![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the purpose of the integumentory system?
|
1)Protect
2)Fluid balance 3)Absorption 4)Synthesis of Vitamin D 5)Sensation/communication 6)with external environment 7)Thermoregulation 8)Immunity 9)Excretion |
|
|
What is the layers of the skin?
|
1) Epidermis
2) Dermis 3) Subcutaneous |
|
|
What does the dermis layer consist of?
|
Mucopolysaccharide
Proteins Collagen Elastic Fibers Oil Production |
|

What this?
|
Dermis Layer of the skin
|
|
|
What is the purpose of apocrine glands and where are they located?
|
*Sweat Glands of your body
*Axilla (underarm), *Perianal (near the anal area) *Areole, (nipple) *Periumbilical (around the belly button), *Genital area, *External ear canal, *Eyelids |
|

What is this?
|
Inflamed aprocrine gland due to Overproduction of sweet
|
|
|
What is the purpose of subcutaneous tissue?
|
Fatty Connective Tissue
Protect underlying structure from physical trauma |
|
|
What is the Ecrine glands?
|
*Eccrine: glands are sweet glands
|
|
|
What is the Melnaocytes for?
|
Pronuce pigment
|
|
|
Where is the hair folicles located?
|
*Majority of hair folicles are located in the dermal layer of skin
|
|
|
What is goosebumps from?
|
*Goosbubs due to contraction of rector pili muscle
|
|
|
What is nails made of?
|
Made of a tough protein called keratin
|
|
|
What is the purpose of nails?
|
protect distal portions of the digits and aid in picking up objects
|
|
|
Are there any nerve endings in nails?
|
NONE
|
|
|
What does cyanosis of the skin meen?
|
oxygen saturation less than 80% (really poor prefusion within the lungs)
|
|
|
What is central cyanosis?
|
Change in skin color and the mucous membranes, cause lips, fingers, toes to look blue
|
|
|
What is Peripheral cyanosis?
|
(Related to cardiac output)
Change in color in lips (Bluish hue) Change in color in nail beds Overal bluish hue |
|
|
What is finger clubing?
|
*Deficient of oxygen for long term (Chronic lack of oxygen: Hypoxia)
*The normal angle is 160 degrees *Chronic tissue hypoxia result in an increase in agle *Tips normally thickened, sometimes discolored nailes *Normally people w/ emphysema, lung cancer |
|
|
Ghat is some manifistations in the skin due to impaired digestive system?
|
1)Jaundice
2)Xanthomas 3)Papules |
|

What is this
|
Joundice of the skin
|
|

What is this, due to what?
|
Xanthoma, due to digestive impairment.
|
|

What is this and causes it?
|
due to digestive impairment to secrete toxins
|
|

What is this?
|
Macule
Flat Larger, up to 10 cm in diameter Normally benign |
|

What is this?
|
1) Compound Nevi (Skin mole)
2) Discoloured acumelation of nevis cells on the epidermis 3) Could eventually be cancerous 4) Look at color (are there changes in color) 5) Size 6) Edges (regular/iregular) |
|

What is this extreme example of?
|
Necrosis
|
|

What is this?
|
Ecchymosis
Bruises Blood vesels under the skin rupture |
|

What is this?
|
Hematoma
*Fluid filed *Collectio of blood outside the vesel *Sometimes need surgeon lanse it w/ a scalple to releive some of the presure *Describe size *Warm or cold *Does it deter range of motion |
|

What is this?
|
Furuncle
*An infected perifolicle *Has a white head that may meen a accumelation of puss that there may be a staph infection *Make sure the client’s tempereture is normal |
|

What is this?
|
An Abcess
*Larger and deaper than a furruncle *Could have bacteria in it |
|

what is this?
|
Pitting edema
Indentation in the skin Measured on a scale of 1-4 |
|
|
What may increase the skin pigmentation?
|
1)urinary problem: not being able to dicard elements in urine
2)Hypofunction of Adrenal Gland |
|

What is this a example of?
|
Alopecia
|
|

What is this?
|
Lupus Erythematosus
|
|

What is this?
|
Mongolian spots
|
|

What is this?
|
Hemangioma Simplex
|
|

What is this?
|
Milia
Collection of sebum from sweat glands |
|

What is this?
|
Chloasma
|
|

What is this?
|
Linea Nigra
Hormonal skin pigmentation |
|
|
What is Actinic Keratosis?
|
red-tan scaly plaques. in sun exposed skin. premalignant may develop in squamous cell carsinoma
|
|
|
What is Seborrheic Keratoses?
|
Seborrheic Keratoses, sometimes called barnacles, can be dangerous-looking but they are actually benign
|
|
|
What is the tenting of the skin due to?
|
Tenting of the skin is directly related to a person’s fluid balanse
|
|

What is this?
|
Senile Lentigines.. Liver spots which look like hyperpigmented freckles, found on hands and the arms.
|
|

What is this?
|
Cutaneous tag
|
|

What is this
|
Cutaneous horn
Grows long Thick base Suspiceous lesion Surgically removed because it could lead to cancer |
|

What is this?
|
Cherry angioma
|
|
|
What is diorphoresis a indicationof?
|
Diorphoresis
|
|
|
How would one describe lesions?
|
1)Size
2)Shape 3)Color 4)Texture 5)Exudate 6)Tenderness 7)Surface relationship (raised, flat, depressed) 8)Blanching or pulsation of vascular lesions 9)Pattern, configuration, and distribution |
|
|
What are the different patern configurations of lesions?
|
1)Round/oval
2)Discrete (separate and appart) 3)Grouped 4)Confluent (blending of several lesions) 5)Linear 6)Annular/circular 7)Iris (appendiges) 8)Reticular (meshlike) |
|

Hat is this?
|
Cafe au lait : rounder flat, people are born with it
|
|

What type of shape is this rash?
|
Confluent rash: look like fungal infection
|
|
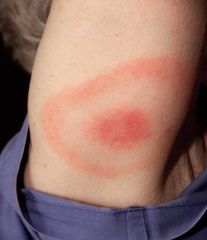
What is the patern of this rash
|
Iris
|
|
|
What are the distrebution of lesions?
|
Diffuse
Scattered Localized Dermatone Hairy areas Extensor/Flexor Surfaces Sun-exposed areas Interiginous (folds) areas |
|

what is this?
|
Petechiae: Deposite of blood under the skin that is less than 0.5cm in diameter
|
|

What is this?
|
Telengiectasis: on older people, or people that have allot of fluid in abdoment
Also in people that have vit b diffitiences |
|

What is this?
|
Spider angioma
|
|

What is this?
|
Mole (nevi)
Any mole should be less than 0,5 cm |
|
|
What is a macule?
|
Solely a color change, flat and circumscribed, less than 1 cm. (freckles, flat nevi, measles, scarlet fever)
|
|
|
What is a Patch?
|
Macule that are larger than 1 cm. (Cafe au lait, chloasma, measles rash)
|
|
|
What is a papule?
|
Something you can feel i.e. solid, elevated, curcuscribed. less than 1cm in diameter. Due to superficial thickening in the epidermis (mole, lichen, planus, molluscum, wart)
|
|
|
What is plaque?
|
Papules coalesce to form surface elevation wider than 1cm
|
|
|
What is a wheal?
|
Superficial, raised, transient, and erythematous; slightly irregular shape due to edema ( fluid held diffusely in the tissue) (mosquito bite
|
|
|
What is a hive?
|
coalesce of wheals to form extensive reation, intensely pruritic
|
|
|
What is carotenemia?
|
yellow orange tinge caused by increased levels of carotene in the blood and skin
|
|
|
What is a vesicle?
|
Elevated cavity containing free fluid, up to 1 cm, clear serum flows if ruptured. (herpes)
|

