![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
15,000 children acquire per year with many with permanent disability
|
HIB
|
|
|
4 million effected each year with nearly 3,000 deaths
|
Measles
|
|
|
most teratagenic virus
|
Rubella
|
|
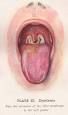
One of the most common causes of death in school aged children killing 10,000 people annually
|
Diptheria
|
|
|
Estimated 150,000 cases per year in infants with thousands of deaths (most death in children under age of 1yr)
|
Pertussis
|
|
|
the state where a sufficient proportion of a population is immune to an infectious disease to make its spread from person to person unlikely
|
Community (herd) immunity
|
|
|
Vaccines are primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention
|
primary
|
|
|
resistance developed in response to an antigen and usually characterized by the presence of an antibody produced by the host (either infecting agent or vaccine)
|
active immunity
|
|
|
Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host, acquired naturally by an infant from mother or artificially by administration of an immune globulin
|
Passive immunity
|
|
|
Onset and Duration of Immunity through immunization (active immunization)
|
Onset usually within 1 month
Duration usually years to life |
|
|
Onset and Duration of Immunity through Passive immunization - Immune Globulin (given post exposure to select infecting agents)
|
Onset - within hours of dose
Duration - usually 6-9 months |
|
|
If anaphylaxis hx with Neomycin avoid which immunizations:
|
IPV, MMR, Varicella
|
|
|
If anaphylaxis hx with Streptomycin, polymyxin B, and neomycin avoid which immunizations:
|
IPV, Vaccinia (smallpox)
|
|
|
If anaphylaxis hx with Bakers Yeast avoid which immunizations:
|
Hepatitis B
|
|
|
If anaphylaxis hx with Gelatin, neomycin avoid which immunizations:
|
Varicella Zoster
|
|
|
If anaphylaxis hx with Gelatin avoid which immunizations:
|
MMR
|
|
|
Deeper wounds are at risk for .... due to its anaerobic properties
|
Tetanus
|
|
|
Which vaccine protects against strep pneumonia
|
pnuovax
|
|
|
max age for flu mist
|
49 y/o
|
|
|
T or F
Immune globulin is a concentrated solution of antibodies derived from pooled donated blood |
True
|
|
|
Live attenuated Vaccines
|
MMR,
Varicella, FluMist, Zostavax, Rotavirus |
|
|
Populations to use caution when giving live attenuated vaccine:
|
pregnancy,
immune suppression, HIV infection with CD4 count <200, infants with severe combined immunodeficiency |

