![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Identify the theory of Patricia Benner discussed in class.
|
Theory of novice to expert passes through 5 levels of proficiency when acquiring and developing general or specialized nursing skills
|
|
|
Describe the following level of proficiency according to the Benner's Novice to Expert theory: novice.
|
Beginning nursing student or any nurse entering a situation in which there is no previous level of experience (e.g., an experienced operating room nurse chooses to now practice in home health)
|
|
|
Describe the following level of proficiency according to the Benner's Novice to Expert theory: advanced beginner.
|
nurse who has had some level of experience with the situation. This experience may only be observational in nature, but the nurse is able to identify meaningful aspects or principles of nursing care
|
|
|
Describe the following level of proficiency according to the Benner's Novice to Expert theory: competent.
|
nurse who has been in the same clinical position for 2 to 3 years. This nurse understands the organization and specific care required by the type of patients (e.g., surgical, oncology, or orthopedic patients)
|
|
|
Describe the following level of proficiency according to the Benner's Novice to Expert theory: proficient.
|
nurse with more than 2 to 3 years of experience in the same clinical position. This nurse perceives a patient's clinical situation as a whole, is able to assess an entire situation, and can readily transfer knowledge gained from multiple previous experiences to a situation; nurse focused on managing care as opposed to performing skills and managing
|
|
|
Describe the following level of proficiency according to the Benner's Novice to Expert theory: expert.
|
nurse with diverse experience who has an intuitive grasp of an existing or potential clinical problem
|
|
|
Identify the 5 levels of proficiency according to Benner's theory.
|
Novice
Advanced Beginner Competent Proficient Expert |
|
|
Identify 6 issues influencing healthcare in the workplace.
|
-Language Barriers
-Personal bias -Cultural competence -Inaccurate assumptions -Gender biases -Increased Acuity |
|
|
Identify 9 issues influencing healthcare in the community.
|
-Increasing geriatric population
-Myth of “melting pot” -Lack of Health Care Insurance -Poor access to Health Care -High unemployment rate in Las Vegas -Transient population -Poor education/illiteracy -Limited public resources -Growing shortage of primary care physicians |
|
|
nursing code of ethics for professional registered nurses
|
principles of right and wrong to provide patient care
|
|
|
Describe the role of 'advocate'.
|
protects the patient's human and legal right to make choices about his or her care; provide additional information to help a patient decide whether or not to accept a treatment or find an interpreter to help family members communicate their concerns
|
|
|
evidence-based practice
|
integrates best current evidence with clinical expertise and patient/family preferences and values for delivery of optimal health care.
|
|
|
The examination for RN licensure is ________ in every state in the United States
different/the same |
the same
|
|
|
Identify why the NCLEX-RN is the same in every state.
|
Provides a minimal standard of knowledge for a registered nurse in practice
|
|
|
Health care reform will bring changes in the emphasis of care; identify the model that is expected from health care reform?
|
Moving from an acute illness to a health promotion, illness prevention model
|
|
|
Identify the 2 types of nurses that have the authority to write prescriptions.
|
Nurse practitioner
Certified clinical nurse specialist |
|
|
nurse researcher
|
investigates problems to improve nursing care and to further define and expand the scope of nursing practice
|
|
|
Describe the following type of education: in-service education.
|
instruction or training provided by a health care agency or institution
|
|
|
The Nursing Process is the _______________.
|
foundation of clinical decision making.
|
|
|
Describe the role of 'caregiver'.
|
you help patients maintain and regain health, manage disease and symptoms, and attain a maximal level function and independence through the healing process
|
|
|
Describe the role of 'educator'.
|
explain concepts and facts about health, describe the reason for routine care activities, demonstrate procedures such as self-care activities, reinforce learning or patient behavior, and evaluate the patient's progress in learning
|
|
|
The ____________ is the most independently functioning nurse.
|
advanced practice registered nurse (APRN)
|
|
|
clinical nurse specialist (CNS)
|
an APRN who is an expert clinician in a specialized area of practice
|
|
|
certified nurse-midwife (CNM)
|
an APRN who is also educated in midwifery and is certified by the American College of Nurse-Midwives
|
|
|
certified registered nurse anesthetist (CRNA)
|
an APRN with advanced education in a nurse anesthesia accredited program; provide surgical anesthesia under the guidance and supervision of an anesthesiologist
|
|
|
nurse administrator
|
manages patient care and the delivery of specific nursing services within a health care agency
|
|
|
nurse educator
|
works primary in schools, staff development departments, and patient education departments; responsible for teaching current nursing practice, trends, skills, etc.
|
|
|
Identify the 5 steps for evidence-based practice.
|
Ask a clinical question.
Collect the most relevant and best evidence. Integrate all evidence with one's clinical expertise and patient preferences and values in making a practice decision or change. Evaluate the practice decision or change. Share the outcomes of EBP changes with others. |
|
|
Identify the 5 issues you must address when asking a clinical question.
|
P: What is the patient population you are interested in?
I: What is the intervention of interest? C: What are you trying to compare? O: What outcome are you trying to measure? T: What is the time frame? Note: PICOT |
|
|
Identify the PICOT values for the following clinical question.
Do nursing students (P) perform better on final exams (O) after they have had at least 8 hours of sleep (I) as opposed to students who “cram” (C) all night (during one semester)? |
P - nursing students
I - students who have had 8 hours of sleep C - students who cram all night O - perform better on exams T - one semester |
|
|
Identify the PICOT values for the following clinical question.
What is the duration of recovery for patients with total hip replacement who developed a post-operative infection as opposed to those who did not within the first six weeks of recovery? |
P - patients with hip replacement
I - develop post-op infx C - don't develop post-op infx O - duration of recovery T - first 6 weeks of recovery |
|
|
Identify the PICOT values for the following clinical question.
In men, does having a vasectomy (compared to not having one) increase the risk of getting testicular cancer in the future? |
P - males
I - getting vasectomy C - not getting vasectomy O - getting testicular cancer T - not specified |
|
|
Identify the PICOT values for the following clinical question.
In infants born prematurely, compared to those born at full term, what is the subsequent lifetime prevalence of sensory deafness? |
P - newborn infants
I - premature C - full-term O - sensory deafness T - lifetime |
|
|
Identify the PICOT values for the following clinical question.
Does hand washing among healthcare workers reduce hospital acquired infections? |
P - healthcare workers
I - handwashing C - not handwashing O - reduced HAIs T - not specified |
|
|
Identify what each of these stand for: PICOT.
|
P - population
I - intervention C - comparison O - outcome T - time frame |
|
|
peer-reviewed article
|
one reviewed by a panel of experts familiar with the topic or subject matter of the article before it was published
|
|
|
Why are meta-analyses and systematic reviews the perfect answers to PICOT questions?
Where are they found on the hierarchy of evidence? |
Because they rigorously summarize current evidence; found at the very top
|
|
|
randomized controlled trials (RCT)
|
most precise form of experimental study and therefore is the gold standard for research; review of several RCTs is better than a single RCT
|
|
|
Identify the 7 stages on the hierarchy of evidence.
|
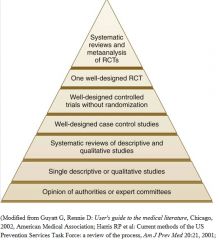
|
|
|
quantitative vs. qualitative research
|
quantitative - precise measurement and quantification based on numerical data and statistical analysis
qualitative - study of phenomena that are difficult to quantify or categorize such as patient perception of illness; interviews, story telling, written transcripts |
|
|
Identify which of the following requires inductive reasoning: quantitative vs. qualitative research.
|
Qualitative research
|
|
|
inductive reasoning
|
how probable is it that a conclusion is true
Example: If 90% of humans are right handed and “Joe” is human, than the probability of Joe being right handed is 90%. |
|
|
Identify which type of research (quantitative or qualitative) the following example is related to: experimental research.
|
Quantitative
|
|
|
Identify which type of research (quantitative or qualitative) the following example is related to: surveys.
|
Quantitative
Note: Surveys is gathering a large amount of data to describe a population, not personal interview surveys. |
|
|
Identify which type of research (quantitative or qualitative) the following example is related to: story telling.
|
Qualitative
|
|
|
Identify which type of research (quantitative or qualitative) the following example is related to: nonexperimental research.
|
Quantitative
|
|
|
Identify which type of research (quantitative or qualitative) the following example is related to: written transcripts.
|
Qualitative
|
|
|
Identify which type of research (quantitative or qualitative) the following example is related to: grounded theory.
|
Qualitative
|
|
|
Identify and define the 3 research methods associated with qualitative research.
|
Ethnography- explores cultural phenomena
Phenomenology- explores structures of subjective experiences and consciousness. Grounded theory- discovery of theory through analysis of data. |
|
|
Identify and define the 3 levels of critical thinking.
|
basic critical thinking - learner trusts that the experts have the right answers for every problem
complex critical thinking - analyze and examine choices more independently; ability to look beyond expert opinion commitment - makes choices w/o assistance and accepts accountability for choices |
|
|
The _______ is comparable to the nursing process.
|
scientific method
|
|
|
critical thinking
|
active, purposeful, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one's thinking and the thinking of other individuals
|
|
|
Identity the characteristics of critical thinkers. (4)
|
Open-mindedness
Creativity Confidence Continual inquiry |
|
|
Identify 3 ways you can become a great critical thinker.
|
Experience
Commitment Active curiosity toward learning |
|
|
Identify the 2 types of specific critical thinking.
|
Diagnostic reasoning and inference
Clinical decision making |
|
|
clinical decision making
|
requires careful reasoning in choosing best options for the best patient outcomes (based on patient condition and priority of problems)
|
|
|
diagnostic reasoning and inference
|
collect patient data and analyze them to determine the patient’s problems
|
|
|
_____________ are necessary for you to acquire clinical decision-making skills.
|
Clinical learning experiences
|
|
|
Identify and describe the 3 methods a nurse needs to develop critical thinking skills.
|
Reflective journaling (reflection)
Meeting with colleagues (shared experiences, viewpoints) Concept mapping (visual representation of pt's problems and interventions) |
|
|
Outcomes are _______. (3)
|
Patient-centered
Measurable Have a time frame |
|
|
Which of the following is a well-written outcome? Explain why.
A, Patient will understand why he takes insulin. B. Patient will verbalize why he takes insulin. |
B. Patient will verbalize why he takes insulin.
It is better because the patient verbalizing his understanding is measurable. You CANNOT measure if a patient understands without you testing their knowledge on it. |
|
|
Identify and briefly define the 5 steps of the nursing process.
|
Assessment- gather information
Diagnosis- identify problem Planning-set goals (outcomes) and appropriate nursing interventions Implementation- perform nursing actions Evaluation- determine if goals are met Tip: ADPIE |
|
|
Identify which level of critical thinking the following statement relates to: anticipates when to make choices without others' assistance.
|
Commitment critical thinking
|
|
|
Identify which level of critical thinking the following statement relates to: analyzes and examine choices more independently.
|
Complex critical thinking
|
|
|
Identify which level of critical thinking the following statement relates to: weighs benefits and risks when making a decision.
|
Complex critical thinking
|

