![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
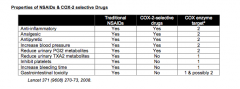
What are the 11 NSAIDS? Which one is COX-2 selective?
1. Which two are the highest in global sales?
2. Which one is formulated with misoprostol, a synthetic PGE1 analog used to prevent gastric or duodenal ulcers
3. For which one is a rectal preparation available?
4. For which one is a parenteral preparation available? |
Acetaminophen Aspirin Diclofenac (1,2) Ibuprofen (1) Indomethacin (3) Ketoprofen Ketorolac (4) Naproxen Piroxicam Sulindac Celecoxib (COX-2 selective) |
|
|
What is the only NSAID that does not ameliorate pain and inflammation through REVERSIBLE inhibition of COX? |
Aspirin |
|

First column (yes or no) Second column (yes or no) Third column (1 or 2) |
|
|
|
What two drugs show more of a COX-2 selectivity? |
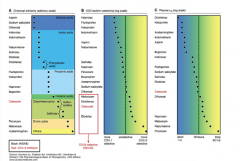
Celecoxib and diclofenac |
|
|
Which NSAID is a salicylic acid? |
Aspirin |
|
|
Which two NSAIDS are acetic acids? |
Sulindac Diclofenac |
|
|
Which three NSAIDS are proprionic acids? |
Ketoprofen Naproxen Ibuprofen |
|
|
Which NSAID is a diarylheterocyclic? |
Celecoxib |
|
|
Which NSAID is an enolic acid? |
Piroxicam |
|
|
Which NSAID has the shortest half-life? Longest? |
Shortest = Diclofenac Longest = Piroxicam |
|
|
Which NSAID carries the highest risk? What is its specificity?
Which NSAID carries the lowest risk? What is its specificity? |
Ketorolac = COX1>>>COX2 Ibuprofen = COX1 = COX2 |
|
|
What is the difference between aspirin and other NSAIDS in terms of COX 1 inhibition? |
COX-1 inhibition => inhibits thromboxane formation Aspirin IRREVERSIBLY does this, so the platelet becomes completely deactivated (must wait for new platelet formation seven days later) |
|
|
Which blood pressure medications do NSAIDS seem to decrease the effect of? |
ACEIs or ARBs |
|
|
Which NSAID shows the highest incidence of liver damage? (in normal clinical doses) |
Sulindac |
|
|
Which NSAID has the highest liver safety profile among NSAIDs? |
Ibuprofen |
|
|
What should you monitor in patients on NSAIDS? |
LFTs |

