![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cardiac Terminology
Mediastinum Pericardium Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium |
Mediastinum- the chest cavity that contains the heart
Pericardium - protective covering surrounding the heart Epicardium - outer layer of the heart continuous with the pericardium Myocardium- middle layer of the heart:muscle Endocardium - inner layer of the heart, continuous with the tunica intima of blood vessels |
|
|
|
The valves that separate the atria from ventricles?
|
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
Muscles that attach chordae tendineae? |
Papillary muscles
|
|
|
Valve that separates right atrium from right ventricle?
|
Tricuspid valve
Valve that separates left atrium from left ventricle? |
Bicuspid (mitral) valve
|
|
|
What are the cords that hold valve leaflets?
|
Chrodae tendineae
What are the valves that prevent reflux of blood into ventricle that connect ventricle to arteries? |
Semi-lunar valves
|
|
|
Valve that prevents back flow of blood from pulmonary artery into right ventricle?
|
Pulmonic valve
Valve that prevents back flow of blood from aorta into left ventricle? |
Aortic valve
|
|
|
The _______ is the contraction phase of the heartbeat while the _______ is the relaxation phase.
|
The Systole is the contraction phase of the heartbeat while the Diastole is the relaxation phase.
Which one lasts longer and why? |
The diastole, the atria and ventricles are filling
|
|
|
What is the percentage of ventricular blood volume that is pumped out with each contraction, also known as stroke volume/end diastolic volume?
|
Ejection fraction (EF)
What is LVEF? |
left ventricular ejection fraction, a measure of the heart's functionality
> 50% normal 35 - 50% weakened myocardium <35% very bad |
|
|
How can EF be determined?
|
1. echocardiography measurements
2. gated mycardial perfusion imaging studies 3. MUGA (multi-gated acquisition scan) - the gold standard for LVEF |
|
|
|
What is the dominant pacemaker of the heart?
|
Sinoatrial (SA) node
paces at 60-100 bpm Secondary pacemaker along the conductive tissue pathway? |
Atrioventricular (AV) node
40-60 bpm |
|
|
What is the network of fibers that conducts impulses throughout ventricular walls?
|
Purkinje fibers
what is its other functionality? |
also a pacemaker, at 20-40 bpm
|
|
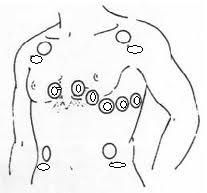
Identify the electrodes for a 12 lead EKG
|

What is a lead and how do you get 12 from 10 electrodes?
|
leads are views, 6 from the 4 arm electrodes and 6 from the chest
|
|
|
How can you determine the heart rate from an EKG tracing?
|
Count the number of large boxes between 2 R waves and divide into 300
OR count the number of small boxes and divide by 1500 |
|
|
|
What is Sinus Arrhythmia?
|
SA node paces irregularly
the R-R interval is irregular P wave, PR interval and QRS complex all normal |
|
|
|
What is Atrial Arrhythmias?
|
P waves differ and premature atrial contraction
|
|
|
|
What is Atrial fibrillation?
|
A-fib, many sites in the atria are generating depolarization waves
no distinguishable P wave PR not measuable Rate 100-160 bpm Rhythm irregular |
|
|
|
What is Atrial Flutter?
|
P wave is replaced with multiple flutter waves
Rate around 110 bpm Rhythm - regular |
|
|
|
What is First Degree AV block?
|
prolonged PR interval (>5 sm blocks(.20sec))
caused by delayed conduction through the AV node |
|
|
|
What is ventricular tachycardia?
|
Rate 180 - 190 bpm, rhythm is regular but abnormal tissues in ventricles generate rapid contractions giving poor cardiac output
Emergency situation |
|
|
|
What is Ventricular Fibrillation?
|
V-fib
Rate 300+ disorganized elec signals cause the ventricles to quiver instead of contracting no blood being pumped to brain or body Defibrillator ASAP! |
|
|
|
What is Myocardial Infarct (MI)?
|
Rhythm is regular and rate is 80 bmp and P wave and QRS complex normal but ST segment does not return to baseline
What is 0 bpm, flat rhythm |
Asystole
CPR and defibrillation needed! |
|
|
What is the procedure called where the dye is introduced into coronary arteries and stents and balloon catheters are used if needed?
|
PTCA - percutaneous transluminal coronary angiography
|
|

