![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
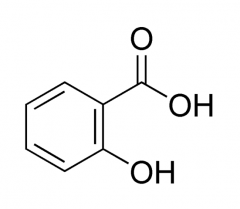
|
SALICYLIC ACID -enhanced via esterification -strong organic acids and readily for salts with alkaline materials -potent anti-inflammatory activity -mild analgesic and antipyretic activity -toxicities: GI irritation, HSR, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and ototoxicity participates in transacetylation reactions in vitro |
|
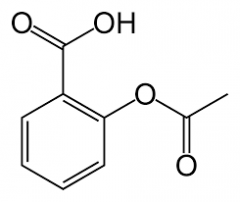
|
ACETYLSALICYLIC ACID -caused by esterification of salicylic acid |
|
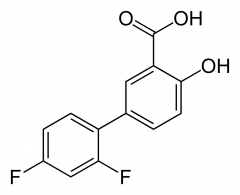
|
DIFLUNISAL -increased lipophilicity -increased potency -competitive inhibitor -longer half life -duration 2-3 hr -not able to pass the BBB as readily |
|
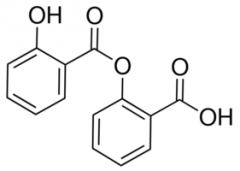
|
SALSALATE -prodrug of salicylic acid |
|
|
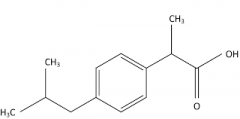
IBUPROFEN -arylacetic acid -strong organic acid (pKa 3-5) which for water soluble salts with alkaline reagents -the alpha-CH3 increases COX inhibitory activity and reduces toxicity -the S (+) enantiomer is the most potent COX inhibitor -metabolism: 2C19 & 2C9 also glucuronidation -half life 2-5 hr |
|
|
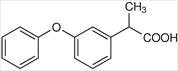
FENOPROFEN -arylacetic acid -strong organic acid (pKa 3-5) which for water soluble salts with alkaline reagents -the alpha-CH3 increases COX inhibitory activity and reduces toxicity -the S (+) enantiomer is the most potent COX inhibitor -half life 2-5 hr |
|
|
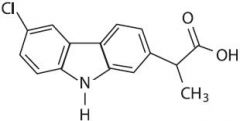
CARPROFEN -arylacetic acid -strong organic acid (pKa 3-5) which for water soluble salts with alkaline reagents -the alpha-CH3 increases COX inhibitory activity and reduces toxicity -the S (+) enantiomer is the most potent COX inhibitor -half life 2-5 hr |
|
|
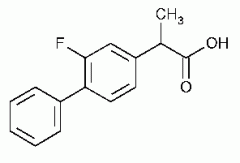
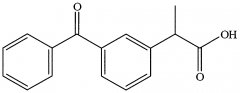
FLURBIPROFEN -arylacetic acid -strong organic acid (pKa 3-5) which for water soluble salts with alkaline reagents -the alpha-CH3 increases COX inhibitory activity and reduces toxicity -the S (+) enantiomer is the most potent COX inhibitor -half life 2-5 hr -favors COX-1 more |
|
|
KETOPROFEN -arylacetic acid -strong organic acid (pKa 3-5) which for water soluble salts with alkaline reagents -the alpha-CH3 increases COX inhibitory activity and reduces toxicity -the S (+) enantiomer is the most potent COX inhibitor -half life 2-5 hr |
|
|
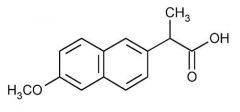
NAPROXEN -arylacetic acid -strong organic acid (pKa 3-5) which for water soluble salts with alkaline reagents -the alpha-CH3 increases COX inhibitory activity and reduces toxicity -the S (+) enantiomer is the most potent COX inhibitor -half life 12-15 hr -not marketed as a racemate -metabolism: 3A4 OOD and glucuronidation |
|
|
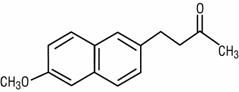
NABUMETONE -prodrug -has a non-acidic ketone functionality which is quickly metabolized to give the naphtylacetic acid derivative which is the active form of the drug -analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties -some COX-2 selectivity -half life 24 hr -most common side effect is GI upset but still less than other drugs |
|
|
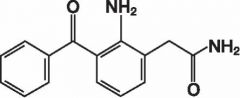
NEPAFENAC -prodrug -amide is hydrolyzed into the active acid -used in controlling pain associated with cataract surgery via eye drops -ADR: loss of visual acuity, pressure in the eye, itching and watering of the eyes, and sensitivity to light |
|
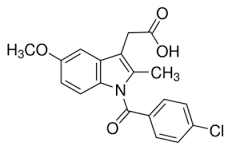
|
INDOMETHACIN -benzoylated indole nitrogen -the CH3 at the 2 position of the indole ring prevents free rotation about the C-N bond and keeps the 2 aromatic rings in the correct relationship for analgesic activity -= selectivity for COX-1 and COX-2 -glucuronidation of carboxyl group increasing the resemblance to 5-HT giving CNS effects -glucuronidation of the resulting phenol -amide is more susceptible to hydrolysis -OOD by 2C9 -half life 4.5 hr |
|
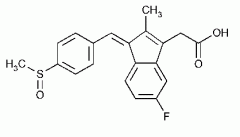
|
SULINDAC -prodrug -reduction to the sulfide which is then capable of inhibiting COX -may be oxidized to the inactive sulfone -all can undergo glucuronidation -not as potent as indomethicin half life 8 hr |
|
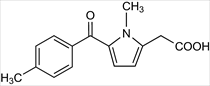
|
TOLMETIN -metabolized by oxidation to a benzylic alcohol initially and eventually to an acid -metabolites are glucuronidation and eliminated -half life 2-7 hr -highly protein bound -ADR: CV risk, GI irritation, use during pregnancy or asthma, and allergic reaction |
|
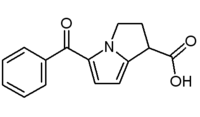
|
KETOROLAC -may produce opioid like analgesia having greater analgesic effects than anti-inflammatory effects but devoid of respiratory depression -more potent than indomethacin -used to treat post-operative pain as an alternative to morphine derivatives -not recommended beyond 5 days due to toxicities and GI effects |
|
|
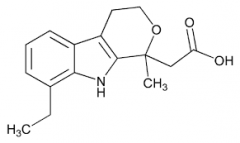
ETODOLAC -very COX-2 selective -rapidly and well absorbed -highly protein bound -decreased GI effects -half life 7 hrs -rash and CNS effects most commonly seen -not as potent |
|
|
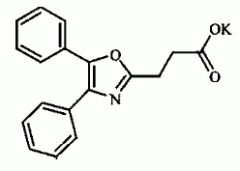
OXAPROZIN -COX-1 selective -half life 51 hr -once a day dosing |
|
|
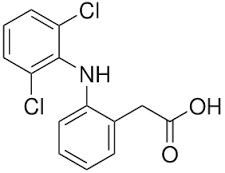
DICLOFENAC -anthranilates -derived from 2-arylacetic acid -very potent -potential liver damage -very COX-2 selective -may also inhibit lipooxygenase (leukotriene synthesis) - slowly absorbed in the GI -half life 2-4 hr -mild analgesic and occasionally for inflammatory diseases -ADR: N/V, diarrhea, ulceration,HA,drowsiness, and hematopoietic activity |
|
|
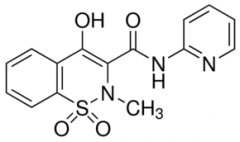
PIROXICAM -acidic (pKa 6.3) -slowly absorbed after oral administration -half life 50 hr -readily glucuronidated and excreted -can form tautomers and resonance structures |
|
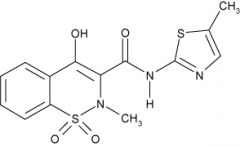
|
MELOXICAM -very COX-2 selective -well absorbed after oral and IM administration -metabolized into 4 inactive metabolites -excreted in the urine and feces -shorter half life 20 hr -once a day dosing |
|
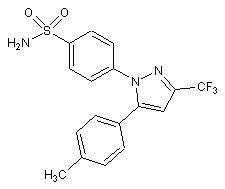
|
CELECOXIB -ionic bonding with Arg 513 -reduced GI effects -hematological effects -increase Na+ and H2O retention -metabolism: oxidation of the benzylic CH3 followed by conversion to the acid then glucuronidation -half life 11 hr -increased MI and stroke risk COX-2 selective |

