lipases |
D. The drug blocks lipases |
|
|
Lipids are primary fuels A. True B. False |
B. False |
|
|
In your blood lipid profile medical report, which line will show the "bad cholesterol?" A. Hdl B. Chylomricon C. Ldl D. Vldl |
C. Ldl |
|
|
In your blood lipid profile report, which one will show the "good cholesterol?" A. Hdl B. Chylomricon C. Vldl D. Vdl |
A. Hdl |
|
|
If one gets on a cholesterol free diet, what will happen to this person? A. The person will slowly develop a chronic disease B. The person will develop an acute disease C. Nothing. The person will be perfectly fine |
C. Nothing. The person will be perfectly fine |
|
|
What does the vldl acronym stand for?
A. Vital lipids degrading lipase B. Very long duration lipoprotein C. Very low degradation lipoprotein D. Very low density lipoprotein |
D. Very low density lipoprotein |
|
|
Is there a metabolic limit for how much fat can be stored in the human body? A. There is no limit B. Of course, there are sophisticated metabolic controls that block fat storage after a limit was reached |
B. There is no limit |
|
|
An overweight or an obese person has plenty of energy stored in his body. Those energy stores could last for two weeks. Then why is this person hungry after only a few hours? A. The brain is only fueled by glucose. The amount of lipids stored is irrelevant B. This person's hunger is psychological, due to his poor habits |
A. The brain is only fueled by glucose. The amount of lipids stored is irrelevant |
|
|
Calculate the energy content of a food item containing the following 10 grams of sucrose 5 grams of amylopectin starch 7 grams of fiber 3 grams unsaturated fats 10 grams of tryglycerides 3 grams of cholesterol A. 212 kcal B. 290 kcal C. 177 kcal D. 156 kcal E. 193 kcal |
C. 177 kcal |
|
|
Calculate the energy content of a meal, if it contains the following Starch 10g Sucrose 9g Fiber 11g Protein 25g Triglycerides 5g Saturated fatty acids 7g Cholesterol .5g Retinol 0.01g Ascorbate .5g Niacin .1g Ethanol 15g A. 513 kcal B. 479 kcal C. 457 kcal D. 389 kcal E. 262 kcal |
D. 389 kcal |
|
|
Calculate the daily protein needs for a person weighing 132 pounds A. 45g B. 60g C. 132g D. 105.6g E. 264g |
A. 48g |
|
|
What is the meaning of a complete protein? A. It is completely satisfying B. It contains the essential amino acids C. It is completely digestible D. It completely covers nutritional needs E. It contains all 20 amino acids |
B it contains the essential amino acids |
|
|
The main role of proteins is A. To provide building blocks B. To provide energy C. To provide Co enzymes D. To provide minerals E. To provide oxygen |
A. To provide building blocks |
|
|
What differentiates amino acid types from each other?
A. The amino groups B. The R groups C. The carboxyl groups D. The hydroxyl groups E. The central carbon atom |
B. The R groups |
|
|
What happens to the amino groups during amino acid metabolism A. It enters glycolysis B. It enters beta oxidation C. It enters the Krebs cycle D. It is turned directly into ATP E. It is transformed in UREA |
E. It is transformed into UREA |
|
|
Who breaks down proteins? A. Amylase B. Lipase C. Lysozyme D. Phosphotases E. Proteases |
E. Proteases |
|
|
Which one is an inactive protease? A. Trypsinogen B. Pro amylase C. Trypsin D. Lipaseogen E. Pepsin |
A. Trpsinogen |
|
|
A diabetic patient decides to eat insulin. What happens to the contaminated insulin?
A. It is obsorbed into the bloodstream and the blood glucose levels are lowered B. It is obsorbed into the bloodstream and the blood glucose levels are increased C. It transits through the GI react without being obsorbed D. It is combined with intrinsic factor to foam vitamin B12 E. It is digested into amino acids which are then used as building blocks |
E. It is digested into amino acids which are then used as building blocks |
|
|
A child has a neutral nitrogen balance. What is your take on this? A. This is bad news, the child is sick B. This is completely normal C. This is bad news, the balance should be negative |
A. This is bad news, the child is sick |
|
|
Some fishermen were drifting for 1 week on a broken boat before being rescued. They had no food, but had enough water to survive the ordeal. What will be their nitrogen balance? A. They will have a negative balance B. They will have a neutral balance C. They will have a positive balance |
A. They will have a negative balance |
|
|
What should vegans do with regard to their protein intake? A. They should abandon veganism and switch to meat eating B. They can allow themselves to eat a narrow range of foods C. They should always mix their food sources D. They should buy extra protein powders as supplements |
C. They should always mix their food sources |
|
|
What is true of glycolysis A. It is anaerobic B. It starts with acetyl COA C. it starts with pyuvate D. It is aerobic E. It makes a lot of ATP |
A. It is anaerobic |
|
|
What does the word glycolysis mean? A. An increase in glycogen B. A decrease in glycogen C. A blood glucose level regulation D. Sugar breakdown E. A sweet lysozyme |
D. Sugar breakdown |
|
|
What does ATP stand for? A. Autonomous tri phase B. Automatic thermic phase C. Adenosine tri pyruvate D. Adenosine tri phosphate E. Adenosine tetra phosphate |
D. Adenosine tri phosphate |
|
|
Fatty acids are broken down via which pathway?
A. De-amination B. Glycolysis C. Beta oxidation D. Anabolic synthesis E. Protease degradation |
C. Beta oxidation |
|
|
Who is the ultimate biological fuel that powers everything in the cell? A. Glucose B. Acetyl COA C. ATP D. Fatty acids E. Amino acids |
C. ATP |
|
|
When burned down carbon atoms are eliminated, they leave the body how? A. Through breath B. Through sweat C. Through urine D. Through feces |
A. Through breath |
|
|
The Krebs cycle starts with which compound? A. Acetyl COA B. Pyruvate C. Glucose D. Fatty acids E. Carbon dioxide |
A. Acetyl COA |
|
|
What is true of the Krebs cycle? A. It is anaerobic B. It starts with glucose C. All catabolic pathways converge on it D. It powers explosive motions such as sprinting or jumping E. It is located in the cytoplasm |
C. All catabolic pathways converge on it |
|
|
What is true of beta oxidation? A. It is aerobic B. It is anaerobic C. It connects to glycolyis D. It produces pyruvate E. It starts with glucose |
A. It is aerobic |
|
|
Which are the signs of methanol toxicity? A. Fatty liver disease B. Cirrhosis C. Blindness D. Multiple sclerosis E. Anemia |
C. Blindness |
|
|
What is the antidote for methanol toxicity A. Ethanol B. Vitamin C C. Antibiotics D. Tocopherol E. Folate |
A. Ethanol |
|
|
If the brainstem is affected by ethanol, what is the main concern? A. Abstract thinking is inhibited B. Speech and language abilities are inhibited C. Bodily balance and fine tuned motions are inhibited D. Social self control is inhibited E. Coma: basic life functions are inhibited |
E. Coma: basic life functions are inhibited |
|
|
Which cancer has a strong correlation to ethanol consumption? A. Skin cancer B. Brain cancer C. Colon cancer D. Pancreatic cancer E. Bone cancer |
D. Pancreatic cancer |
|
|
What is true of micronutrients? A. They build the body up B. They build reserves C. They provide energy D. Small quantities are needed to be consumed E. They are enzymes |
D. Small quantities are needed to be consumed |
|
|
Which vitamin is water soluable? A. Vit a B. Vit d C. Vit c D. Vit k E. Vit e |
Vit. C |
|
|
A person with vitamin A deficiency should eat which food from this list? A. Eggs B. Carrots C. Beans D. Steak E. Apple |
B. Carrots |
|
|
What is another name for vitamin B3? A. Retinol B. Niacin C. Tocopherol D. Calcitriol E. Ascorbate |
B. Niacin |
|
|
Pregnant women should supplement their diet with which vitamin? A. Retinoic acid B. Folate C. Ascorbate D. Calcitriol E. Niacin |
B. Folate |
|
|
Which one is the true vitamin D? A. Cholesterol B. D2 C. D3 D. Calcidiol E. Calcitriol |
E. Calcitriol |
|
|
Deficiency of vitamin D may cause which disease on this list? A. Night blindness B. Scurvy C. Keratinization D. Spina bifida E. Multiple sclerosis |
E. Multiple sclerosis |
|
|
Which vitamin can be accumulated to toxic levels from this list? A. Ascorbate B. Retinoic Acid C. Riboflavin D. Cobalamin E. Folate |
B. Retinoic acid |
|
|
Cancer patients should avoid taking which supplements? A. Ascorbate B. Folate C. Retinoic Acid D. Riboflavin E. Cobalamin |
B. Folate |
|
|
Diabetics should avoid taking which supplement? A. Beta carotenoid B. Tocopherol C. Cobalamin D. Niacin E. Folate |
D. Niacin |
|
|
Which vitamin is an anti oxidant on this list? A. Niacin B. Ascorbate C. Folate D. Cobalamain E. Calcitriol |
B. Ascorbate |
|
|
Newborn babies should get which shot? A. Vit k B. Cobalamin shot C. Calcitriol shot D. Ascorbate shot |
A. Vit k shot |
|
|
Intrinsic factor is required for the obsorption of which vitamin? A. Ascorbate B. Cobalamin C. Niacin D. Riboflavin E. Tocopherol |
B. Cobalamin |
|
|
Tocopherol is A. A lipid soluble Co enzyme B. A lipid soluble anti oxidant C. A water soluble Co enzyme D. A water soluble anti oxidant |
B. A lipid soluble anti oxidant |
|
|
Smoking depletes which vitamin levels? A. Niacin B. Folic acid C. Riboflavin D. Cobalamin E. Ascorbic acid |
E. Ascorbic acid |
|
|
If you want to get vit b12 from food sources, which food should they eat from the list? A. Beans B. Spinach or kale C. Meats D. Nuts E. Bannanas |
C. Meats |
|
|
A patient suffers from keratinization disease. You suspect which deficiency? A. Vit A B. Vit b2 C. Vit b3 D. Vit c E. Vit d |
A. Vit a |
|
|
An excess of vitamin E may cause what? A. Internal bleeding B. Scurvy C. Osteomalacia D. Spina bifida E. Night blindness |
A. Internal bleeding |
|
|
Which vitamin plays a role in maintaining healthy mitochondria? A. Vit b2 B. Vit b3 C. Vit 12 D. Folate E. Vit c |
B. Vit b3 |
|
|
Vitamin K deficiency puts one at risk of what? A. Uncontrolled bleeding B. Poor skin quality C. Failing vision D. Weak bones E. Anemia |
A. Uncontrolled bleeding |
|
|
Which vitamin can be stored in the liver from this list? A. Ascorbate B. Niacin C. Riboflavin D. Cobalamin E. Folate |
D. Cobalamin |
|
|
How much blood does an average person have? A. 2 liters B. 5 liters C. 7 liters D. 10 liters E. 15 liters |
B. 5 liters |
|
|
Which genders body has more water by percentage? A. Females have more water B. Males have more water C. Genders are equal. Both genders have equal amounts of water D. This completely depends on each individual regardless of gender |
B. Males have more water |
|
|
An average person will be functional without water for what period of time? A. 1 day B. 2 days C. 3 days D. 4 days E. 5 days |
C. 3 days |
|
|
An average person will survive without water for how long?
A. 1 day B. 2 days C. 4 days D. 5 days E. 7 days |
E. 7 days |
|
|
Which one is the main extracellular osmotic ion? A. Ca+ B. Na+ C. K+ D. Cl- E. Mg2+ |
B. Na+ |
|
|
Which one is the main intracellular osmotic ion? A. Ca2+ B. Na+ C. K+ D. Cl- E. Mg2+ |
C. K+ |
|
|
Water molecules can freely move across cell membranes A. True B. False |
A. True |
|
|
The phenomenon of osmosis exists because A. The cell membrane blocks water flow B. Water molecules trapped in hydration shells cannot cross the membrane anymore C. Biomolecules have solution shells D. The cell magnetically captures water |
B. Waters molecules trapped in hydration shells cannot cross the membrane anymore |
|
|
What happens to cells placed in hypertonic solution? A. The cells are at equilibrium and no changes occur B. The cells swell as water rushes in C. The cells shrink |
C. The cells shrink |
|
|
What happens to cells placed in hypotonic solution? A. The cells are at equilibrium and no changes occur B. The cells swell as water rushes in C. The cells shrink |
B. The cells swell as water rushes in |
|
|
How does the sodium potassium exchange pump work? A. One na exchanged for one k in any direction B. Two na are pumped out for one k pumped in C. Two na are pumped out for three k pumped in D. Three na are pumped out for two k pumped in E. Three na pumped in for two k pumped out. |
D. Three na are pumped out for two k pumped in |
|
|
Why drinking sea water is dangerous? A. Because it is hypertonic B. Because it is hypotonic C. Because it is isotonic D. Because it us toxitonic E. Because it is physiotonic |
A. Because it is hypertonic |
|
|
Intravanous injections must be how? A. Hypertonic B. Isotonic C. Hypotonic |
B. Isotonic |
|
|
You must perform emergency rehydration on a patient. What do you do? A. Give the patient plenty of water B. Give the patient an enema C. Give the patient a bath D. Give the patient plenty of sports drinks E. Give the patient intravanous rehydration |
E. Give the patient intravanous rehydration |
|
|
Your friend ran 6 miles, and she is thrilled that she lost 4 pounds during the run. What do you tell her? A. Sorry, you only lost water weight. B. Great job |
A. Sorry, you only lost water weight |
|
|
Chlorea patients die because of what reason?
A. They die of calorie loss B. They die of a heart C. They die of dehydration D. They die of overhydration E. They die of hepatitis |
C. They die of dehydration |
|
|
Which one is the ion lost in sweat? A. Ca B. Na C. K D. Cl E. Mg |
B. Na |
|
|
Calcium is what? A. A water soluble vitamin B. A trace mineral C. A major mineral D. A macronutrient E. A lipid soluble vitamin |
C. A major mineral |
|
|
Iron is what? A. A water soluble vitamin B. A trace mineral C. A major mineral D. A macronutrient E. A lipid soluble vitamin |
B. A trace mineral |
|
|
BMR stands for what? A. Biochemical metabolic rate B. Body mass rate C. Body mass index D. Basal metabolic rate E. Basal metabolic rate |
D. Basal metabolic rate |
|
|
BMR costs approximately how much energy? A. 1% B. 10% C. 30% D 60% E 70% |
D 60% |
|
|
BMR correlates with which tissue? A. It correlates with bone mass B. It correlates with adipose tissue C. It correlates with brain size D. Is correlates with muscle mass |
D. Is correlated with muscle mass |
|
|
A person is deficient in leptin. What are the symptoms? A. No visible symptoms B. The person is always famished C. The person is always satiated D. The person is always thirsty E. The person becomes very muscular |
B. The person is always famished |
|
|
BMI stands for what? A. Biochemical metabolic rate B. Body mass rate C. Body mass index D. Basal metabolic index E. Body metabolic rate |
C. Body mass index |
|
|
Which one is the BMI range for an overweight person? A. Between 5 and 10 B. Between 10 and 20 C. Between 18 and 25 D. Between 25 and 30 E. Between 30 and 35 |
D. Between 25 and 30 |
|
|
Which one is the BMI formula? A. Kilos2 / height in m B. Height in m2 / kilos C. Kilos / height in m2 D. 100 lbs for the first 5 feet and 5 lbs for each extra inch E. Kilos / height in m |
C. Killos / height in m2 |
|
|
Use the Hamwi formula to calculate the ideal weight of a 6'2" male A. 100kg B. 100lbs C. 190kg D. 190lbs E. 250lbs |
D. 190lbs |
|
|
What is the maximal safe heart rate for a 25 year old? A. 60 beats per min B. 85 beats per min C. 120 beats per min D. 160 beats per min E. 195 beats per min |
E. 195 beats per min |
|
|
The heart muscle is supplied with blood by circulation? A. By the systemic circulation B. By the pulmonary circulation C. By the coronary circulation D. By the portal circulation |
C. By the coronary circulation |
|
|
Blood is pumped into the heart muscle during which phase? A. The systolic phase B. The diastolic phase C. During both systolic and diastolic phase |
B. The diastolic phase |
|
|
When the heart beats faster, what happens? A. The systoles become larger B. The systoles become shorter C. The diastoles becomes longer D. The diastoles become shorter E. Both systoles and diastoles remain unchanged |
D. The diastoles become shorter |
|
|
Which one is the last product of glycolysis? A. Pyruvate B. Glucose C. Acetyl COA D. Lactic acid E. Carbon dioxide |
A. Pyruvate |
|
|
Which one is the first metabolite in the Krebs cycle? A. Pyruvate B. Glucose C. Acetyl COA D. lactic acid E. Carbon dioxide |
C. Acetyl COA |
|
|
What is the 'oxygen debt'? A. Too much glucose is produced by the cori cycle B. Too much carbon dioxide is produced by the Krebs cycle C. The Krebs cycle starts consuming lactic acid D. Too much pyruvate is produces anaerobically by glycolysis E. Too much urea is produced by amino acid catabolism |
D. Too much pyruvate is produced anaerobically by glycolysis |
|
|
The organs running the cori cycle are... A. The brain alone B. The brain and liver C. The muscle and liver D. The muscle and brain E. The muscle and lungs |
C. The muscle and liver |
|
|
To lose 5 pounds of body fat, how many miles one would need to cover? A. 10 miles B. 25 miles C. 45 miles D. 75 miles E. 175 miles |
E. 175 miles |
|
|
Smart people will eat how much fish from Florida waters? A. None B. 1-2 fish a week, as recommended by our trustworthy government C. As much as we want. The government is always exaggerating in their warnings |
A. None |
|
|
A normal pregnancy lasts for how long? A. 9 weeks B. 20 - 22 weeks C. 28 - 30 weeks D. 38 - 40 weeks E. 45 - 50 weeks |
D. 38 - 40 weeks |
|
|
Mother's with a normal BMI should be gaining how much weight during pregnancy? A. 5 lbs B. 10 lbs C. 20 lbs D. 30 lbs E. 50 lbs |
D. 30 lbs |
|
|
How many extra calories need to be consumed in the 3rd trimester? A. Zero B. 200 C. 350 D. 500 E. 900 |
D. 500 |
|
|
Which mother should not breastfeed from this list? A. Teenage mother B. Athletic mother C. Chemotherapy patient mother D. Asthmatic mother E. Diabetic mother |
C. Chemotherapy patient mother |
|
|
What is mothers milk called during the 1st week of lactation? A. Coelacanth B. Colostomy C. Colostrum D. Colosterium E. Colossian |
C. Colostrum |
|
|
When are babies to transition to solid foods? A. During the 1st month B. During the 2nd or 3rd month C. Between 4 - 6 months D. After 1 year E. After 2 years |
C. Between 4 - 6 months |

