![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Monosaccharides, disaccharides & polysaccharides
|
α-1,4 & α-1,6
|
|
|
salivary amylase
|
produced in the mouth; initiates the breakdown of polysaccharides
|
|
|
pancreatic amylase
|
continues digestion in the proximal small intestine
|
|
|
Glucose, galactose, and fructose
|
ultimately transported to the liver where they undergo further metabolism
|
|
|
Carbohydrates are equivalent to __ kcal/gram
|
4 kcal/gram
|
|
|
Protein digestion starts in the _____
|
stomach
|
|
|
proteolytic enzymes
|
start to breakdown the proteins in the stomach. Digestion continues in the duodenum
|
|
|
Amino acids are absorbed through multiple mechanisms and ultimately transported to the _____
|
liver
|
|
|
proteins are equivalent to __ kcal/gram
|
4 kcal/gram
|
|
|
Almost all dietary lipids are in the form of _____ (>97%), _____ & _____ make up the remaining amount.
|
TAG, phospholipds & cholesterol
|
|
|
Lipid digestion begins in the mouth with _____ and continues in the stomach through the action of _____.
|
lingual lipase, gastric lipase
|
|
|
The bulk of lipid digestion occurs in the _____.
|
small intestines
|
|
|
Once assembled into chylomicrons, lipids are transported by the lymphatic vessels to the _____ and subsequently transported to the bloodstream. Lipids then enter the _____ where they are repackaged into _____.
|
thoracic duct, liver, VLDLs
|
|
|
Fats are equivalent to __ kcal/gram.
|
9 kcal/gram
|
|
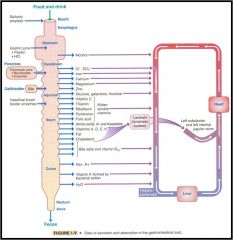
digestion overview
|
digestion overview
|
|
|
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
|
current standard for measuring nutritional adequacy and is composed of four reference values
|
|
|
Estimate Average requirement (EAR)
|
average daily nutrient intake level estimated to meet the requirement of half the healthy individuals in a particular life stage and/or gender group
|
|
|
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
|
average daily dietary nutrient intake level sufficient to meet the nutrient requirement of nearly all (98%) of healthy individuals in a particular life stage and gender group
|
|
|
Adequate Intake (AI)
|
recommended average daily nutrient intake level based on observed or experimentally determined approximations or estimates of nutrient intake by a group of healthy peopled. AI is used when RDA cannot be determined.
|
|
|
Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)
|
highest average daily nutrient intake level likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects to almost all individuals in the general population. As intake increases above the UL the potential risk of adverse effects may increase.
|
|
|
The RDA for folic acid is ___ mg.
|
0.4 mg; FDA recommends that most breads, flours, corn meals, pastas, and rice to be enriched with folic acid.
|
|
|
macronutrients
|
proteins, carbohydrates and fats
|
|
|
nicronutrients
|
vitamins and minerals
|
|
|
alcohol is equivalent to __ kcal/gram
|
7 kcal/gram
|
|
|
Energy Density
|
measure of the energy (kcal) a type of food provides compared to the amount of food consumed (grams)
|
|
|
Nutrient Density
|
amount of a nutrient compared the amount of energy obtained from that nutrient. For example, one serving of fat-free milk is equal to 85 calories and it delivers 300 mg of calcium. Therefore the nutrient density is 300/85 or 3.5 mg of calcium/kcal
|
|
|
Empty kcal foods
|
foods that only provide energy without provide any beneficial nutrients. For example, soda pop is an empty kcalorie food
|
|
|
carbohydrate DRI range
|
45-65%
|
|
|
fiber DRI
|
14g/1000 calories
|
|
|
fats DRI range
|
20-35%
|
|
|
protein DRI range
|
10-35%
|

