![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
macronutrients (3)
|
carbs, fats, proteins
required in large amounts provide energy |
|
|
micronutrients (2)
|
vitamins(organic), minerals(inorganic)
required in small amounts allow chemical reactions to efficiently utilize macros |
|
|
major vs trace minerals
|
major:
> 100 mg daily > 5 g in body trace: <100 mg daily <5 g in body |
|
|
kcal
|
carbs: 4 kcal/g
fats: 9 kcal/g proteins: up to 4 kcal/g |
|
|
3 types of quakery
|
food fadism
health fraud misdirected claims |
|
|
CARS
|
credibility
accuracy reasonableness support |
|
|
a healthy diet is... (4)
|
adequate- proves enough energy, nutrients
moderate- right amount of food to maintain weight varied balanced |
|
|
DRIs (4)
|
EAR- meets the needs of 50%
RDI- meets needs of 97-98% AI- assumed to be adequate UL- highest amount likely to pose no risk |
|
|
DRIs for energy/macros (2)
|
EER- average intake predicted to maintain energy balance
AMDR- portion of energy that should come from each macro 45-65% carbs 20-35% fats 10-35% proteins |
|
|
Mediterranean Diet
|
DAILY- grains, legumes, cheese, yogurt, veggies, fruits, olive oil*
WEEKLY- poultry, fish, eggs MONTHLY- meat, sweets |
|
|
Generic claims Canada allows on food labels (5)
|
Na/K and high blood pressure
Ca/Vitamin D and osteoporosis Saturated/Trans fat and heart disease veg/fruit and cancer protection sugar and cavities |
|
|
hunger vs appetite
|
hunger is physiological and non-specific
appetite is psychological and specific |
|
|
3 things that help the HYPOTHALAMUS trigger feelings of SATIATION
|
NERVES- detect pressure change in stomach/small intestine
HORMONES (7)- insulin, glucagon, neuropeptide y, galanin, cck, serotonin, ghrelin FOOD- amount and type |
|
|
digestion begins during....
|
cephalic phase
think about/see food |
|
|
Gastric Juice components (4)
|
HCl
pepsinogen --> pepsin gastric lipase mucus |
|
|
diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (5)
|
GER- heart burn
GERD- severe heart burn caused by relaxed/damaged lower esophagus sphincter IBS- food moves too fast/slow thru the colon IBD- CROHNS: small intestine blocked - ULCERATIVE COLITIS: starts @ anus and goes up colon; interferes with water reabsorption |
|
|
types of carbs
|
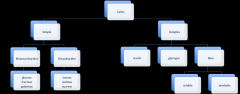
|
|
|
fibre
|
DIETARY- non digestible part of plants
FUNCTIONAL- extracted from plants and added to food (cellulose, guar gum, pectin, psyllium) SOLUBLE- absorbs water and forms a gel; slows absorption of glucose INSOLUBLE- attracts water and speeds up passage of food |
|
|
digestion of carbs
|
MOUTH: amylase breaks starch into polysacc's
STOMACH: HCl destroys amylase- no digestion SMALL INTEST: pancreatic amylase (and lactase, maltase, sucrase) breaks starch into mono/disacc's LIVER: sugars carried here and converted to glycogen |
|
|
microbiome
|
prebiotics!
non digestible food ingredients that benefit host stimulate certain bacteria to grow "functional food" BIFIDOBACTERIA & LACTIC ACID BACTERIA improve intestinal health, immune system, lowers LDL |
|
|
diets high in simple sugars cause....
|
cavities, gum disease, high LDL, low HDL, obesity
|
|
|
diets high in added fructose....
|
high blood triglycerides
insulin resistance (pre-diabetes) higher body weight |
|
|
regulation of glucose in blood
|
INSULIN- from beta cells; glucose --> glycogen
GLUCAGON- from alpha cells; glycogen --> glucose |
|
|
diabetes: type 1 vs type 2
|
TYPE 1:
10% of all childhood people don't produce enough insulin TYPE 2: most common cells are unresponsive to insulin |
|
|
hypoglycemia
|
REACTIVE: too much insulin produced after a mea
FASTING: too much insulin produced even when not eating |
|
|
ketones
|
when there is not enough energy in the body from carbs, ketones get made
dangerous to a fetus leads to high blood acidity and KETOACIDOSIS |
|
|
triglycerides
|
3 fatty acid tails
1 glycerol backbone 95% of fat in diet SATURATED: H around every carbon MONOUN: one double bond (C18:1) POLYUN: multiple double bonds (C18:2) |
|
|
trans vs cis bond
|
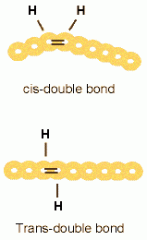
hydrogenation of unsaturated fats leads to trans.
** no kink! cis bonds give a kink! (can't pack together) |
|
|
phospholipids
|
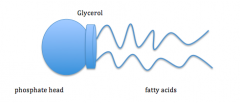
2 fatty acid tails
glycerol backbon PHOSPHATE HEAD soluble** made in body |
|
|
sterols
|
lipids with carbon rings
contain hydroxyl group and long carbon chain made in the body |
|
|
digestion of fats
|
MOUTH: minor
STOMACH: lipase, minor SMALL INTEST: major site bile is secreted and disperses fat into MICELLES pancreatic enzymes break triglyceride into 2 fatty acids and monoglyceride, & phospholips break in a phosphoglycerol and fatty acids ** 2 fatty acids fall off then things are rebuilt into lipoproteins(chlyomicrons) and are transported in the lymphatic system |
|
|
omega-3
|
n-3
double bond on third carbon ALA ** linolenic short chain; found in canola, flax, veg oils EPA & DHA long chain; can be made from linolenic; in cold water fish **lower heart attack risk, help eyes, nerves, and immune system ** regulate triglycerides: lower blood triglycerides lower VLDLs lower blood clots raise HDL |
|
|
omega-6
|
n-6
double bond on 6th carbon LINOLEIC ACID in veg oils; main dietary fat ARACHIDONIC ACID made from linoleic; in animal tissues; essential to brain and cell membrane ** regulate cholesterol: lower cholesterol synthesis lower LDL |
|
|
how much fat? (healthy person)
|
AMDR: 20-35%
saturated: <10% trans: absolute minimum |
|
|
types of blood lipids (4)
|
chlyomicrons: transport dietary fat to tissues
VLDL: transport triglycerides to tissues LDL: transport cholesterol to tissues HDL: takes cholesterol from tissues to liver :) * mainly made of protein |
|
|
heart disease associated with....
|
high total cholesterol
high LDL low HDL high LDL:HDL ratio high VLDL |
|
|
heart disease recommendations....
|
max 30% of energy from fat
polyun = 10% *omega-3s! monoun = remaining ~ 20% NO SATURATED FAT |
|
|
diets high in sat. fat cause....
|
decreased removal of LDL from blood
high chlyomicrons and VLDL promotes liver to make cholesterol blocked arteries heart disease |
|
|
diets high in trans fat cause....
|
high LDL
low HDL ** double bad effect |
|
|
high fat diets and cancer
|
high fat diet linked to lung, breast, colorectal, prostate cancer
increased timor growth and spread |
|
|
natural trans fats
|
Conjugated Linolenic Acid (CLA)
* not on trans label inhibits growth and spread of cancer Vaccenic Acid (VA) reduces high LDL, VLDL, and inflammation |
|
|
proteins are made of....
(the answer is not amino acids) |
C, H, O, N, S
acid group, amine group, central carbon, side chains |
|
|
essential amino acids
|
9
cannot be made in body ** lysine and phenylalanine |
|
|
non-essential amino acids
|
can be made in body by transferring the AMINE GROUP off one amino acid to another acid/carbon chain
* TRANSAMINATION **aspartic acid and glutamic acid |
|
|
conditionally essential amino acids (4)
|
during certain times we need more of one amino acid
- infection, growth arginine, glutamine, cysteine, tyrosine |
|
|
protein turnover
|
proteins in body are constantly being broken down and remade
**0.2-.04% turned over each day all AA must be in the cell at the same time to complete a protein- ones that aren't are LIMITING AMINO ACIDS |
|
|
functions of proteins
|
enzymes
hormones transport (lipoproteins) membrane bound proteins fluid balance acid base buffer antibodies *energy |
|
|
edema
|
low blood proteins, fluids don't diffuse out of tissues, swelling occurs
|
|
|
proteins used for energy
|
some AA can provide glucose (GLUCOGENIC)
GLUCONEOGENESIS nitrogen in urine |
|
|
abnormalities in AA metabolism
|
PKU
people cannot ingest any more phenylalanine that necessary MSUD maple syrup urine cannot break down large chain AA's |
|
|
digestion of proteins
|
MOUTH: chewing
STOMACH: begins; HCl denatures protein; pepsin breaks them into polypeptides SMALL INTEST: main site; proteases(from pancreas) break down peptides further; peptidases break them into AA's LIVER: AA's get absorbed and go to here |
|
|
nitrogen balance
|
POSITIVE:
consume more than you need growing kids, pregnant woman, athletes NEGATIVE: consume less than you need *starvation BALANCED: consume enough to replace losses and sustain turnover |
|
|
protein quality
|
DIGESTIBILITY:
animal protein digests better than plant (fibre) AMOUNT OF ESSENTIAL AA: types and proportions similar to proteins in body ** high biological value ** complete proteins (have all 9) |
|
|
how do you fix incomplete proteins?
|
mutual supplementation of complementary foods
|
|
|
too much protein?
|
not an issue unless you have kidney problems (already excreting too much N)
but.. are you getting enough of everything else? |
|
|
benefits of a vegetarian diet (5)
|
low blood pressure
low risk of heart disease low risk of cancer low risk of kidney stones less digestive problems |
|
|
challenges of a vegetarian diet (6)
|
*vitamin B12 - yeast, fermented food
vitamin D riboflavin *iron calcium zinc - depends on soil |
|
|
2 types of Protein-Energy Malnutrition (PEM)
|
MARASMUS:
severely inadequate intake of all nutrients (typical picture of starving african kid) KWASHIORKOR: early weaning of a child first year of life results in edema too! |

