![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Transit Time |
Entire time it takes for food to get out of GI tract |
|
|
Digestive Hormones |
Gastrin Ghrelin Secretin Cholecystokinin Gastric Inhibitory Peptide |
|
|
Gastrin |
Simulates the secretion of hydrochloric acids (HCI) |
|
|
Ghrelin |
Stimulates appetite Quickens gastric emptying |
|
|
Secretin |
Slows gastric secretion & movement
Increases water and bicarbonate ions coming from the pancreas |
|
|
Cholecystokinin |
Makes gallbladder excrete bile |
|
|
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide |
Decreases gastric secretions and movement |
|
|
Cephalic Phase |
Senses send signals to brain |
|
|
Salivary Amalyse |
Breaks down carbs and lysozomes |
|
|
Journey of Food through GI tract |
Mouth (mechanical and chemical digestion)-> epiglottis closed over passage to lungs-> food travels down pharynx-> goes through esophagus (peristalsis) -> gastroesophageal sphincter-> goes into stomach( gastric secretions start digestion of carbohydrates)(signals go to brain to aid in secretions) -> goes through pyloric sphincter (regulates how much chyme goes to the intestine)-> small intestine (segmentation) (digestion and absorption of many nutrients)-> pancreas and gallbladder (send bile, bicarbonate ions(neutralize the acid that is in chyme) and pepsinogen)large intestine (absorption of water, some vitamins and minerals). |
|
|
Ghrelin |
Stimulates appetite Quickens gastric emptying |
|
|
Secretin |
Slows gastric secretion & movement
Increases water and bicarbonate ions coming from the pancreas |
|
|
Cholecystokinin |
Makes gallbladder excrete bile |
|
|
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide |
Decreases gastric secretions and movement |
|
|
Cephalic Phase |
Senses send signals to brain |
|
|
Salivary Amalyse |
Breaks down carbs and lysozomes |
|
|
Journey of Food through GI tract |
Mouth (mechanical and chemical digestion)-> epiglottis closed over passage to lungs-> food travels down pharynx-> goes through esophagus (peristalsis) -> gastroesophageal sphincter-> goes into stomach( gastric secretions start digestion of carbohydrates)(signals go to brain to aid in secretions) -> goes through pyloric sphincter (regulates how much chyme goes to the intestine)-> small intestine (segmentation) (digestion and absorption of many nutrients)-> pancreas and gallbladder (send bile, bicarbonate ions(neutralize the acid that is in chyme) and pepsinogen)large intestine (absorption of water, some vitamins and minerals). |
|
|
Digestion with pancreatic amalyse |
Digests starches to sugars |
|
|
Ghrelin |
Stimulates appetite Quickens gastric emptying |
|
|
Secretin |
Slows gastric secretion & movement
Increases water and bicarbonate ions coming from the pancreas |
|
|
Cholecystokinin |
Makes gallbladder excrete bile |
|
|
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide |
Decreases gastric secretions and movement |
|
|
Cephalic Phase |
Senses send signals to brain |
|
|
Salivary Amalyse |
Breaks down carbs and lysozomes |
|
|
Journey of Food through GI tract |
Mouth (mechanical and chemical digestion)-> epiglottis closed over passage to lungs-> food travels down pharynx-> goes through esophagus (peristalsis) -> gastroesophageal sphincter-> goes into stomach( gastric secretions start digestion of carbohydrates)(signals go to brain to aid in secretions) -> goes through pyloric sphincter (regulates how much chyme goes to the intestine)-> small intestine (segmentation) (digestion and absorption of many nutrients)-> pancreas and gallbladder (send bile, bicarbonate ions(neutralize the acid that is in chyme) and pepsinogen)large intestine (absorption of water, some vitamins and minerals). |
|
|
Digestion with pancreatic amalyse |
Digests starches to double sugars |
|
|
Digestion of fiber |
Can't be digestion by enzymes
Goes to the large intestine |
|
|
Digestion done by microvilli |
Make double sugars into simple sugars by using enzymes |
|
|
Digestion by Pancreatic Proteases from microvilli and pancreas |
Makes polypeptides into amino acids |
|
|
Digestion by bile & pancreatic lipases |
Divides large fat-> pancreatic lipases digest triglycerides |
|
|
Digestion done by microvilli |
Make double sugars into simple sugars by using enzymes |
|
|
Digestion by Pancreatic Proteases from microvilli and pancreas |
Makes polypeptides into short amino acids or amino acids-> absorbed by mucosal cells to become single amino acids-> passed to the blood |
|
|
Digestion by bile & pancreatic lipases |
Divides large fat-> pancreatic lipases digest triglycerides-> short chain fatty acids are absorbed by mucosal cells-> go into blood
Long chain fatty acids combine with bile to divide-> transport particles take absorbed lipids and go directly to the blood with passing through the liver |
|
|
We do what during digestion? |
Make and burn energy |
|
|
We do what during digestion? |
Make and burn energy |
|
|
Gbv |
Ggcc |
|
|
We do what during digestion? |
Make and burn energy |
|
|
Gbv |
Ggcc |
|
|
Large intestine |
Contains rectum, colon, and anus
May keep feces up to 24 hours |
|
|
Probiotics |
A undigested substance in the colon
Stimulates growth or health of some bacteria |
|
|
Probiotics |
Live bacteria that live in the colon after consumption and than give health benefits to body |
|
|
Probiotics |
A undigested substance in the colon
Stimulates growth or health of some bacteria |
|
|
Probiotics |
Live bacteria that live in the colon after consumption and than give health benefits to body |
|
|
What immune cells are in GI tract |
Phagocyte Lymphocytes Antibodies |
|
|
Probiotics |
A undigested substance in the colon
Stimulates growth or health of some bacteria |
|
|
Probiotics |
Live bacteria that live in the colon after consumption and than give health benefits to body |
|
|
What immune cells are in GI tract |
Phagocyte Lymphocytes Antibodies |
|
|
Peyers Patch |
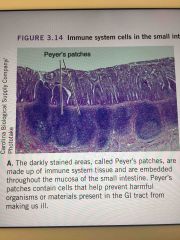
Back (Definition) I |
|
|
Probiotics |
A undigested substance in the colon
Stimulates growth or health of some bacteria |
|
|
Probiotics |
Live bacteria that live in the colon after consumption and than give health benefits to body |
|
|
What immune cells are in GI tract |
Phagocyte Lymphocytes Antibodies |
|
|
Peyers Patch |
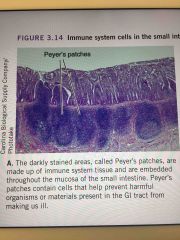
Back (Definition) I |
|
|
Are antacids good or bad |
Bad |
|
|
Peptic Ulcers |
Open sores that form from the esophagus to the upper portion of the small intestine
Caused by Helicobacter Pylori ( acid resistant) |
|
|
Alternative Feeding Methods |
Tube Total Parenteral Nutrition |
|
|
Liver |
Most nutrients go here |
|
|
Role of lymphatic system |
Fluid balance Immune function Absorption of lipids |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Provide the energy |
|
|
Catabolic reactions |
Release energy in chemicals |
|
|
Anabolic Reactions |
Combine chemicals to substances |

