![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lipid Definition
|

|
|
|
What are Fats/Lipids
|

|
|
|
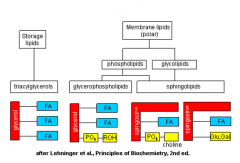
Simple V.s. Compound Lipids
|

|
|
|
Lipid Diagram
|
|
|
|
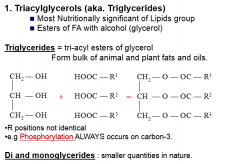
Triglycerides
|
simple lipid
|
|
|
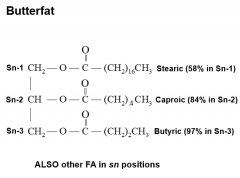
Butterfat
|
simple lipid
|
|
|
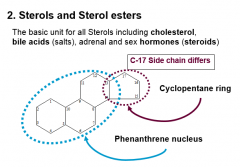
Sterols and Sterol Esters
|
simple lipids
|
|
|
Sterols in Nature
|

|
|
|
Waxes
|

simple lipids
|
|
|
Tocopherols
|
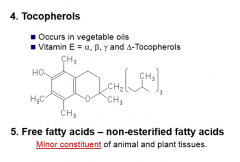
simple lipids
|
|
|
Compound Lipids
|

|
|
|
Lecithin
|
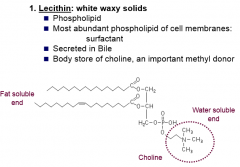
compound lipid
|
|
|
7-Dehydrocholesterol
|
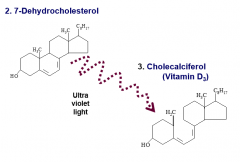
compound lipid
|
|
|
Glycocholic Acid
|
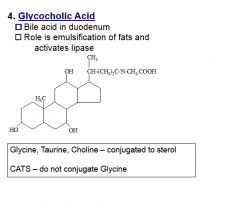
compound lipid
|
|
|
Prostaglandin F2a
|
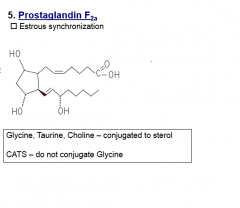
compound lipid
|
|
|
Classifications: Glycerol V.s. Non-Glycerol Based
|
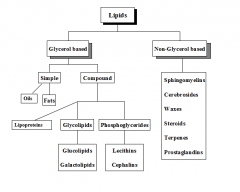
|
|
|
Fatty Acids
|

|
|
|
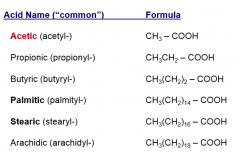
Fatty Acid Nomenclature
|

|
|
|
Chain Length Classification
|
Short Chain: 2-6 C
Medium Chain: 8-12 C Long Chain: 14-24 C |
|
|
Saturated Fatty Acids
|
Have NO double bonds
|
|
|
Fatty Acid Structures
|
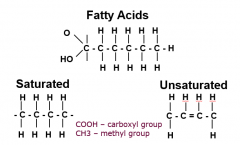
|
|
|
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
|
-with 18 carbons; HAVE double bonds
-some carbons linked by double C=C bond -monoenes -dienes -trienes |
|
|
Monoenes
|

|
|
|
Dienes
|

|
|
|
Trienes
|
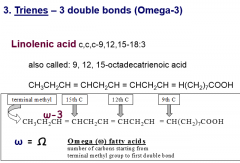
|
|
|
Cis Configuration
|
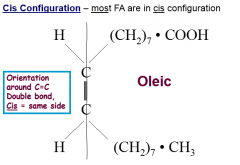
|
|
|
Trans Configuration
|
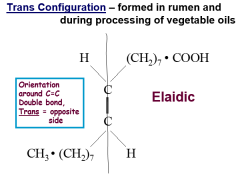
|
|
|
Cis V.s. Trans Orientation
|
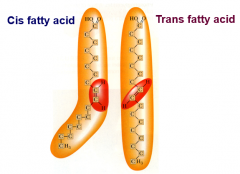
|
|
|
Dietary Fat & Human Health
|
-Trans fatty acids may increase risk of heart dz
-80-90% of trans FA's consumed in partially hydrogenated veggie oils -omega-3 FA reduce bl. cholesterol & triacylglycerol levels -conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) inhibits carcinogenesis |
|
|
Melting Point of Fatty Acids: Length of Carbon Chain
|
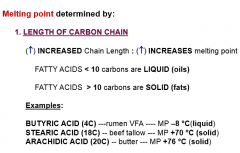
|
|
|
Melting Point of Fatty Acids: Degree of Unsaturation
|
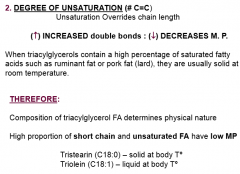
|
|
|
Comparing FA's in Foods
|
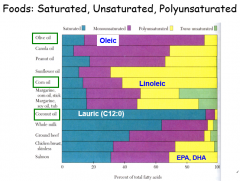
|
|
|
Saturated V.s. Unsaturated FA's in Tissues
|

|
|
|
Biohydrogenation
|
Saturation of fatty acids by microbial activity
|
|
|
Hydrogenated fat
|
A fat whose component fatty acids have been chemically saturated
|
|
|
Lipolysis
|
The activity of breaking ester bonds by hydrolysis to cleave fatty acids from glycerol
|
|
|
Chemical Hydrogenation of Fatty Acids: Margarine
|
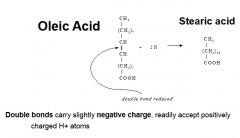
|
|
|
Ruminal Hydrogenation
|
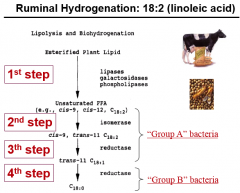
|
|
|
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
|

|
|
|
Metabolic Roles of Polyunsaturated FA's
|

|
|
|
Rancidity
|

|
|
|
Fatty Acid Peroxidation
|

|
|
|
Factors Affecting FA Peroxidation
|

|
|
|
Controlling Peroxidation
|
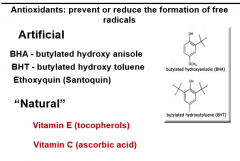
|
|
|
Lipid Functions
|

|
|
|
Fat Deposition
|
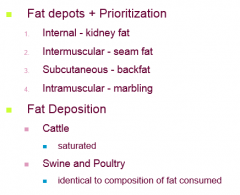
|
|
|
Characteristics of Lipids in Plants
|

|
|
|
Characteristics of Lipids in Animals
|
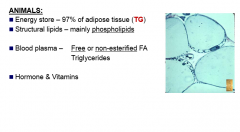
|
|
|
In the Feed
|

|
|
|
Fat Content of Feed
|

|
|
|
Facts about Fats/Lipids
|

|
|
|
Use Depends on Energy Intake
|

|
|
|
Yes, Carbs can be made into Fats
|
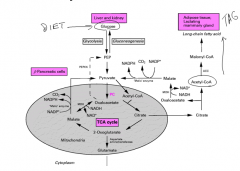
|
|
|
Fatty Acid Requirement
|

|
|
|
What Does "Essential" Mean?
|

|
|
|
Essential FA Functions
|

|
|
|
Deficiency Symptoms
|
-Scaly Skin
-Loss of hair, feathering -Poor growth and performance -Reproductive failure -Hemorrhage |
|
|
Which FA's are Truly Essential?
|

|
|
|
Essential FA's in Ruminants
|

|
|
|
Fat in the Rumen
|

|
|
|
Fate of Lipids in the Body
|
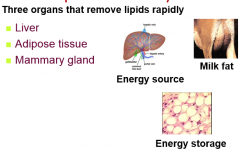
|
|
|
Bile
|

|
|
|
Fat Absorption
|

|
|
|
Lipid Digestion
|

|
|
|
Pancreatic Lipase
|
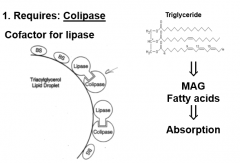
|
|
|
Problems with Fat
|

|

