![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
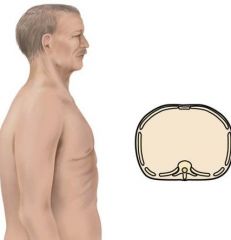
Identify and describe the pictured condition.
|
Note equal anteroposterior-to-transverse diameter and that ribs are horizontal instead of the normal downward slope; associated with normal aging and also with chronic emphysema and asthma as a result of hyperinflation of lungs
|
|
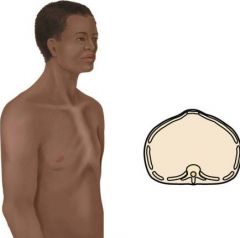
Identify and describe the pictured condition.
|
A forward protrusion of the sternum, with ribs sloping back at either side and vertical depressions along costochondral junctions (pigeon breast)
|
|
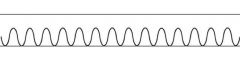
Identify and describe the pictured respiratory pattern.
|
Normal adult respiratory pattern
Rate: 10-20 breaths Depth: 500-800 mL Pattern: Even |
|
|
Identify the 4 functions of respiratory system.
|
• Supply O2 to the body for energy production
• Remove CO2 as a waste product of energy • Maintain Homeostasis (acid base balance of arterial blood) • Maintain Heat Exchange |
|
|
Identify the nationality that has a high incidence of TB.
|
Asians
|
|
|
Identify the 2 cultures that have larger chest volumes than Native Americans and Asians.
|
Caucasians and African Americans
|
|
|
Identify 5 possible chief complaints related to thorax/lungs.
|
• Wheezing
• Difficulty breathing • Mucous • Chest pain (related to lungs) • Cough |
|
|
Describe the test for tactile fremitus, including what it's for and how to do it.
|
Palpable vibration, should be even on both sides.
Have pt say "99" as you move the ball of your hands over pt's front/bank in specified locations. |
|
|
Identify the purpose of percussion and how you would perform it.
|
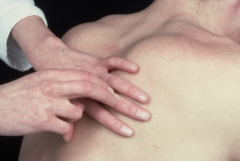
Note resonance or dullness over the lung fields
Put finger on lung fields and tap between two topmost knuckles |
|
|
Identify the 3 adventitious sounds.
|
Crackles
Wheezing Rhonchi/coarse |
|
|
Describe the following adventitious sound: crackles.
|
short, crackling, popping sounds
Tip: Rice Crispies |
|
|
Describe the following adventitious sound: wheezing.
|
high pitched squeak/whistle
|
|
|
Describe the following adventitious sound: rhonchi.
|
low-pitched hoarse sounds
|
|
|
Identify the 3 special lung assessment tests.
|
Bronchophony
Egophony Whispered pectoriloquy |
|
|
Describe the test for bronchophony, including what it's for and how to do it.
|
pt repeats “99" while you auscultate; should hear sound but should NOT be able to distinguish it; if you can hear 99, result is abnormal
|
|
|
Describe the test for egophony, including what it's for and how to do it.
|
pt repeats “ee-ee-ee-ee,” should hear “ee-ee-ee” through stethoscope; positive for egophony when E sounds like letter A
|
|
|
Describe the test for whispered pectoriloquy, including what it's for and how to do it.
|
pt whispers a phrase like “1-2-3", should be faint, muffled, and almost inaudible ; positive result when whisper sounds clear
|
|
|
Identify the ratio of a normal chest.
|
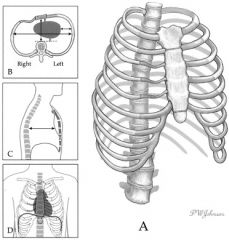
2 : 1
|
|
|
tachypnea
|
increased RR, rapid shallow breathing (>20 respirations per minute)
|
|
|
bradypnea
|
slow breathing pattern, (<10 respirations per minute)
|
|
|
Cheyne-Stokes respirations
|
respirations gradually wax and wane, with periods of apnea, in a regular pattern, usually a sign of a poor prognosis (Common and it’s a sign of death)
|
|
|
pleural effusion
|
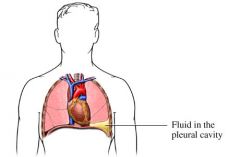
collection of excess fluid in the intrapleural space
|
|
|
pneumothorax
|
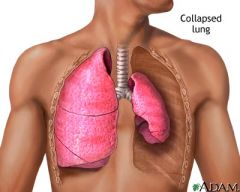
free air in pleural space causes lung collapse
|
|
|
tuberculosis (TB)
|
positive PPD and positive CXR, very contagious, characterized by
a productive cough in which the sputum is usually purulent and thick. Incidence is on the rise.
|
|
|
bronchitis
|
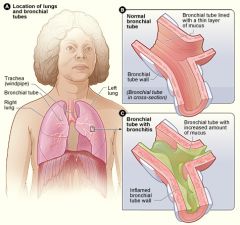
Inflammation of bronchi, may have partial obstruction of bronchi
from secretions or inflammation causing constriction.
Characterized by hacking, “mucousy” wet and often productive cough. Crackles with auscultation, usually CXR will be clear. |
|
|
pneumonia
|
Infection of the lung parenchyma, alveoli become consolidated with bacteria and fluid.
Lung sounds will auscultate crackles or be diminished, especially in the bases, percussion will illicit a dull sound |
|
|
asthma
|
Reactive airway disease, an allergic response or hypersensitivity to allergens, irritants, microorganisms, and exercise.
Characterized by bronchospasm, inflammation and very thick mucous production in the airways. Most common presenting symptoms are wheezing (usually expiratory), dyspnea, chest tightness or decreased air exchange/movement, and anxiety |
|
|
Identify the locations to check for tactile fremitus posteriorly.
|
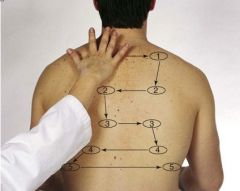
Note: 5 locations bilaterally
|
|
|
Identify the locations to check for percussion posteriorly.
|
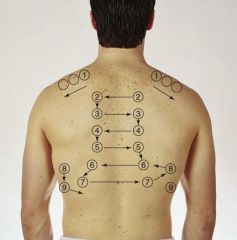
Note: 9 locations bilaterally
|
|
|
Identify the locations to auscultate posteriorly.
|
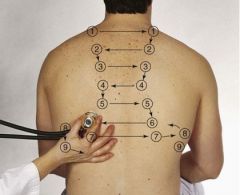
Note: 9 locations bilaterally
|
|
|
Identify the locations to check for percussion and to auscultate anteriorly.
|
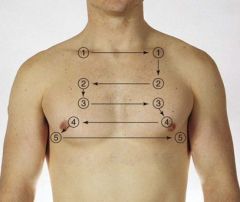
Note: 5 locations bilaterally
|
|
|
Identify the 3 components of the thoracic cage.
|
Sternum (breastbone)
Ribs (12) Thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
Identify the lobes in the right lung and left lung anteriorly.
|
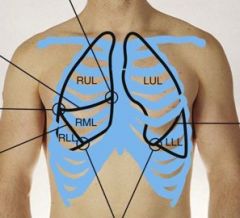
Right lung - 3 lobes
Left lung - 2 lobes |
|
|
Identify the lobes in the right lung and left lung posteriorly.
|
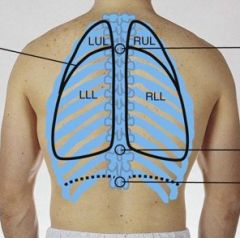
Right lung - 2 lobes
Left lung - 2 lobes |
|
|
Identify the 3 reference lines for the thoracic cage.
|
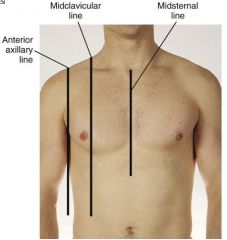
• Midsternal
• Midclavicular • Axillary Line - posterior, mid and anterior axillary line |
|
|
The _______ contain the lungs.
|
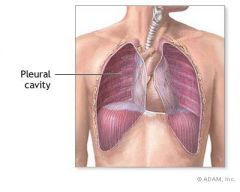
pleural cavities
|
|
|
pleurae
|
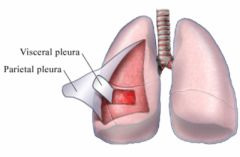
thin, slippery envelope between the lungs and chest wall; two kinds: visceral and parietal
|
|
|
Identify the function of the trachea.
|
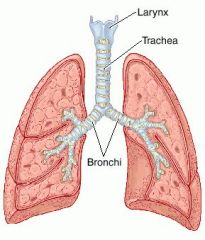
transport gases between the environment and lung parenchyma
|
|
|
Identify this sound.
|
Wheezing
|
|
|
Identify the subjective data required for a respiratory assessment. (7)
|
Cough
SOB Chest pain w/ breathing Hx of respiratory infx Smoking Enviromental exposure Self-care behaviors |
|
|
If you percuss a dull sound in the lungs, what does this mean?
|
abnormal density in the lungs (like consolidation) seen with pneumonia, pleural effusion, atelectasis, and tumor
|
|
|
Identify the 3 normal breath sounds.
|
Bronchial
Bronchovesicular Vesicular |
|
|
Decreased breath sounds occur due to ______.
|
obstruction
|
|
|
Increased breath sounds occur due to _______ because _________.
|
consolidation and compression b/c it makes lungs more dense resulting in more transmission of sound
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt has wet, hacking, productive cough. When you auscultate, you hear crackles, but the CXR is clear. |
bronchitis
|
|
|
eupnea
|
normal adult respiration
|
|
|
apnea
|
cessation of breathing
|
|
|
consolidation
|
the solidification of portions of lung tissue as it fills up with infectious exudate, as in pneumonia
|
|
|
Decreased fremitus occurs when _______.
|
anything obstructs transmission of vibrations.
|
|
|
Increased fremitus occurs with __________.
|
compression or consolidation of lung tissue.
|
|
|
Identify the lung borders.
|
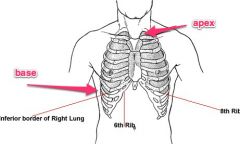
Apex - highest point
Base - lower border |
|
|
Describe the mediastinum of the thoracic cavity.
|
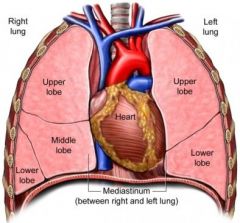
middle section containing the esophagus, trachea, heart and
great vessels |
|
|
vertebra prominens
|
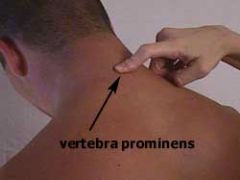
most prominent bony spur at base of neck
|
|
|
angle of Louis/manubriosternal angle
|
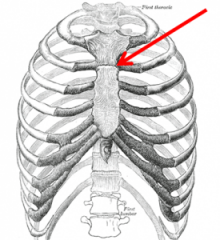
articulation of the manubrium and body of the sternum; continuous with second rib
|
|
|
The nurse is assessing an older adult patient who reports a decreased tolerance for exercise and that she must work harder to breathe. Which question assists the nurse in determining if these are normal changes related to aging?
a. "How old are you?" b. "When did you first notice these symptoms?" c. "Do you or have you ever smoked cigarettes?" d. "How often do you exercise?" |
b. "When did you first notice these symptoms?"
|
|
|
The patient's pulse oximetry reading is 89%. What is the nurse's priority action?
a. Recheck the reading with a different oximeter b. Apply supplemental oxygen and recheck the oximeter reading in 15 minutes c. Assess the patient for respiratory distress and recheck the oximeter reading d. Place the patient in the recovery position and monitor frequently |
c. Assess the patient for respiratory distress and recheck the oximeter reading
|
|
|
The nurse is taking a history on a patient who reports sleeping in a recliner chair at night because lying on the bed causes shortness of breath. How is this documented?
a. Orthopnea b. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea c. Orthostatic nocturnal dyspnea d. Tachypnea |
a. Orthopnea
|
|
|
Which assessment finding is an objective sign of chronic oxygen deprivation?
a. Continuous cough productive of clear sputum b. Audible inspiratory and expiratory wheeze c. Chest pain that increases with deep inspiration d. Clubbing of fingernails and a barrel-shaped chest |
d. Clubbing of fingernails and a barrel-shaped chest
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
A pt has unequal chest expansion and tactile fremitus is decreased. Per auscultation, breath sounds are decreased and when percussed, lungs were hyperresonant. There were no adventitious lung sounds. |
Pneumothorax
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Tactile fremitus decreased and chest expansion not symmetrical. Percussion reveals dull to flat sounds with no adventitious sounds. |
Pleural effusion
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Chest expansion not symmetrical, with lungs percussed dull. Per auscultation, crackles were heard. Also, pt had an increased RR. |
Pneumonia
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
A patient comes in with wheezing (during expiratory), shortness or breath, and anxiety. |
Asthma
|
|
|
hyperresonance
|
lower pitched booming sound found when too much air is present
|

