![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Digestion:
|
The mechanical and chemical breakdown of food
|
|
|
Absorption:
|
The process of nutrients entering the body
|
|
|
GI tract: food in...
|
mouth
|
|
|
GI tract: Bolus in...
|
Esophagus
|
|
|
GI tract: Chyme in...
|
Duodenum
Ileum Jejunum |
|
|
CI tract: Waste in...
|
Cecum
Ascending colon Transverse colon Descending colon |
|
|
Time for each meal to digest
|
3-4 hours
|
|
|
Time for each meal to transit
|
24-72 hours
|
|
|
GI tract secrets: (3)
|
Hormones
Enzymes Mucus |
|
|
4 steps of digestion
|
1. Cephalic phase
2. Mouth 3. Pharynx 4. Esophagus |
|
|
Explain Cephalic phase
|
Sight, sound, taste, smell of food stimulates gastric secretions in the stomach
|
|
|
Explain digestion in the mouth
|
Saliva and salivary amylase combined with chewing softens and breaks down food and fiber
|
|
|
Explain digestion in the pharynx
|
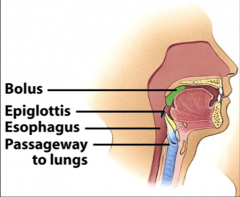
Swallowing bolus, passes through the esophagus
|
|
|
Explain digestion in the esophagus
|
Peristalsis passes bolus to stomach through a sphincter
|
|
|
Epiglottis
|
Muscle that closes entryway to lungs when bolus passes through
|
|
|
|
|
|
Salivary Amylase
|
Secrete saliva to break down food
Enzymes break down carbohydrates and lipids Mucus lubricates the food for easier swallowing Water, salts help mix food |
|
|
In stomach bolus mixed with...
|
acid to form chyme
|
|
|
Role of Gastrin
|
Stimulates the release of gastric juice from the lining of the stomach
|
|
|
Gastric juice made of
|
HCL and pepsinogen
|
|
|
Role of pepsinogen
|
pepsin (actual enzyme) breaks down protein into amino acids
|
|
|
After stomach, chyme enters____ through____
|
small intestine through the pyloric sphincter
|
|
|
Time it takes for chyme to leave the stomach
|
2-6 hours
|
|
|
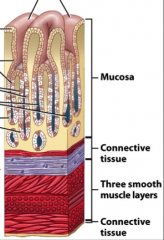
4 layers of tissue in wall of GI tract:
|
1. Mucosa
2. Connective tissue 3. Smooth muscle 4. Connective tissue |
|
|
Role of mucosa
|
Secrets mucus into lumen
|
|
|
Role of first layer of connective tissue in GI tract
|
supports, provides nutrients to mucosa and provides nerve signals for muscle contractions
|
|
|
Role of smooth muscle in GI tract
|
Contracts to mix and propel food
|
|
|
Role of second connective tissue in GI tract
|
support and protection
|
|
|
Enzyme in stomach
|
Pepsin
|
|
|
Hormone in stomach
|
Gastrin
|
|
|
|
|
|
What does gastrin do?
|
-Stimulates production of stomach acid and pepsinogen
-Maintains a narrow pH range (1.5-1.7) -Increases gastric motility and emptying of the stomach |
|
|
Gastrin secreted by...
|
cells in the pyloric region and upper duodenum
|
|
|
Gastrin stimulated by...
|
food entering the stomach and thoughts of food
|
|
|
Stomach emptying depends on...(3)
|
1. Size and composition of the meal
2. pyloric sphincter rate of food entering the small intestine 3. Emotions |
|
|
Length of small intestine
|
20 feet
|
|
|
Order of small intestine
|
1. Duodenum
2. Jejunum 3. Ileum |
|
|
Length of Duodenum
|
12 inches
|
|
|
Length of Jejunum
|
8 feet
|
|
|
Length of Ileum
|
11 feet
|
|
|
Small intestine is the main sight of...
|
digestion and absorption of water, vitamins, minerals, sugars, fats and proteins
|
|
|
Secretions to aid in digestion in small intestine:
|
1. Bile-emulsifies fat
2. Pancreatic juice- 3. Intestinal digestive enzymes-breaks down proteins and sugars into single units |
|
|
Brush border enzymes
|
intestinal digestive enzymes, microvilli
|
|
|
Inner surface of intestine covered in ____ which are covered in _____
|
Villi; microvilli
|
|
|
Each villus contains a _____ and a ______
|
blood vessel; lymph vessel
|
|
|
Peristalsis
|
Ring of contraction that propels material through the GI tract
|
|
|
Segmentation
|
Back-and-forth action that breaks down the food
|
|
|
Mass movement
|
Peristaltic wave that contracts over a large area of the large intestine to help eliminate waste
|
|
|
Liver produces ____
|
bile
|
|
|
Gallbladder releases____ into _____
|
bile into small intestine
|
|
|
CCK signals
|
to release bile and enzymes into small intestine
|
|
|
All enzymes are...
|
proteins
|
|
|
Enzymes convert____ into____
|
substrates into products
|
|
|
CCK stimulates
|
gallbladder to release bile and pancreatic enzymes
|
|
|
Passive diffusion
|
Intestinal wall is permeable
Going from high concentration to lower concentration No energy required |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion
|
Carrier shuttles substances into the absorptive cells
Going from high concentration to low concentration No energy expanded |
|
|
Active transport
|
nutrients carried across cell membrane
Requires ATP energy |
|
|
Osmosis
|
water equilibriate level of salts against membranes
|

