![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define gout. What is it caused by?
|
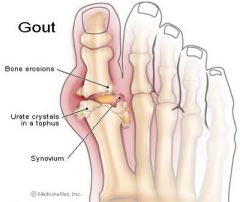
Gout is an inflammatory joint disease caused by the deposit of uric acid crystals.
|
|
|
Describe the pathophysiology of gout.
|
- The end product of purine metabolicsm is uric acid.
- abnormal purine metabolism = decreased secretion of urates & increased blood levels of uric acid. |
|
|
What's so bad about having too much uric acid?
|
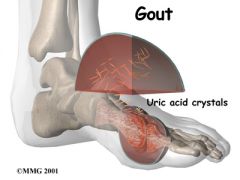
Uric acid forms a precipate in areas where blood flow is slowest.
|
|
|
What can cause gout? (3)
|
- a genetic defect in purine metabolism can cause overproduction of uric acid.
- chronic renal failure - decreased uric acid excretion |
|
|
What is the normal uric acid level?
|
3 - 7 mg/100 ml.
a little different for males & females so go look that up if you want to know. |
|
|
What is secondary gout?
|
Secondary gout is caused by another disorder (or treatment).
- eg. conditions of rapid cell turnover (leukemia, multiple myeloma, anemias, psoriasis) - some medications - alcoholism and starvation |
|
|
What lab tests help diagnose gout?
|
ESR: increased
Uric Acid: increased WBC: increased (20,000) Synovial fluid: has uric acid or sodium urate crystals |
|
|
What's a tophi?
|
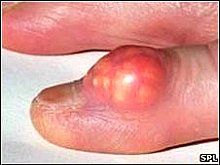
Tophi are sodium urate crystals. They deposit in peripheral areas (toe, hands, ear) or in kidneys (renal urate lithiasis)
|
|
|
There are three stages of gout.
Describe them. |
1. Hyperuricemia - asymptomatic
2. Acute, sudden onset - redness, swelling pain - one joint - 90% toe - "exquisite" - fever - anorexia - increased HR 3. Chronic gout: tophi - permanent changes in multiple joints - movement restricted - renal and cardiac problems |
|
|
How is gout treated with diet?
|
Low purine diet. Purine is found in shellfish and organ meats. ew.
|
|
|
What is the big anti-gout medication? How does it act? What's the dosage?
|

Colchicine: inhibits the migration of WBC into synovial fluid.
0.6 - 1.2 mg initial dose then 0.6 per hour until pain relieved or see toxicity (N/V/D) If given IV: depresses bone marrow |
|
|
What do uricosuric drugs do? Give an example.
|
Uricosuric drugs improve uric acid excretion. Don't start during acute attack & don't take with aspirin. ex: probenecid (Probalan) (Benemid)
|
|
|
What are Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors? Give some examples.
|
Inhibits the activity of xanthine oxidase which is an enzyme involved in purine metabolism. So, these block uric acid production.
|
|
|
Gout - Nursing - describe some interventions
|
1. pain management
2. encourage fluids to 3 quarts/day 3. lose weight. 4. no alcohol 5. avoid foods high in purine (shellfish/organ meat/ew) 6. avoid fasting 7. reduce stress |
|
|
What are two complications of gout?
|
Renal calculi and GI bleeding (from NSAIDS)
|
|
|
What NSAID is great for patients having a gout attack?
|
Indocin: 2-7 days, high dose treats gout attack.
|

