![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Vitamin A |

>RBP - Retinol Binding Protein - Moves Vit A from liver to body. >Beta Carotine - precursor & antioxidant. >Unbinded (excess) Vit A - free radical |
|
|
Vitamin D |
>Synthesized by Sun. Dehydrocholesterol + UV light = Vit D3. D3 must be activated in liver and kidneys. 36 hrs from D3 to D. >Functions -Bone growth/remodeling. GI absorption of bone minerals. Also increases kidney retention and mobilization from bones to maintain calcium at 1% in blood when deficient. >Deficiency - Ricketts (kids), osteomalacia (adults), osteoporosis. >Toxicity - Hypercalcemia - blood vessels, kidneys, heart, lungs, tissues around joints. >5mcg/day <50 / 10mcg/day 51-70 / > 15mcg > 70 / UL 50mcg/day |
|
|
Vitamin E |
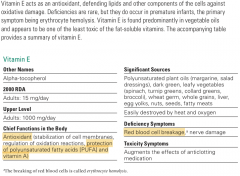
>90% stored in liver. >Protects LDL from oxidation. >Deficiency - Hemolysis, Card-Vasc Disease, Cataracts >Toxicity - Rare, interferes w/ Vit K |
|
|
Vitamin K |
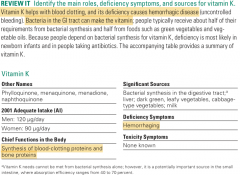
|
|
|
Water - Intake |
> Thirst and satiety influence water intake, apparently in response to changes sensed by the mouth, hypothalamus, and nerves.When water intake is inadequate, the blood becomes concentrated - dehydration (esp. athletes & elderly) > 1 to 1.5ml/kcal > At least 3l/day - 7-11 cups |
|
|
Water - Insensible Losses |
>Metabolically we produce 200-300ml/day >500ml/day is lost for waste product excretion. >Lungs & Skin lose 1500-2000ml/day |
|
|
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) |
When blood volumes are low the pituitary gland will release ADH to tell kidneys to capture, rather than excrete, water. |
|
|
Angiotensin |
Angiotensin is a powerful vasoconstrictor that narrows the diameters of blood vessels, thereby raising the blood pressure.A |
|
|
Aldosterone Hormone |
Angiotensin stimulates the release of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone signals the kidneys to excrete potassium and to retain more sodium, and therefore water, because when sodium moves, water follows. Again, the effect is that when more water is needed, less is excreted. |
|
|
Electrolytes |
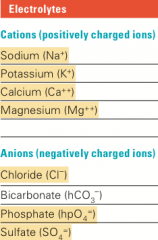
>Have a charge associated with them. >Attracts water. -Solvents follow solute -Because h20 is polar >Often called ions (atoms w/ charge) >Loss of fluids = loss of electrolytes. (Esp. Na+,Cl-,K+) >To remember the difference between cations and anions, think of the “t” in cations as a “plus” (+) sign and the “n” in anions as a “negative.”
|
|
|
Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT) |
oral rehydration therapy (ORT)—a simple solution of sugar, salt, and water, taken by mouth—to treat dehydration caused by diarrhea. |
|
|
Major Minerals |
>Not organic, no carbon, can't be damaged >How food is grown has impact on bioavailability of minerals. >Iodine - costal regions
|
|
|
Bioavailabity and the binders phytates & oxalates |
The bioavailability of minerals varies. Some foods contain binders that combine chemically with minerals, preventing their absorption and carrying them out of the body with other wastes. Examples of binders include phytates, which are found primarily in legumes and grains, and oxalates, which are present in rhubarb and spinach, among other foods. These foods contain more minerals than the body actually receives for use. bioavailability: the rate at and the extent to which a nutrient is absorbed and used. >Cooking can potentially remove binders allowing for higher mineral absorption. |
|
|
Sodium, Na+ |

>Functions: Nerve conduction, muscle contraction, pH balance. >Salt is 40% sodium. >Sources: 75% processed foods, 15% added during cooking, 10% natural in food. >Toxicity: Hypertension, edema (swelling), osteoporosis due to calcium excretion. >1tsp of salt is 2,300mg of sodium, the UL. |
|
|
Chloride, Cl- |
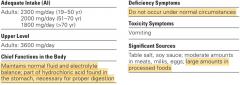
>Chloride is the major anion outside cells >It associates closely with sodium. >Role in fluid balance, >Part of the stomach’s hydrochloric acid (HCl). >Deficiency and toxicity aren't common or big problems. |
|
|
Potassium, K+ |
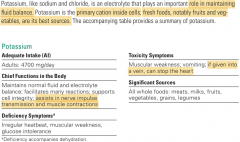
>Reduces high blood pressure - counteracts sodium. >Toxicity: overuse of supplements leads to Hyperkalemia >Used in lethal injections. |
|
|
Calcium, |
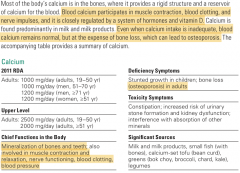
>AI: <20 1300mg/day / 20-50 1000mg/day / >Most abundant mineral in body. >99% in bones/teeth. 1% blood (vital to life and prioritized over bones) >Sodium and high protein cause calcium excretion. |
|
|
Phosphorus |
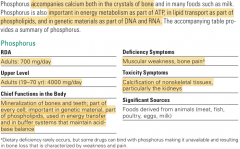
>Phosphorus is the second most abundant mineral in the body. >About 85 percent of it is found combined with calcium in the hydroxyapatite crystals of bones and teeth. Toxicity: Calcium excretion |
|
|
Magnesium |
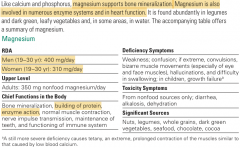
> 50% in bones and 50% in tissue. >Functions: PRO synth, DNA synth, 7 of 10 steps of gycolosis, blood clotting. >We are able to store magnesium >Toxicity: Kidney disease from supplementation. |
|
|
Sulfer |
Part of the R Groups (side chains) in Amino Acids. |

