![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
243 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
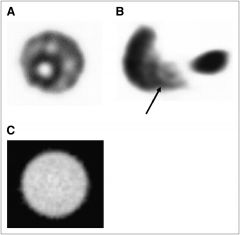
Name this artifact. Cause?
|
Ring Artifact. Caused by nonuniformity (collimator defect, being off peak, PMT gain imbalance)
|
|
|
Tc99m. Energy? Half-life?
|
140 keV, 6 hours
|
|
|
Gallium-67. Energy? Half-life?
|
92, 184, 300 keV, 72 hrs
|
|
|
I-123. Energy? Half-life?
|
159 keV, 13 hrs
|
|
|
I-131. Energy? Half-life?
|
364 keV, 7 days.
|
|
|
F-18. Energy? Half-life?
|
511 keV, 110 minute
|
|
|
Thallium-201. Energy? Half-life?
|
135, 167 keV, 73 hrs.
|
|
|
Delayed nephrogram on DTPA renal scan in setting of administered ACEI?
|
Renal artery stenosis.
|
|
|
What is the rescue drug for adverse effects of Dipyridamole (persantine?)
|
Aminophylline
|
|
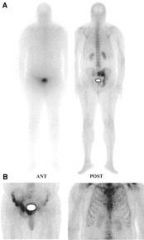
Name this artifact. Cause?
|
Off peak artifact (anterior only). Wrong photopeak selected for gamma camera.
|
|
|
What flood sources are commonly used for nuc med QC and why?
|
Cobalt-67. Long half-life (270 days), similar keV to tec (144 keV).
Also use a Tc flood where Tc is dissolved in a liquid. |
|
|
What is expected with "center of rotation" artifact?
|
Gross blurring of the image. Not often seen now due to advances in tube technology and computer correction.
|
|
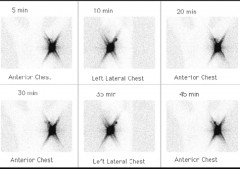
Name this artifact. Cause?
|
Star artifact. Seen when a source yields photons of such high energy that they blow through the collimator. Ex. I-131 post ablation.
|
|
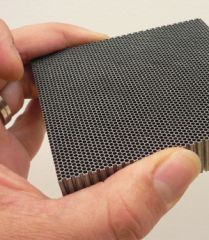
What is this?
|
Collimator.
|
|
|
Why pretreat with phenobarbital when conducting neonatal HIDA?
|
To increase biliary secretion by stimulating hepatic enzymes, thus decreasing false positives for biliary atresia.
|
|
|
Differentiation between neonatal hepatitis and biliary atresia on HIDA?
|
In neonatal hepatitis, uptake may be delayed but bowel activity should be seen at 24 hours. No bowel activity seen with biliary atresia.
|
|
|
What are the three phases of a 3-phase bone scan and at what time intervals are images obtained?
|
At injection (flow), 5 minute (blood pool), and 2-4 hours (delayed).
|
|
|
3 common causes of bone scan "superscan"
|
Diffuse metastases, dialysis, renal osteodystrophy
|
|
|
2 causes of poor bone uptake on delayed phase bone scan?
|
Renal failure or vascular insufficiency (inability to clear tracer from soft tissues)
|
|
|
Appearance of Pagets/Fibrous dysplasia on bone scan?
|
Red hot. Most of bone length involved.
|
|
|
Appearance of Reflex sympathetic dystrophy on 3 phase bone scan?
|
Hot on all three phases.
|
|
|
Apperance of AVN/Legg-Calve-Perthes disease on bone scan?
|
Epiphyseal photopenia in early process, hot as healing progresses.
|
|
|
Cause of diffuse liver uptake on bone scan?
|
Usually colloid formation from aluminum excess.
|
|
|
Contiguous foci of uptake in ribs on bone scan more likely to be ______.
|
Post-traumatic. Non-contiguous uptake needs CT to further eval.
|
|
|
How long after chemotherapy should pass before bone scan?
|
6 months. Otherwise may get false positives from healing bone.
|
|
|
What is the evaluation for osteomyelitis after surgery/hardware placement?
|
Bone scan. If positive, get In-111 WBC scan. If negative -> not infection. If positive -> get sulfur colloid scan. Sulfur colloid will either show concordance, in which case uptake is normal marrow, or discordance, in which case it is osteomyelitis.
|
|
|
DDx bone scan hot on flow and blood pool.
|
Cellulitis
|
|
|
DDx bone scan hot on all three phases.
|
Osteomyelitis, RSD, Fracture, Osteoid osteoma (will be hotter centrally), Osteosarcoma
|
|
|
Proper workup for a single solitary focus of uptake in bone scan in a rib?
|
CT (it's likely either fracture, fibrous dysplasia, or neoplastic)
|
|
|
Proper workup for single solitary focus of uptake on bone scan for all locations except rib?
|
Get a plain film. MRI to follow if normal plain film.
|
|
|
Two radiotracers which bind to brain parenchyma in brain death study?
|
HMPAO-Tc99m (Ceretec), ECD-Tc99m (Neurolyte)
|
|
|
Main purpose of using collimation in nuclear medicine?
|
To determine the geometric field of view (ie only allowing gamma rays from within the region of interest). Blocks scatter as a secondary purpose.
|
|
|
What isopes require high energy collimator? (2)
|
I-131, F-18
|
|
|
Purpose of Radionuclide cystography (RNC)?
|
To evaluate for reflux in a known refluxer. Less anatomic detail so not used for initial eval (although RadPrimer suggests that it is used for initial eval in girls as less anatomic detail needed?). Less radiation than VCUG.
|
|
|
Indication for DMSA-Tc99m Renal Scan?
|
DMSA Is a cortical agent so this is done to detect acute pyelonephritis and scarring.
|
|
|
How often is constancy checked on dose calibrator and what is used?
|
Daily. Use Cs-137. Half life of 30 years.
|
|
|
How often is linearity checked on dose calibrator?
|
Quarterly
|
|
|
How often is accuracy checked on dose calibrator?
|
Annually
|
|
|
How often is Geometry checked on dose calibrator?
|
At installation, after repair, or moving instrument.
|
|
|
What QC must be performed daily on geiger counter?
|
Battery check and sealed source check.
|
|
|
What daily QC is performed WITH geiger counter?
|
Survey of hot lab and body of nuc med techs.
|
|
|
How does a well counter differ from ionization chamber (including dose calibrators and geiger counters)?
|
Uses a NaI crystal probe instead of gas chamber. Measures radioactivity in counts per minute. Used for swipe test.
|
|
|
What is the annual dose limit for a radiation worker?
|
50 mSv
|
|
|
What is the dose limit for a pregnant radiation worker?
|
5 mSv
|
|
|
What is the annual dose limit for a nonradiation worker?
|
1 mSv
|
|
|
What is the estimated background dose per year?
|
3 mSv
|
|
|
Are gamma cameras capable of energy discrimination?
|
Yes. This is why energy peaking is necessary.
|
|
|
Appearance of focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) on sulfur colloid Tc99m exam?
|
Hot (contains both kupfer cells and hepatocytes)
|
|
|
Appearance of Fibrolamellar HCC, adenoma, and hemangioma on Sulfur colloid Tc99m exam?
|
Cold.
|
|
|
How and how often is uniformity checked on a gamma camera?
|
Extrinsic (with collimator in place)- Daily. Extrinsic can be checked with Cobalt 57 sheet for flood source but Cobalt is too hot without collimator. May use a Tc flood or point source which is farther away than 3x the detector diameter. Should not see individual PMTs or lines.
|
|
|
How and how often is spatial resolution checked on a gamma camera?
|
Weekly. Checked with bar line phantom placed on top of uniform flood source (Tc or Co). Can usually see 3 of the 4 bar lines.
|
|
|
What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic uniformity?
|
Intrinsic checked without collimator. Extrinsic checked with collimator in place.
|
|
|
What is used for SPECT QC?
|
Jaszczak phantom.
|
|
|
What is required to make positron emitting isotopes?
|
Cyclotron.
|
|
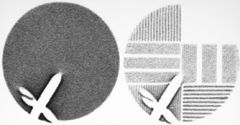
What caused this?
|
Cracked crystal.
|
|
|
Difference between solid and liquid meals in a Tc99m-sulfur colloid gastric emptying exam?
|
Solid more sensitive to gastroparesis and follows linear kinetics. Liquid follows exponential kinetics.
|
|
|
When is imaging obtained for Gallium-67 citrate exam?
|
At 48 hours.
|
|
|
For which three indications is Gallium-67 superior to Indium-111?
|
1) Spine Discitis/Osteomyelitis.
2) Pulmonary inflammation. 3) Splenic abscess. |
|
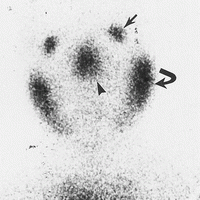
What is this sign and where is it seen?
|
Panda sign. Sarcoid.
|
|
|
When is imaging obtained for a HIDA exam?
|
Every minute for 60 minutes, then at 4 hours.
|
|
|
What is given to measure gallbladder ejection fraction and what is normal?
|
CCK (or analog Sincalide) given over 3 minutes. Normal EF >35%.
|
|
|
What is the procedure for pretreatment in a patient for HIDA scan who has been fasting >24 hours?
|
Give CCK (0.02ug/kg over 3 minutes), wait 30 minutes, perform HIDA.
|
|
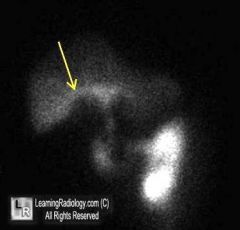
What is this imaging sign and where is it seen?
|
Rim sign, Acute cholecystitis.
|
|
|
For what three indications is Indium-DTPA used?
|
CSF Leak, Cisternography (NPH), and Ventriculostomy shunt testing.
|
|
|
Persistence of Indium DTPA in lateral ventricles rather than cerebral convexities at 24 hours is postive for ____.
|
Normal pressure hydrocephalus.
|
|
|
When is imaging obtained for an Indium-111 WBC Scan?
|
24 hours.
|
|
|
How to differentiate Indium 111 wbc scan from gallium?
|
Spleen hotter than liver with Indium 111. No bowel activity with Indium 111.
|
|
|
Gallium or Indium better for Inflammatory bowel disease or bowel infection?
|
Indium-111 is better because it does not normally show bowel uptake.
|
|
|
How long must pass after CT with iodinated contrast before Iodine imaging or ablation attempted?
|
8 weeks.
|
|
|
When is imaging performed for Iodine-123 Thyroid scan?
|
24 hours.
|
|
|
3 methods to determine when safe to release patient s/p I-131 therapy?
|
1) Administered activity of <33mCi.
2) Dose rate of I-131 at 1 meter from patient <7 mrem/hr 3) NRC "release equation" shows public dose is less than 0.5 rem (5 mSv) |
|
|
General I-131 doses for:
1) Graves disease? 2) Multinodular goiter? 3) Cancer? |
1) 10 mCi
2) 20 mCi 3) 75-100 mCi if low risk of recurrence. 100-200 mCi if high risk of recurrence. |
|
|
Where is uptake normally seen on a treatment I-131 scan?
|
Stomach, colon, salivary glands, liver (very faint).
|
|
|
Recommendations for pregnancy/nursing for patients after I-131?
|
Wait at least 6 months before becoming pregnant. Stop all breastfeeding for current child (i.e. don't restart). Subsequent children are okay.
|
|
|
In what 4 settings should the dose of MAA be decreased from 300,000 particles to 100,000 for a VQ scan?
|
1) Pulmonary arterial hypertension.
2) Pediatric. 3) Pregnancy. 4) R to L shunt. |
|
|
What are the three phases of quantification for nuc med renal scan with MAG3 or DTPA?
What is the cutoff for normal split function? What are the normal limits for washout? |
1) Flow curves- will be delayed for all pathology except ATN.
2) Split function- ROI around each kidney and count until tracer in collecting system. Greater than 40/60 discrepency is abnormal. 3) Washout- Post Lasix clearance. <10 min normal. 10-20 min borderline. >20 min abnormal (i.e. obstruction). |
|
|
What is implied by decreased bilateral uptake on DTPA renal scan after captopril administration?
|
Bilateral renal artery stenosis or patient hypotension.
|
|
|
What is meant by "tubular back diffusion" in the setting of DTPA renal scan?
|
Finding seen in post-transplant ATN where abnormal kidney will light up and fade away without urinary excretion.
|
|
|
What are the five marrow distributing radiopharmaceuticals?
|
1) Tc99m sulfur colloid
2) Tc99m-MDP 3) Gallium-67 4) F18-FDG 5) Indium-111 WBC |
|
|
What is given before MIBG exam and why?
|
Lugols solution (KI) to saturate, and thus protect, the thyroid in the setting of radioactive iodine.
|
|
|
What are four pathologies that can be seen on MIBG exam?
|
1) Pheochromocytoma.
2) Neuroblastoma. 3) Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor. 4) Medullary thyroid cancer. |
|
|
How does Molybdenum become Tc99m?
|
Beta minus decay in a generator.
|
|
|
How much Tc99m is in each morning elution from the Moly generator?
|
3000 mCi
|
|
|
At what age must the Tc99m elution be discarded (i.e. no longer allowed for patient use)?
|
12 hours.
|
|
|
NRC guidelines on how much Molybdenum activity is allowed per Tc99m elution?
|
0.15 uCi of Mo per 1 mCi of Tc99m. (Thin lead is placed around vial in dose calibrator to block lower energy Tc99m gammas)
|
|
|
Where is chromatography used?
|
After injection kit of Tc99m is made. This measures the fraction of unbound free Tc99m relative to Hydrolzyed Tc99m.
|
|
|
For what is MUGA Tc99m RBC scan performed?
|
Assess EF. (Multiple Gated Acquisitions)
|
|
|
How is thallium heart study performed?
|
Imaged immediately after stress portion. Wait 3 hours, image again for redistribution phase. If there was reversible defect, it will now fill-in.
|
|
|
Septum hotter than lateral wall on Myocardial perfusion imaging? 2 diagnoses.
|
Hypertension or HOCM.
|
|
|
What happens on myocardial perfusion imaging with LBBB?
|
Ficticious septal reversible tracer defect and paradoxical septal wall motion. In this case, don't do exercise stress (increased risk of sudden death).
|
|
|
If gastric activity decreases quality of myocardial perfusion imaging, what can you do?
|
Give patient a glass of water and reimage.
|
|
|
What is the significant of transient ischemic dilation (usually seen on thallium exam)?
|
Indicates triple vessel disease and adverse outcomes even without significant perfusion defects.
|
|
|
What is the cause of artifactual anterior perfusion defect on myocardial perfusion imaging? Inferior?
|
Breast tissue for anterior, obesity/GI uptake for inferior.
|
|
|
What is the rescue drug for adverse reaction to dobutamine?
|
metoprolol.
|
|
|
Three contraindications to using adenosine or dipyridamole (persantine) for myocardial stress?
|
1) Heart block. (so use dobutamine)
2) Hypotension (may worsen) 3) Severe asthma (causes bronchospasm) |
|
|
Two contraindications to Dobutamine myocardial stess?
|
1) Aortic stenosis.
2) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. |
|
|
Which walls of the left ventricle are normally larger (helps with orientation)?
|
The lateral and inferior walls.
|
|
|
To within what percentage must the administered dose match the prescribed dose by NRC guidelines?
|
10%
|
|
|
Approximately how many half-lives are required before radioactive trash can be moved to general trash?
|
Usually 10. Regardless, must demonstrate no activity above background.
|
|
|
How to identify an octreotide scan?
|
It is the only one with hot kidneys and spleen.
|
|
|
What tumors are imaged with Octreotide In-111?
|
Anything with somatostatin receptors. Better than MIBG for Carcinoid. Also see pancreatic neuroendocrine, neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma, medullary thyroid cancer. (Also small cell carcinoma and meningioma apparently).
|
|
|
Three uses of Pertechnetate scan?
|
Meckels, Thyroid, Testicles.
|
|
|
Ddx of a positive Meckel's scan?
|
Meckel diverticulum or Duplication cyst with gastric mucosa.
|
|
|
If all 4 parathyroid glands are hot on imaging, what is the likely diagnosis?
|
Parathyroid hyperplasia.
|
|
|
How is imaging for parathyroid performed?
|
Two ways:
1) Sestimibi Tc99m- localizes to thyroid and parathyroid but washes out from thyroid, leaving only parathyroid activity. 2) Pertechnetate and Thallium- Thallium localizes to thyroid and parathyroid. Pertechnetate localizes to thyroid only. Subtraction images yield only parathyroid activity. |
|
|
For how long should patients fast before PET scan? What is the target glucose before this study?
|
Fasting for 4 hours. Target glucose <200.
|
|
|
What is the equation for calculation of SUV on PET?
|
SUV(t) = c (t) / (injected activity (t)/body weight) where c is the measured radioactivity concentration in the tissues at time "t"
|
|
|
Parietotemporal hypometabolism on brain PET suggests what?
|
Alzheimers
|
|
|
Frontotemporal hypometabolism on brain PET suggests what?
|
Pick's disease.
|
|
|
What tracers are used for intra-ictal nuc med imaging?
|
HMPAO or ECD.
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a seizure focus on an inter-ictal study?
|
It is COLD
|
|
|
What type of labeling is needed for Tc99m RBC bleeding scan?
|
In vitro for best results
|
|
|
What bleeding rates are detectable on Tc99m RBC scan vs. Angio?
|
0.1 mL/min for nuc med scan for 1 mL/min for angio.
|
|
|
What and how much tracer is used for Sentinel lymph node scintigraphy?
|
1 mCi of Tc99m Sulfur colloid
|
|
|
How to differentiate shin splints vs. stress fracture on bone scan?
|
Shin splints positive on delayed only (linear uptake).
Stress fracture positive on all three phases and will localize. |
|
|
For what is heat damaged RBC scan performed?
|
To eval for splenosis, accessory spleens
|
|
|
Should the liver or spleen be hotter on Tc 99m Sulfur colloid exam? What if it's not?
|
Liver should be hotter. If spleen hotter, may be cirrhosis.
|
|
|
What is thyrogen?
|
Synthetic TSH. Can be given prior to I-131 exam instead of thyroid withdrawal.
|
|
|
What two subtypes of thyroid cancer tend not to show up on I-131 exams?
|
Medullary and Anaplastic.
|
|
|
What is normal Radioiodine uptake (RAIU)?
|
9-31%
|
|
|
"Clumping" of MAA on perfusion portion of V/Q scan is caused by what?
|
Blood being aspirated into the syringe.
|
|
|
Brain activity seen on a V/Q scan implies what?
|
A right to left shunt.
|
|
|
What four items are always included on a written directive?
|
1) Patient name.
2) Radioactive drug given. 3) Dosage. 4) Route of administration. |
|
|
What is considered a major spill of the following?
1) Tc99m 2) Thallium 3) Gallium 4) Indium 5) I-131 6) I-123 |
1) >100 mCi
2) >100 mCi 3) > 10 mCi 4) > 10 mCi 5) > 1 mCi 6) > 10 mCi |
|

What is this?
|
Xenon ventilation system.
|
|

What is this?
|
Technetium generator.
|
|
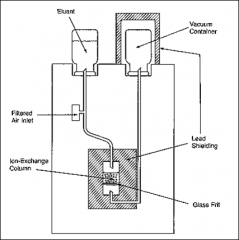
What is this?
|
Diagram of technetium generator.
|
|

Is this proper?
|
Yes, technetium generators are stored in leaded containers when not in use.
|
|
|
What is the maximum permissible amount of Aluminum that can be in the Technetium collection vial?
|
10 ug/mL. Will show liver uptake on exam if administered.
|
|
|
Where should a ring dosimeter be worn?
|
Palmar side of index finger.
|
|
|
Where should a whole body radiation badge be worn?
|
Near the collar.
|
|
|
How many times does the radiopharmaceutical appear on a written directive?
|
Twice. Once for the order and once for the amount actually given.
|
|
|
Which radioisotope causes the biggest travel headaches?
|
I-131, which may be detectable by radiation sensitive equipment for up to 3 months. So patients should get a letter for travel with 24 hour contact information.
|
|
|
What are the steps in the event of a minor spill?
|
1) Notify persons in the area that a spill has occurred
2) Cover the spill with paper towels 3) Wearing protective clothing, gloves, lab coat, clean up the spill with paper towels 4) Place the paper towels clean side out into a plastic bag 5) Place the bag into a radioactive waste container 6) Survey the area with a Geiger Muller counter 7) Report the incident to the Radiation Safety Officer |
|
|
What three radioisotopes will place you into the major spill category at patient doses?
|
I-131, In-111, Ga-67
|
|
|
What are the steps in the event of a major spill?
|
NOTIFY RSO IMMEDIATELY. Then:
1) Notify all individuals in the vicinity and clear the area 2) Prevent the spread of the spill with paper towels 3) Shield the source if possible, use lead bricks or the thick acrylic plastic shields 4) Close access to the area 5) Decontaminate personnel by removing contaminated clothing and washing contaminated skin |
|
|
What does a white, level I radioactive sticker indicate?
|
< 0.5 mrem/hr max on surface
|
|
|
What does a yellow, level III radioactive sticker indicate?
|
50-200 mrem/hr on surface or 1-10 mrem/hr at 1 meter.
|
|
|
How long from receipt of package do you have to inspect a radioactive delivery?
|
3 hours if received during normal working hours. Next day if not.
|
|
|
What number of counts per minute on the swipe test should prompt you to contact RSO?
|
6600
|
|

What is this used for?
|
Fume hood- used for mixing volatile radiopharmaceuticals. Look for piece of paper hanging down. If on, paper should be up.
|
|
|
Who needs to wear a radiation badge?
|
Anyone expected to receive 1/10 of the annual occupational exposure limit of 5 rem (50 mSv)
|
|
|
What is the institutional limit for radioactive waste through the "hot" sink?
|
1 Ci per year
|
|
|
What happens to all radioactive waste with half-life greater than 120 days?
|
Must be transferred to RSO, cannot be discarded per the usual method (10 half lives, geiger, trash)
|
|
|
What are the three terms of NRC Medical Events?
|
1) Patient receives >5 rem whole body or 50 rem to an organ, tissue, or skin from administering the wrong pharmaceutical, wrong route of administration, to the wrong patient, or wrong mode of treatment.
2) Same as above but as the result of deviation from the prescribed dose. 3) Any event resulting in unintended permanent functional damage to an organ or physiological system as determined by a physician. |
|
|
How long does one have to notify the NRC of a Medical Event by phone? And with written report?
|
24 hours for call, 15 days for report.
|
|
|
By Federal and State law, all doses must be within ____ of the prescribed dose.
|
20%
|
|
|
What is the definition of a "controlled area", "restricted area"? "radiation area"?
|
Controlled area is outside restricted area but within site boundary. Limit of 1mSv per year.
Restricted area is that where a dose rate >2 mrem/hr or >1 mSv per year is expected. Radiation area is where a dose rate >5 mrem/hr is expected- conspicious posting required. |
|
|
How long should breast feeding cease after Technetium? Thallium? Gallium? Indium?
|
24 hours for Tc99m
1 week for the others. |
|
|
How often must an employer inform employees of dosimetry results?
|
At least annually.
|
|
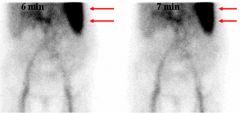
Name that study.
|
Tagged RBC GI Bleeding scan. Tc99m-RBC.
|
|
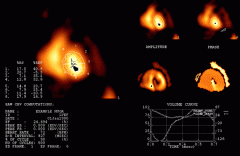
Name that study.
|
MUGA. Tc99m-RBC.
|
|

Name that study.
|
HIDA scan. Tc99m-HIDA (or newer DISIDA)
|
|
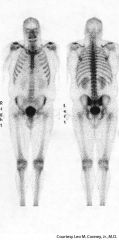
Name that study.
|
Bone scan. Tc99m-MDP
|
|
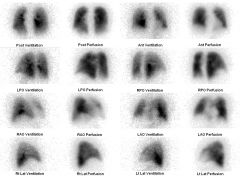
Name that study.
|
V/Q scan. Tc99m-DTPA and Tc99m-MAA
|
|
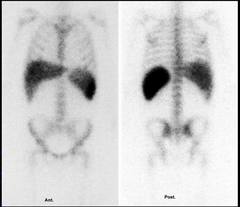
Name that study.
|
Indium-WBC scan. Indium-111 WBC.
|
|
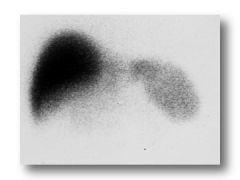
Name that study.
|
Sulfur-Colloid LIver/Spleen. May be shown as whole body. Liver should be hotter than spleen (In Indium, spleen is hotter).
|
|
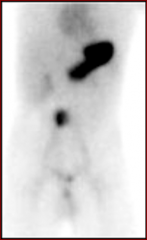
Name that study.
|
Meckel's scan. Pertechnetate.
|
|
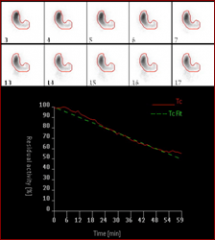
Name that study.
|
Gastric emptying study. Sulfur Colloid.
|
|

Name that study.
|
Cystogram. Sulfur Colloid.
|
|
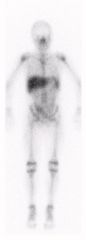
Name that study.
|
Gallium-67 Citrate
|
|
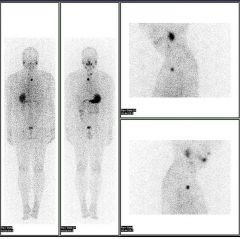
Name that study.
|
Whole body I-123. (After thyroidectomy)
|
|
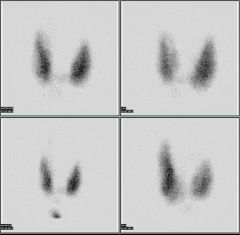
Name that study.
|
I-123 Thyroid scan.
|
|
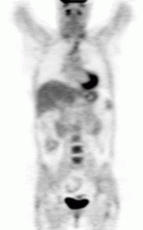
Name that study.
|
PET. F-18 FDG.
|
|

Name that study.
|
Cisternogram. Indium-111 DTPA
|
|
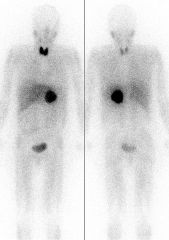
Name that study.
|
I-123 MIBG. Note positive for pheo.
|
|
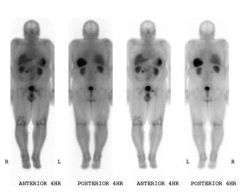
Name that study.
|
Octreotide. In-111 Octreoscan.
|
|
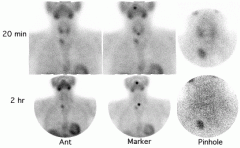
Name that study.
|
Parathyroid scan with sestamibi (washout)
|
|
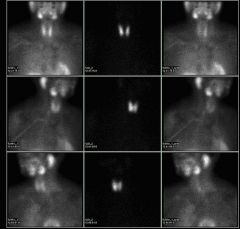
Name that study.
|
Parathyroid subtraction scan. This one is with Tc99m-sestamibi and Iodine-123. Can also be done with Thallium and Pertechnetate.
|
|
|
What is indicated by pulmonary uptake (lung/heart ratio > 0.5) on a TI-201 myocardial perfusion study?
|
Left ventricular dysfunction (? diastolic)
|
|
|
What is the ideal energy for gamma cameras?
|
100-200 keV
|
|
|
Indium-111 Energy? Half-life?
|
172, 245 keV, 67 hours.
|
|
|
Which isotope undergoes gamma decay (aka isomeric transition?)
|
Tc-99m
|
|
|
Which isotopes undergo electron capture (6)?
|
I-123, Ga-67, Th-201, In-111, Xe-127, Co-57
|
|
|
Which isotope undergoes positron emission (B+ decay)?
|
F-18
|
|
|
Which isotopes undergo B- decay?
|
Moly-99, I-131, Xe-133
|
|
|
What is the purpose of stannous ion addition to the Tc-99m eluate? What two chelates don't use stannous addition?
|
Tc-99m must be reduced from valence state of 7+ to 4+ in order to chelate. Sulfur Colloid and DMSA don't use this.
|
|
|
How much Aluminum is allowed in Tc-99m eluate?
|
No more than 10 ug Al per 1 mL Tc-99m eluate.
|
|
|
What three common isotopes are produced in a nuclear reactor?
|
Mo-99, I-131, Xe-133
|
|
|
For how long should breastfeeding cease after I-123?
|
2-3 days.
|
|
|
For how long should breastfeeding cease after Tc-99m?
|
12-24 hours.
|
|
|
For how long should breastfeeding cease after Ga-67?
|
1 month
|
|
|
For how long should breastfeeding cease after Tl-201?
|
2 weeks
|
|
|
What are the four types of collimators? Which is the most commonly used?
|
Pinhole, Parallel-hole, Convergin, Diverging. Parallel-hole most commonly used.
|
|
|
What isotopes require medium energy collimation (400 keV)? (3)
|
Gallium, In-111, Kr-81
|
|
|
What isotope requires low energy collimation?
|
Tc-99m
|
|
|
What two Gamma Camera QC measures are checked monthly?
|
Calibration with a flood source. Center of rotation with Tc point source.
|
|
|
How and how often is SPECT uniformity checked?
|
Quarterly. Checked with lucite cylindrical phantom (Jazczak phantom)
|
|
|
How and how often is SPECT resolution checked?
|
Quarterly. Checked with Tc line and planar phantom.
|
|
|
What four Gamma camera QC items are checked annually?
|
Collimator performance, energy resolution, count rate capability, sensitivity
|
|
|
How often is "peaking the camera" performed?
|
For every patient.
|
|
|
What daily QC is performed on PET camera?
|
"Blank scan" with 511 keV source.
|
|
|
What is the mode of uptake of Thallium-201 into myocardial cells?
|
Active transport via the Na/K pump.
|
|
|
What is the mode of uptake of Tc-99m sestamibi into myocardial cells?
|
By mitochondria.
|
|
|
What are the benefits of tetrofosmin/sestamibi over Thallium for MPI?
|
Higher photopeak for better (higher contrast) imaging and short half-life (6 hours vs. 73 hours) for better radiation safety.
|
|
|
What is the rationale for PET myocardial viability imaging?
|
Ischemic myocardium switches from fatty acid metabolism to preferential glucose metabolism. Glucose load is given before exam to optimize myocardial glucose metabolism. F-18 FDG given in conjunction with myocardial perfusion agent.
|
|
|
What are the findings on PET myocardial viability for Normal, Stunned, Hibernating, or Scarred myocardium?
|

|
|
|
What is the marker for adequate exercise stress?
|
>85% maximum age predicted HR (220-age)
|
|
|
What are the six triggers to stop exercise stress testing?
|
Systolic BP >200
Diastolic BP >120 HR >85% predicted ST depression >3mm Atrial tachycardia/fibrillation Syncope, pallor, blurred vision |
|
|
How does Adenosine work?
|
A2 receptor agonist causes vasodilation and 3-4 fold myocardial blood flow increase.
|
|
|
How does Dipyridamole (Persantine) work?
|
Blocks adenosine deaminase. So similar contraindications to Adenosine.
|
|
|
How does Regadenoson (Lexiscan) work?
|
A2A adenosine receptor agonist.
|
|
|
How does Dobutamine work?
|
Beta 1 and 2 receptor stimulator (inotropic). Causes increased HR, BP, contractility. Reversed by beta-blocker (Esmolol)
|
|
|
Which mets may be missed on bone scan?
|
Lytic (aggressive, no chance for osteoblastic activity)
|
|
|
Tram track cortical uptake in the lower extremities on whole body bone scan suggests what?
|
HPO, Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy
|
|
|
3 phase hot with periarticular uptake on delayed images on bone scan is class for what?
|
RSD (Complex Regional Pain Syndrome)
|
|
|
What is the differential for increased uptake (i.e. greater than 30) on RAIU scan? (4)
|
Graves disease, Multinodular goiter, Single autonomous functioning nodule, chronic thyroiditis
|
|
|
What is the differential for decreased (i.e. less than 10) on RAIU scan? (4)
|
Subacute thyroiditis, Iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis, factitious thyrotoxicosis, amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis.
|
|
|
What is the proper workup of a thyroid nodule with a normal TSH?
|
Biopsy
|
|
|
What is the proper workup of a thyroid nodule with low TSH?
|
Thyroid scan
|
|
|
What separates level II, III, and IV cervical lymph nodes?
|
Hyoid bone separates II, III
Cricoid cartilage separates III, IV |
|
|
What is the dose calculation formula for iodide therapy?
|
Required dose (uCI) = (gland weight in g)(100-180 uCi/g dose)/k(24hr%RAIU)(effective T 1/2)
|
|
|
Below what level of thyroglobulin is post-surgical I-131 tx not indicated?
|
2
|
|
|
What is the management for a patient post negative whole body I-123 dx scan post-surgery/I-131 tx with elevated Tg?
|
Treat once with I-131 (100-150 mCi) and image the treatment dose. Also could do I-124 PET.
|
|
|
Is V/Q safe in pregnancy?
|
Yes. Tc-99m does not cross the placenta.
|
|
|
Over what time period is CCK infused to determined gallbladder EF? What is normal gallbladder EF?
|
30 minutes. EF > 35%
|
|
|
What sign on liver/spleen sulfur colloid scan is associated with SVC Syndrome?
|
"Hot quadrate" sign. Uptake in the quadrate lobe, anterior/medial segment of LHL.
|
|
|
What is the classic finding in Budd-Chiari syndrome on liver/spleen sulfur colloid scan?
|
Greater uptake in caudate lobe.
|
|
|
What is the typical finding of parathyroid hyperplasia on sestamibi parathyroid scan?
|
Negative.
|
|
|
What is the "lambda sign" on gallium scan?
|
Abnormal uptake in the thoracic/mediastinal nodes in sarcoid.
|
|
|
How is MAG3 cleared from kidneys?
|
Tubular secretion.
|
|
|
What is the differential for normal uptake with prolonged nephrogram on a MAG3 renal scan? (4)
|
1. Renal artery stenosis.
2. Acute tubular necrosis. 3. Obstruction. 4. Cyclosporine toxicity. |
|
|
What is the appearance of an infarct (not torsion) on testicular scan?
|
Cold region of testis with rim of uptake.
|
|
|
Which exam is superior to evaluate for vascular graft infection?
|
Indium-111 WBC
|
|
|
What drug increases sensitivity on Meckel's scan and how does it work?
|
Cimetidine. Blocks pertechnetate release from the gastric mucosa.
|
|
|
Why is the first does of Y-90 Zevalin bound to Indium-111?
|
To evaluate biodistribution and ensure that no excess amounts go to liver, bone marrow, etc. If In-111 scan is okay, second does of Y-90 Zevalin is given.
|
|
|
How to proceed in Y-90 Zevalin therapy if platelets less than 100,000? 100,000 to 149,000?
|
Don't give if platelets less than 100,000. Cut dose to 0.3 mCi/kg for second scenario.
|
|
|
What line of cells does Zevalin target?
|
B-cells.
|
|
|
What is considered a positive CSF leak study?
|
Nasal pledget:serum ration > 1.5.
|
|
|
What may be seen on HMPAO imaging in Huntington's disease?
|
Decreased uptake in caudate and putamen.
|
|
|
What causes the "truncation artifact" on PET?
|
Rim of high attenuation due to overestimated attenuation correction from larger FOV on PET than CT.
|
|
|
What causes the "gloved hand" appearance on bone scan?
|
Arterial injection.
|
|
|
To what and how does Thallium-201 decay inside the body? What is the energy of the resultant x-ray?
|
Decays to Hg-201 via electron capture. 70-80 keV.
|
|
|
What three bone mets are classically cold on bone scan?
|
Myeloma, Thyroid, Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
What three organs will have uptake on bone scan in the setting of severe hypercalcemia/metastatic calcification?
|
Stomach, kidneys, lung
|
|
|
What is considered to be normal gastric emptying?
|
Less than 10% tracer retention at 4 hours.
|
|
|
What two cancer types may produce false negative Tc99m MDP bone scans?
|
Renal cell carcinoma and multiple myeloma. anything lytic-thyroid.
|
|
|
Half-life, mechanism, and average soft tissue penetration of Yttrium-90?
|
Yttrium-90 is a beta emitter with a half life of 64.2 hours and average soft tissue penetration of 2.5 mm.
|
|
|
How to calculate ejection fraction on a MUGA scan?
|
(ED-ES)/(ED-background)
|
|
|
What type of purity relates to differences in size of particles (i.e. MAA)?
|
Physical purity
|
|
|
Testing for Molybdenum breakthrough in a technecium eluant tests for what type of purity?
|
Radionuclide purity
|
|
|
Testing bound versus unbound fraction of Tc (i.e. with chromatography) tests what type of purity?
|
Radiochemical purity.
|
|
|
Testing for alumina in the Tc tests for what type of purity?
|
Chemical purity
|

