![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Epidermis
|
outer most layer, thin but tough, replaced every 4 weeks
|
|
|
|
Basal Cell Layer (Stratum Germinativum). What is its major ingredients
|
layer that forms new skin
Keratin (tough fibrous protein) Melanin (brown tones to the skin and hair) Carotene Pigment (orange tones) |
|
|
|
Stratum Corneum
|
horny cell layer consists of dead keratinized cells that are constantly being shed.
|
|
|
|
Dermis
|
inner supportive layer, consist of connective tissue (collagen), nerves,
sensory receptors, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands |
|
|
|
Subcutaneous
|
stores adipose (fat) tissue for energy. Need to know for injection.
|
|
|
|
Name the Appendages of the skin
|
Hair, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails
|
|
|
|
What are components of hair and Name the two types of hair
|
shaft, root, bulb matrix
Vellus Hair and Terminal Hair |
|
|
|
what is Vellus Hair
|
fine hair all over body
|
|
|
|
what is Terminal Hair
|
hair in scalp and eyebrows
|
|
|
|
Sebaceous Glands
|
produce sebum
|
|
|
|
Apocrine Glands and when is it activated
|
produce thick milky secretions, activated in puberty.
|
|
|
|
Nails
|
hard plates of keratin
|
|
|
|
advantage of Darker pigment
|
lower incidence of
skin cancer |
|
|
|
Compare Body odor with different cultures
|
Asians and Native Americans mild body odor compared with
Caucasions and African Americans |
|
|
|
Compare hair amongst different cultures
|
various textures: African Americans tend to be more dry and coarse, while
Asians tend to have straight and silky hair |
|
|
|
Name the types of lesions
|
Vascular Lesions
Secondary Lesions Primary Lesions |
|
|
|
Primary Lesions
|
first lesion that occurs
|
|
|
|
Types of Primary lesions
|
Bulla, Cyst, Macule, Nodule, Patch, Papule, Plaque, Pustule Tumor, Urticaria, Vesicle Wheal,
|
|
|
|
Macule
|
color change, flat, <1cm (freckle)
|
|
|
|
Patch
|
flat, macule that is >1cm (Mongolian spot (bluish in sacral area), café au lait)
|
|
|
|
example of patch
|
(Mongolian spot (bluish in sacral area), café au lait)
|
|
|
|
Papule
|
bump; elevated, solid lesion <1cm, lesion you can feel
|
|
|
|
example of papule
|
mole, wart
|
|
|
|
Plaque
|
papule >1cm in width
|
|
|
|
example of plaque
|
psoriasis
|
|
|
|
Nodule
|
You'll feel it inside skin
solid, elevated, hard or soft >1cm, extends deeper into dermis |
|
|
|
example of nodule
|
intradermal nevi
|
|
|
|
what's a nevi (nevus)
|
mole
|
|
|
|
Tumor
|
>2cm, firm or soft mass
|
|
|
|
example of tumor
|
lipoma (extra fatty tissue), hemangioma
|
|
|
|
Wheal
|
hives. Some small, some big. Raised and flat. superficial, raised lesion
|
|
|
|
example of wheal
|
PPD, insect bite
|
|
|
|
Urticaria
|
(Hive) - multiple wheal like lesions, very itchy
|
|
|
|
Vesicle
|
fluid filled, elevated lesion, <1cm
|
|
|
|
example of vesicle
|
herpes, chicken pox, small
blister |
|
|
|
Bulla
|
>1cm vesicle
|
|
|
|
example of bulla
|
burn, large blister, bullous impetigo
|
|
|
|
Cyst
|
fluid filled cavity, mass extending to dermis or subcutaneous layer. won't know if it's nodule or cyst until they aspirate it.
|
|
|
|
example of cycst
|
sebaceous cyst
|
|
|
|
Pustule
|
pus filled lesion
|
|
|
|
example of pustule
|
acne, pimple, zit
|
|
|
|
define Secondary Lesions
|
lesion that occurs after primary lesion
|
|
|
|
Name 10 types of secondary lesions
|
Atrophic Scar, Crust, Erosion,Excoriation,Fissure, Keloid, Lichenification, Scale, Scar, Ulcer
|
|
|
|
Crust
|
thickened, dried out exudate left when vesicles/pustules burst or dry up
|
|
|
|
example of crust
|
impetigo
|
|
|
|
Scale
|
flakes of skin, silvery or white, from shedding of dead exces keratin cells.
|
|
|
|
example of scale
|
(psoriasis, eczema, seborrhea
dermatitis) |
|
|
|
Fissure
|
linear crack with abrupt edges
|
|
|
|
example of fissure
|
athletes foot, cracks in corners of mouth, rectum from constipation
|
|
|
|
Erosion
|
shallow depression, usually no scar (canker sores)
|
|
|
|
example of erosion
|
superficial abrasion
|
|
|
|
Ulcer
|
deep depression, leaves scar usually.
can go all the way down the bone. |
|
|
|
example of ulcer
|
decubitus ulcer
|
|
|
|
Excoriation
|
self inflicted abrasion, superficial crusting secondary
scratching. something caused it. |
|
|
|
example of excoriation
|
scabies
|
|
|
|
Scar
|
healed lesion, replaced with collagen/connective tissue
|
|
|
|
Atrophic Scar
|
skin level depressed with loss of tissue, thinning
|
|
|
|
example of atrophic scar
|
striae; Stretch marks, from skin stretching
|
|
|
|
Lichenification
|
prolonged intense scratching eventually thickens the skin
|
|
|
|
Keloid
|
elevated scar, feel rubbery
More on darker skin |
|
|
|
great areas for keloid.
|
Upper chest, back, ear, neck
|
|
|
|
Vascular Lesions
|
blood filled lesions
|
|
|
|
types of vascular lesions
|
Spider Angioma
Purpura Petechiae Ecchymosis Hemangioma |
|
|
|
Spider Angioma
|
red, star shaped with solid circular center (wont be on test)
|
|
|
|
Purpura
|
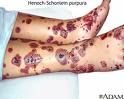
red/purple patch, flat macular hemorrhage.
Bruising like. May cause fever. Flat wont feel it. Can get really big |
|
|
|
Petechiae
|
tiny, pinpoint, hemorrhage <2mm, “little flat blood spots
ranging in color - red, purple, or brown Tiny dots. Sign of not clotting. If in face,would be extensive vomiting, toxic, feverish, will be sign of meningitis. |
|
|
|
Ecchymosis
|
bruise, flat macular lesion of various colors depending on
stage of bruise. |
|
|
|
Hemangioma
|
reddish/blue, solid, spongy collection of benign blood
Vessels elevated. Can extend into dermis. |
|
|
|
what do you need to include when documenting a lesion?
|
color, size, type/name of lesion
|
|
|
|
Name the color variations of lesions
|
Pallor
Erythema Cyanosis Jaundice |
|
|
|
Pallor
|
pale, white
|
|
|
|
Erythema
|
redness (You can say redness or erythema in documentation)
|
|
|
|
Cyanosis
|
bluish, mottled color (lips)
|
|
|
|
Jaundice
|
yellow color
|
|
|
|
what specific questions will you ask the patient with a skin related chief complaint.
|
Previous hx of skin disease
Change in skin color/pigmentation Change in moles, skin lesions, freckles, sores, etc. Change in skin texture Pruritis Excessive bruising Rash/Lesions Medications Hair loss Change in nail texture, color, or shape Self-Care Behaviors Environmental/Occupational Hazards/Exposures |
|
|
|
how to collect Previous hx of skin disease
|
treatment, skin allergies, birthmarks, tatoos,
piercings |
|
|
|
how to collect Change in skin color/pigmentation
|
ask if general or localized
|
|
|
|
Change in skin texture
|
dryness, moisture on tattoos or piercing
|
|
|
|
what is Pruritis
|
itching
|
|
|
|
what is excessive bruising
|
more than 20- 25 bruises at a time or on areas where it hardly gets bruised (ears, abdomen, leg area, neck)
|
|
|
|
how to collect hair loss
|
ask pattern, location, change in hair texture, color
|
|
|
|
how to collect Self-Care Behaviors
|
skin self examination, type of skin care products, how is
skin, hair, nails cared for |
|
|
|
how to gather Objective Data
|
Inspect and Palpate:
Color/General Pigmentation Lesions Temperature Moisture/Dryness Texture Edema Skin Mobility/Skin Turgor Vascular Lesions/Bruising Inspect and Palpate Hair Inspect and Palpate Nails |
|
|
|
how do you note lesions
|
note location, color, size, symmetry, pattern, elevation, odor,
drainage or discharge |
|
|
|
1+ Mild Pitting Edema
|
slight indentation, no visible swelling
|
|
|
|
2+ Moderate Pitting Edema
|
indentation subsides rapidly
|
|
|
|
3+ Deep Pitting Edema
|
indentation remains for a short time, swollen appearance
|
|
|
|
4+ Very deep pitting edema
|
indentation lasts a long time, very swollen
|
|
|
|
how to note hair inspection
|
color, texture, distribution, scalp lesions
|
|
|
|
how to note Nail inspection
|
note shape, contour (nl 160'),
consistency/texture, color, check cap refill |
|
|
|
Impetigo abnormality
|
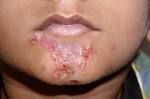
skin infection. Cut on skin, rubbing, opened and infected. Rupture to form thick, honey-colored crusts
|
|
|
|
eczema
|
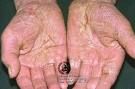
erythmeatous papules and vesicles, with weeping, oozing, and crusts
|
pg259
|
|
|
Diaper Dermatitis/Contact Dermatitis
|
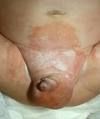
diaper rash maybe from yeast. Imflammatory disease caused by skin irritation from ammonia, heat, moisture, occlusive diapers
|
pg259
|
|
|
Candidiasis
|
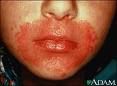
scalding red, moist patches with sharply demarcated borders
aggravated by urine, feces, heat, and moisture |
259
|
|
|
Tinea Corporis
|
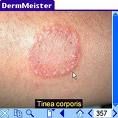
ringworm of the body
scales on chest abdomen, back or arms forming multiple circular lesions with clear centers. |
|
|
|
Tinea Pedis
|
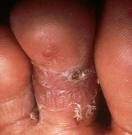
ringworm of the foot.
fungal infection, first appears as small vesicles between toes, sides of fee, soles |
|
|
|
Tinea Capitis
|
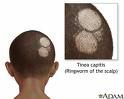
ringworm on scalp
|
|
|
|
Psoriasis
|
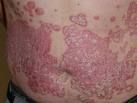
scaly erythematous patch, with silvery scales on top
|
|
|
|
Herpes Zoster/Shingles
|
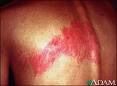
small grouped vesicles emerge along route of cutaneous sernsory nerve, then pustules, then crusts. practically always unilateral, does not cross midline
|
|
|
|
Tinea Versicolor
|
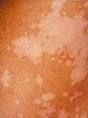
hypopigmented. Fine scaling, round patches of pink, tan, or white that do not tan in sunlight.
|
262
|
|
|
Melanoma
|
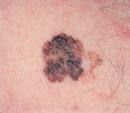
malignant; deadly; usually brown, can be tan, black, pink-red, purple, or mixed pigmentation. often irregular or notched borders. may have scaling, flaking, oozing texture. known ABCDE characteristics for all pigmented lesions
|
|
|
|
signs and symptoms of malignant melanoma
|
Asymmetry, Border irregular, Color variation, diameter greater than 6mm, elavation and enlargement. (ABCDE).
also, change iin mole size, new pigmented lesion, itching, burning, bleeding in a mole |
231
|
|
|
Seborrheic Dermatitis
|
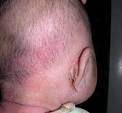
cradle cap. thick yellow white, greasy, adherent scales with mild erythema on scalp and forehead.
|
266
|
|
|
Alopecia Areata
|
hair loss, stress, genetics, diet, endocrine problem
sudden appearance of sharply circumscribed, round or oval balding patch |
|
|
|
Pediculosis Capitis
|
head lice
|
|
|
|
Folliculitis
|
looks like acne. superficial infection of hair follicle. Multiple pustules, whiteheads, with hair visible at center and erythematous base.
|
|
|
|
Nail Clubbing
|
distal edge of nail elevate; angle is greater than 180degrees.
Seen with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and congenital heart disease with cyanosis |
|
|
|
Hirsutism
|
female with excessive hair growth
|
|
|
|
Café au late
|
hyperpigmentation.
large round or oval patch of light-brown pigmentation, usualy present at birth |
|
|
|
Vitiligo
|
not much melanin – hypopigmentation.
|
|

