![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
dietary reference intakes
|
a set of four nutrient based reference values used to plan and evaluate diets
|
|
|
recommended dietary allowances
|
the average daily dietary intake level sufficent to meet the nutrient requirement of 97 to 98% of healthy indivduals life stage and gender group
|
|
|
Estimated Average Requirement
|
the nutrient intake estimated to meet the requirement of half of the healthy indivduals in a particular life stage and gender group.,
|
|
|
Adequate Intake
|
an intake level thought to meet or exceed the requirement of almost all members of a life stage/gender group. An AI is set up when there are insuffcient data to define RDA.
|
|
|
Tolerable Upper Intake Level
|
the highest average daily intake level of a nutrient likely to pose no danger to most individuals in the group.
|
|
|
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges
|
an intake range as a percentage of total calories for energy nutrients.
|
|
|
Estimated Energy Requirements
|
level of calorie intake estimated to maintain weight in normal weight individuals based on age, gender, height, weight, and activity.
|
|
|
daily value
|
a reference created by the FDA for labeling purposes. Actually a group name for two distinct, behind the scenes sets of references values, daily reference values, DRV's and refernce daily intakes (RDIs).
|
|
|
Daily Reference Value (DRV)
|
are established for nutrients and food components that have important health implications but no RDA. for some nutrients they are amounts that should not be exceeded; for others, they are amounts to strive toward. for nutrient intakes that are based on the percentage of calories consumed 2000 calories is the standard used.
|
|
|
Reference Daily Intake (RDI)
|
represents amounts of nutrients people should strive to consume.
|
|
|
Percent Daily Value (%DV)
|
the percent of how much of a particular nutrient or fiber a person should consume based on a 2000 calorie diet.
|
|
|
SSA
|
significant scientific agreement.
|
|
|
herbs
|
plants or parts of plants used to alleviate health problems to promote wellness.
|
|
|
GMP
|
good manufacturing practice
|
|
|
standardization
|
a manufacturing process that ensures product consistency from batch to batch.
|
|
|
functional foods
|
commonly (not legally) defined as foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition. Often used as an all inclusive generic term that includes nutraceuticals.
|
|
|
nutraceuticals
|
generally defined as food that have been altered to provide medicinal benefits beyond basic nutrition. benecol spread (margarine type product) has plant sterols added to help reduce serum cholesterol levels.
|
|
|
organic
|
in a chemical sense, organic means carbon containing. generally, organic refers to living organisms, as such all foods are technically organic.
|
|
|
Organically Grown or Organically Produced
|
foods produced with little or no synthetic fertilizers or pesticides (plants) and no antiobiotics or hormones, (livestock)
|
|
|
food borne illness
|
an illness transmitted to humans via food
|
|
|
Bovine Spongiform Encepalopathy/ BBS
|
mad cow disease, a slowly degenerative, fatal disease affecting the central nervous system of adult cattle.
|
|
|
food biotechnolgy
|
a process that involves taking a gene with a desirable trait from one plant and inserting it into another with the goal of changing one or more of its characterics. Also called genetically engineered food.
|
|
|
food irradation
|
treatment of food with approved levels of ionizing radiation for a prescribed period of time and a controlled does to destoy bacteria and parasites that would otherwise cause foodborne illness.
|
|
|
foodway
|
an all encompassing term that refers to all aspects of food including what is edible, the role of certain foods in the diet, how food is prepared, the use of foods, the number and timing of daily meals, how food is eaten, and health beliefs related to food.
|
|
|
edible
|
foods that are part of an individuals diet
|
|
|
inedible
|
foods that are usually poisonous or taboo
|
|
|
core foods
|
the important and consistently eaten foods that form the foundation of the diet; they are they dietary staples.
|
|
|
secondary foods
|
foods that are widespread in the diet but not eaten consistently
|
|
|
occasional or peripheral foods
|
foods that are infrequently consumed.
|
|
|
ethnocentrism
|
the belief that ones own culture is superior to another or that the cultural practices of another are inapporiate or wrong.
|
|
|
acculturation
|
the process that occurs as people who move to a different cultural area adopt the beliefs, values, attitudes and behaviors of the dominant culture; not limited to immigrants but affects anyone who moves from one community to another.
|
|
|
dietary acculturation
|
the process that occurs as members of a minority group adopt the eating patterns and food choices of the host country.
|
|
|
subgroups
|
a unique cultural group that coexists within a dominant culture.
|
|
|
central obesity
|
obesity characterized by the deposition of excess weight around the abdomen and waist, not the hips and thighs.
|
|
|
arroz con leche
|
rice with milk
|
|
|
flan
|
sweetened egg custard topped with carmelized sugar
|
|
|
atole
|
hot beverage of milk or water, and sugar thickened with cornstarch
|
|
|
cafe con leche
|
coffe with milk.
|
|
|
lacto ovo vegatarians
|
people who include milk products and eggs in their diets but no other sources of animal protein.
|
|
|
kosher
|
a word commonly used to identify jewish diatary laws that define, clean foods, unclean foods, how food animals must be slaughtered, how foods must be prepared, and when foods may be consumed, EX: the timing between eating milk products and meat products).
|
|
|
pareve
|
dairy free
|
|
|
halal
|
islamic dietary laws
|
|
|
haram
|
foods that are prohibited
|
|
|
ahimsa
|
non violence as applied to foods.
|
|
|
convenience foods
|
broadly defined as any product that saves time in food preparation, ranging from bagged fresh salad mixes to frozen package complete meals.
|
|
|
folic acid
|
synthetic form of folate found in mulitvitamins, fortifed breakfast cereals, and enriched grain products.
|
|
|
folate
|
natural form of the B vitiam involved in the synthesis of DNA; only half as available to the body as manmade folic acid.
|
|
|
dietary folate equivalents (DFE)
|
1 DFE = 1 microgram food folate = 0.6 micrograms of folic acid from fortified food or as a supplement consumed with food = 0.5 microgram of a supplement taken on an empty stomach.
|
|
|
healthy weight prior to conception
|
BMI of 19.8-26.0
|
|
|
phenylketonuria (PKU)
|
an inborn error of phenylalanine (an essential amino acid) metabolism that results in retardation and physical handicaps in newborns if it is not treated with a low phenylalanine diet beginning shortly after birth.
|
|
|
nutrient density
|
relatively high in nutrients for the amount of calories provided.
|
|
|
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
|
a condition characterized by varying degrees of physical and mental growth failure and birth defects caused by maternal intake of alcohol.
|
|
|
pica
|
a psycho-behavior disorder characterized by the ingestion of nonfood substances such as dirt, clay, starch, and ice.
|
|
|
preeclampsia
|
a toxemia of pregnancy characterized by hypertension accompanied by proteinuria, edema, or both
|
|
|
ecalmpsia
|
a toxemia of pregnancy that develops with the occurrence of one or more convulsions resulting from preeclampsia.
|
|
|
gynecologic age
|
age of conception minus age of menarche.
|
|
|
is the central of the three divisions of the small intestine and lies between the duodenum and the ileum. The change from the duodenum to the jejunum is usually defined as the ligament of Treitz.
|
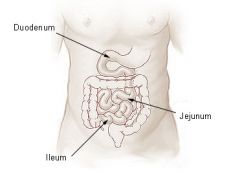
jejunum
|
|
|
dumping sydrome
|
is a complciation of gastric surgeries in which the pyloric sphincter is removed, bypassed, or disrupted.
|
|
|
bolus feeding
|
rapid admininstration of a large valume of formula
|
|
|
gastric residuals
|
the volume of feeding remaining in the stomach from a previous feeding
|

