![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Concrete bridges |
Increased cross section (Inc moment of inertia) Post tensioning (reduces tensile strength & stresses) Clamping (adds stirrups externally) Stitching (overbridging cracks) |
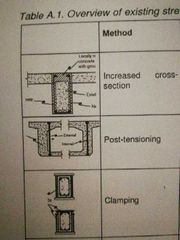
|
|
|
Metallic structures |
Cover plates( welded or bolted); welded to flanges or web; bolted to flanges Addition of new members (ensure carrying capacity) Confinement with reinforced concrete (jack up structure- most applicable to columns) |
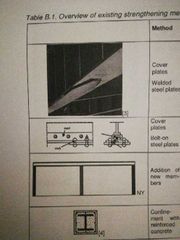
|
|
|
Masonry arch |
Concrete saddle (replace existing fill) Prefabricated liners (structural lining installed beneath arch) Retro- reinforcement (Installation of additional structural reinforcement to the arch to increase structural capacity) |
|
|
|
Fracture mechanics |

|
|
|
|
Methods of fatigue inspection |

|
|
|
|
Dpi |
Liquid applied to the surface which is drawn to the surface through a white powder. |
|
|
|
Methods for fatigue repair |

|
|
|
|
Higher the discount value |
The lesser is the present value of the future cost |
|
|
|
Fatigue in welded details |
Pre existing flaw(microscopic cracks) that can expand Stress conc expected at position of the locally changing geometry High residual stress |
|
|
|
Value you get from the hand out is |
Delta note- fatigue limit |
|
|
|
Frp |
High performance fibre contained in a resin matrix |
|
|
|
Types |
Carbon (CFRP) Aramid (AFRP) Glass (GFRP) |
|
|
|
5 different types of resin |
Phenolics- good fire resistance Polyesters- good general props/odour issues Poly- urethanes-good abrasion prop/poor temp performance Vinyl-esters- good fatigue/odour problems E-poxies- best resistance/ expensive |
|
|
|
Issues with frp |
No codes Relatively new No idea how to examine in the future |
|
|
|
Fibres |
Aramid- toughest Glass - economical Carbon- stiffest |
|
|
|
Why are frps used |
Light/soft/stiff/ durable Aesthetic Good in fire Retrospective strengthening Replacement of components |
|
|
|
AIP DOC |
Drafted by designer and reviewed by TAA (TECHNICAL APPROVAL AUTHORITY) |
|
|
|
AIP KEY COMPONENTS |
Location Structure Loads Analysis Geotech Checks Sig of authority and designer's Technical approval schedule |
|
|
|
Bridge scour analysis |
1. Field inspection 2. Hydraulic analysis 3. Hydrologic analysis 4. Sediment transport 5. Scour analysis 6. Risk estimation |
|
|
|
Scour risk management |
1. Anticipation 2. Assessment 3. Prevention measures 4. Preparation for emergency situation 5. Response 6. Recovery |
|
|
|
Scour risk assessment |
1. Data collection 2. Initial assessment (qualitative data) 3. Detailed assessment (quantitative data) 4. Long term management |
|

