![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
123 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
normal adult WBC values
|
5,000-10,000/mm3
Increases in acute infection; decreases in certain viral or overwhelming infections |
|
|
iatrogenic infection
|
type of HAI from a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure
|
|
|
exogenous infection
|
comes from microorganisms found outside the individual, i.e. salmonella, Clostridium tetani, Aspergillus
|
|
|
endogenous infection
|
occurs when part of the patient's normal flora becomes altered and an overgrowth occurs results, i.e. staphylococci, enterococci, yeasts
|
|
|
What are the body's defenses against infection? (7)
|
Skin multilayered surface, shedding, and sebum
Mouth saliva and mucosa Eyes tearing and blinking Respiratory tract cilia and macrophages Urinary tract urine flushing action and multilayered epithelium GI tract acidity and rapid peristalsis Vaginal flora |
|
|
Identify the 6 parts of the chain of infection.
|
Infectious agent
Reservoir Portal of exit Mode of transmission Portal of entry Host |
|
|
Identify the ideal pH for infectious agents.
|
pH 5-7
|
|
|
fomites
|
inanimate objects
|
|
|
Identify the 6 parts of the chain of infection.
|
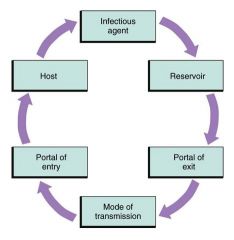
Infectious agent
Reservoir Portal of exit Mode of transmission Portal of entry Host |
|
|
Identify the number one mode of transmission.
|
Healthcare worker's hands
|
|
|
communicable disease
|
infectious disease that can be transmitted directly from one person to another
|
|
|
Infection can develop if the chain of infection remains ______.
|
uninterrupted
|
|
|
Microorganisms on the skin are either resident or transient ______.
|
flora, AKA normal flora
|
|
|
normal flora (resident organisms)
|
permanent residents organisms of the skin, where they survive and multiply without causing illness
|
|
|
virulence
|
ability to produce a disease; typically in reference to an organism
|
|
|
reservoir
|
place where microorganisms survive, multiply, and await transfer to a susceptible host
|
|
|
Identify the 4 most frequent reservoirs for HAIs.
|
Patients
Equipment Environment Healthcare worker's (esp. hands) Tip: PEEH |
|
|
What do organisms require to thrive?
|
a proper environment, including appropriate food, oxygen, water, temperature, pH, and light
|
|
|
_____ temperatures tend to prevent growth and reproduction of bacteria.
|
Cold
|
|
|
bacteriostasis
|
prevents growth and reproduction of bacteria
|
|
|
bactericidal
|
temperature or chemical that destroys bacteria
|
|
|
Identify 6 ports of exit/entry.
|
Blood
Skin and mucous membranes Respiratory tract Genitourinary tract Gastrointestinal tract Transplacental (mother to fetus) |
|
|
Identify the 6 modes of transmission.
|
Direct
Indirect Droplet Airborne Vehicles Vector Tip: DD IA VV |
|
|
mode of transmission: direct
|
person-to-person (i.e. fecal to oral) physical contact between source and susceptible host (e.g. touching patient feces and then touching inner mouth or consuming contaminated food)
|
|
|
mode of transmission: indirect
|
personal contact of susceptible host with contaminated inanimate object (e.g. needles, dressings, environment)
|
|
|
mode of transmission: droplet
|
large particles that travel up to 3 feet during coughing, sneezing, or talking and come in contact with susceptible host
|
|
|
mode of transmission: airborne
|
Droplet nuclei or residue or evaporated droplets suspended in air during coughing or sneezing or carried on dust particles that then come in contact with susceptible host
|
|
|
Identify 'vehicles' for modes of transmission. (5)
|
Blood
Contaminated items Drugs, solutions Food (improperly handled) Water Tip: BCDFW |
|
|
mode of transmission: vector
|
transmission via flies (external) or mosquito, louse, flea, tick (internal)
|
|
|
Identify the 4 stages for the course of infection.
|
Incubation
Prodromal Illness Convalescence Tip: IPIC |
|
|
Why would someone have a fever after surgery?
|
Products getting into blood stream, person is cut up, and surgeons are accessing insides
|
|
|
incubation period
|
interval between entrance of pathogen into body and appearance of first symptoms
|
|
|
prodromal period
|
interval from onset of nonspecific signs and symptoms (malaise, low-grade fever, fatigue) to more specific symptoms
|
|
|
illness stage
|
interval when patient shows signs and symptoms specific to type of infection
|
|
|
convalescence
|
interval when acute symptoms of infection disappear; recovery
|
|
|
susceptibility
|
individual's degree of resistance to pathogens
|
|
|
Identify the two main categories that affects a person's susceptibility.
|
Natural defenses (age, nutritional status, etc.)
Certain risk factors |
|
|
Identify the reason for the increased resistance of certain organisms to antibiotics.
|
Frequent and sometimes inappropriate use of antibiotics over the years in all settings (i.e. acute care, clinics, long-term care)
|
|
|
inflammation
|
cellular response of the body to injury, infection, or irritation
|
|
|
exudate
|
fluid and cells that are discharged from cells or blood vessels (e.g. pus or serum)
|
|
|
leukocytosis
|
an increase in the number of circulating WBCs, which is the response of the body when WBCs are leaving blood vessels to attack infection
|
|
|
medical asepsis
|
"clean technique" includes procedures for reducing the number of organisms present and preventing the transfer of organisms
|
|
|
Identify 3 examples of medical asepsis.
|
Hand hygiene, barrier techniques, and routine environmental cleaning
|
|
|
Standard precautions apply to contact with _______. (4)
|
blood, body fluid, nonintact skin, and mucous membranes from all patients.
|
|
|
sterilization
|
the complete elimination or destruction of all microorganisms, including spores
|
|
|
disinfection
|
process that eliminates many or all microorganisms, with the exception of bacterial spores, from inanimate object
|
|
|
surgical asepsis
|
procedures used to eliminate any microorganisms from an area
|
|
|
Although surgical asepsis is common in surgery and L&D, when do you use it at the bedside? (3)
|
Suctioning the tracheobronchial airway
Inserting IV or urinary catheters Reapplying sterile dressings Tip: SIR |
|
|
sterile field
|
area free of microorganisms and prepared to receive sterile items
|
|
|
A patient in isolation is subject to ________ because of the restricted environment.
|
sensory deprivation
|
|
|
Identify the most effective way to break the chain of infection.
|
Hand hygiene
|
|
|
The nurse wears a gown when _______.
|
blood or body fluids may get on the nurse's clothing from a task that he or she plans to perform.
|
|
|
When a nurse is performing surgical hand asepsis, the nurse must keep hands _______ elbows.
above/below |
above
|
|
|
What is the best method to sterilize a straight urinary catheter and suction tube in the home setting?
|
Boiling water
|
|
|
A patient has an indwelling urinary catheter. Why does an indwelling urinary catheter present a risk for urinary tract infection?
|
It obstructs the normal flushing action of urine flow.
|
|
|
Identify 5 common nursing interventions for infection control.
|
-Monitor client’s body temperature
-Inspect urine for foul odor -Inspect IV site for redness, swelling, drainage -Observe client for evidence of cough -Teach client and family proper hand washing technique |
|
|
Identify nursing actions/concerns for a systemic infection. (5)
|
Fever
I & O Increased BMR increases Nutritional requirements Cells need oxygen, rest |
|
|
Identify nursing actions/concerns for a localized infection. (3)
|
Remove debris
Assess infected drainage Supportive care for healing wounds |
|
|
No fresh flowers or potted plants should not in patients that are _______.
|
immuno-compromised
|
|
|
Which mode of transmission requires the N-95?
|
Airborne
|
|
|
Identify 3 diseases that can spread via the airborne transmission.
|
TB
Varicella (chicken pox) Measles |
|
|
Identify 4 diseases that can spread via the droplet transmission.
|
Pertussis
Influenza Mumps Meningitis Tip: PIMM |
|
|
Identify which mode of transmission requires the use of a mask when within 3 feet of a patient.
|
Droplet
|
|
|
immune response
|
how your body recognizes and defends itself against bacteria, viruses, and substances that appear foreign and harmful
|
|
|
Normal body floras help to resist infection by _______. (2)
|
releasing antibacterial substances and inhibiting multiplication of pathogenic microorganisms.
|
|
|
phagocytosis
|
the process of phagocytes (type of WBC) "eating" microorganisms and dead or damaged cell; part of inflammation process
|
|
|
Identify 6 conditions that increase susceptibility to infection.
|
Stress
Poor nutrition Increasing age Inherited conditions Chronic disease Teatments or conditions that compromise the immune response Tip: SPIICT |
|
|
Identify the 4 major sites for health care–associated infections (HAIs).
|
Wounds, surgical or traumatic
Urinary tract Respiratory tracts Bloodstream Tip: WURB |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Escherichia coli.
|
Colon
Gastroenteritis, UTI |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Staphylococcus aureus.
|
Skin, hair, anterior nares, mouth
Wound infections, pneumonia, food poisoning, cellulitis |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Streptococcus (group A).
|
Oropharynx, skin, perianal area
Strep throat, rheumatic fever, scarlet fever, impetigo, wound infection |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Streptococcus (group B).
|
Adult genitals
UTI, wound infection, postpartum sepsis, neonatal sepsis |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
Droplet nuclei from lungs, larynx
Tuberculosis |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
|
Genitourinary tract, rectum, mouth
Gonorrhea, pelvic inflammatory disease, infectious arthritis, conjuctivitis |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Rickettsia rickettsii.
|
Wood tick
Rocky Mountain spotted fever |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Staphylococcus epidermidis.
|
Skin
Wound infection, bacteremia |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: HIV.
|
Blood, semen, vaginal secretions
AIDS |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Candida albicans.
|
Mouth, skin, colon, genital tract
Candidiasis, pneumonia, sepsis |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Hep B/C.
|
Blood and certain body fluids, sexual contact
Hep B/Hep C |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Hep A.
|
Feces
Hepatitis A |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Herpes simplex virus 1.
|
Lesions of mouth or skin, saliva, genitalia
Cold sores, aseptic meningitis, STD, herpetic whitlow |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Aspergillus organisms.
|
Soil, dust, mouth, skin, colon, genital tract
Aspergillosis, pneumonia, sepsis |
|
|
Identify the major reservoir(s) and major infections/diseases caused by the following organism: Plasmodium falciparum.
|
Blood
Malaria |
|
|
normal adult iron level
|
60-90 g/100 mL
Decreases in chronic infection |
|
|
normal adult erythrocyte sedimentation rate
|
15 mm/hr (men)
20 mm/hr (women) Increases in presence of inflammatory process |
|
|
Identify the possible outcome for the following susceptibility risk factor: chronic disease.
|
Pneumonia, skin breakdown, venous stasis ulcers
|
|
|
Identify the possible outcome for the following susceptibility risk factor: high-risk behaviors (lifestyle).
|
STI, HIV, viral infections, yeast infections, liver failure, HBV, HCV
|
|
|
Identify the possible outcome for the following susceptibility risk factor: occupation (miner, unemployed, homeless).
|
Black lung disease, pneumonia, TB, poor intake, lack of access to medical care, stress
|
|
|
Identify the possible outcome for the following susceptibility risk factor: heredity (sickle-cell disease, diabetes).
|
Anemia, delayed-healing
|
|
|
Identify the possible outcome for the following susceptibility risk factor: travel history.
|
Meningitis, acute respiratory distress
|
|
|
Identify the possible outcome for the following susceptibility risk factor: trauma.
|
Sepsis, secondary infection
|
|
|
Identify the possible outcome for the following susceptibility risk factor: nutrition.
|
Impaired immune response
|
|
|
You need to obtain specimens with ______ gloves and _______ equipment.
|
Clean gloves and sterile equipment
|
|
|
TRUE/FALSE
You need to double bag contaminated items to prevent accidental exposure. |
FALSE
CDC only recommends use of single, intact , standard size linen bag |
|
|
Why it it necessary to bag linen or trash?
|
Prevent accidental exposure to personnel and contamination of surrounding environment
|
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: sebum.
|
Skin
Contains fatty acid that kills some bacteria Excessive bathing |
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: saliva.
|
Mouth
Wash away particles; contains microbial inhibitors (e.g. lysozyme) Poor oral hygiene, dehydration |
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: tearing and blinking.
|
Eye
Blinking reduces entry, tearing washes away particles containing pathogens Injury, exposure (e.g. splash of infectious material) |
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: cilia lining airway, coating w/ mucous.
|
Respiratory tract
Traps inhaled microbes and sweeps them outward to be expectorated or swallowed Smoking, high concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide, cold air, decreased humidity |
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: puberty causing low pH.
|
Vagina
Inhibit growth of many microroganisms Antibiotics and oral contraceptives |
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: macrophages.
|
Respiratory tract
Engulf/destroy microorganisms reaching alveoli of lung Smoking |
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: rapid peristalsis in small intestine.
|
Small intestine/GI tract
Prevents retention of bacterial contents Delayed motility due to fecal impaction or mechanical obstruction |
|
|
For the following defense mechanism, identify its location, action, and the factor(s) that may alter it: acidity of gastric secretions.
|
GI tract
Prevents retention of bacterial contents Taking antacids |
|
|
Identify the 4 types of isolation precautions in order of most serious to least serious. What tier are they in?
|
Tier 2
Airborne Droplet Contact Protective equipment |
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution in which you would have to wear an N-95 respirator.
|
Airborne precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution in which droplet nuclei are smaller than 5 microns.
|
Airborne precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution in which droplet nuclei are larger than 5 microns.
|
Droplet precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants.
|
Protective precaution
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had C. difficile infection.
|
Contact precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had pertussis.
|
Droplet precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had mumps.
|
Droplet precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had TB.
|
Airborne precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had measles.
|
Airborne precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had diphtheria.
|
Droplet precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had MRSA.
|
Contact precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had chickenpox (varicella).
|
Airborne precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had rubella.
|
Droplet precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had Mycoplasma/meningococcal pneumonia/sepsis.
|
Droplet precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had varicella zoster.
|
Airborne precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had scabies.
|
Contact precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that was immunocompromised.
|
Contact precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a young patient that had scarlet fever.
|
Droplet precautions
|
|
|
Identify the type of isolation precaution required for a patient that had streptococcal pharyngitis.
|
Droplet precautions
|

