![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
True labour definition |
regular painful contractions with progessive dilation and effacement of the cervix |
|
|
|
Preterm |
20 to 36+6 weeks |
|
|
|
Term |
37 to 41 +6 weeks |
|
|
|
Posterm |
>42 weeks |
|
|
|
Braxton-Hicks |
false labour relieved by rest or sedation (coffee + BZD lol) |
|
|
|
The cervix dialtes ___ in the latent phase to ____ in the active phase |
0-3 cm 4-10cm |
|
|
|
Effacement of the cervix |
thinning or lengthening of the cervix |
|
|
|
How do you time a contration? |
from the begining of one contraction to the begining of the next one |
|
|
|
4 key questions on maternal triage |
1. Contractions (length, when, pain) 2. Bleeding 3. Fluid (colour, gush...) 4. Fetal movement |
|
|
|
Breech |
bum or legs exit first |
|
|
|
cephalic presentation |
normal presentation where the head enters the pelvis first |
|
|
|
transverse presentaiton |
sideways baby normal till week 26 afterwards should be head down or at least breech |
|
|
|
compound presentation |
A 'compound presentation' is the medical term when the baby's hand and arm (or on rare occasions a foot) comes down to lie alongside the baby's head during the pushing phase so that they are born at the same time |
|
|
|
Most common fetal position (i.e position is fetus relative to maternal pelvis) |
LOA |
|
|
|
OP |
most rotate to OA but may cause a prolonged 2nd stage of labour |
|
|
|
OT leads to arrest of ____________ |
dilatation |
|
|
|
Mentum |
1. On the human face, the mentum refers to the protruding part of the chin. |
|
|
|
Brow presentation |
head partially extended requires C/S |
|
|
|
Face presentation |
head fully extended - mentum posterior ALWAYS requires C/S mentum anterior delivers vaginally |
|
|
|
What are the STATIONS referring to in a delivery? |
the relation of the presenting part to the ischial spines where 0 = engaged -5 to -1cm = above +1 to 5cm below |
|
|
|
Biparietal diameter of a baby |
9.5cm |
|
|
|
4 stages of labour STAGE 1 |
1. a. latent phase: uterine contractions infrequent and irregular and slow cervical dilation (3-4cm and effacement b. active phase: rapid cervical dilation (full) with painful and regular contractions 2-3mins and 45-60sec.
|
|
|
|
Rate of cervical dilatation |
1.2cm/h nulliparous 2.5cm/h multiparous |
|
|
|
STAGE 2 labour |
from full dilatation to delivery of the baby - mum feels the desire to bear down and push with each contraction |
|
|
|
3rd stage labour |
separtion and expulsion of the placenta can last upto 30mins before you need to intervene. Start oxytocin IV drip 10U IM after delivery of anterior shoulder in anticipation of placental delivery |
|
|
|
Routine oxytocin 10U @ 3rd stage labour reduces the risk of _____ by >40% |
PPH |
|
|
|
Signs of placental separation |
gush of blood lengthening of the cord uterus becomes globular fundus rises |
|
|
|
4th stage of labour |
first hour postpartum monitor vital signs and bleeding repair lacerations ensure uterus is contracted examine the placenta and umilical cord |
|
|
|
8 movements of the fetus during delivery |
1. floating head before engagement 2. engagement, descent and flexion 3. further descent and internal rotation 4. complete rotation and begins extension 5. Complete extension 6. restitution (external rotation) 7. Delivery of anterior shoulder 8. Delivery of posterior shoulder |
|
|
|
What are the negative effects of pain and anxiety during labour? |
they produce catecholamines which directly inhibit uterine contractility |
|
|
|
NOn-pharm pain relief techniques |
- maternal movement (counter pressure, abdo compression) - activating peripheral sensory receptors (superficial heat and cold, immersion in water, massage, TENS, intradermal injection of sterile water - ENHANCE descending inhibitory pathways (attention, distraction, hypnosis, music, biofeedback) |
|
|
|
Pharmacological methods |
NO (entonox) narcotics pudendal nerve block perineal infiltration with LA regional anesthesia (epidural, CSE, spinal) |
|
|
|
Brow presentation |
A brow presentation can be thought of as “midway” between a face presentation (maximal nuchal extension) and an occiput presentation (maximal nuchal flexion). The anterior fontanelle and frontal sutures are prominent on vaginal exam. Management of a brow presentation is expectant. A persistent brow presentation usually requires a cesarean delivery, |
|
|
|
When do you require fetal HR monitoring? |
On an abnormal ausclultation Prolonged labour Induced or augmented labour |
|
|
|
Variable deceleration |
Variable onset, shape and duration and is the most common periodicity in labour. Due to compression of the cord or forceful contractions in second stage labour
COMPLICATED VARIBLE: slow return to baseline can be <70bpm for >60secs |
|
|
|
Late deceleration |
Uniform shape with onset late in contraction. Due to fetal hypoxia and acidic maternal hypotension Usually a sign of uteroplacental insufficiency |
|
|
|
Factors affecting fetal heart rate |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Indications for a fetal scalp blood sampling |
Atypical fetal heart rate Heavy meconium Unexplained low variabilitoes, respective late declarations, complex variable deceleration, fetal cardiac arrhythmias |
|
|
|
Fetal scalp blood sampling interpretation of results |
Ph >= 7.25 normal Ph 7.21-7.24 repeat in 30 mins and consider delivery of rapid drop Ph <= 7.20 fetal acidosis delivey is indicated |
|
|
|
Contraindications to fetal scalp blood sampling |
Blood dyscrasia (vWD, haemophillia) Active maternal infection (HIV, herpes) |
|
|
|
Managing an abnormal FHR |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Uterine contractions effect on fetal oxygenation |
Dec due to decreased uteroplacental blood flow |
|
|
|
Early deceleration |
Early onset and uniform shape and mirrors a contraction |

|
|
|
Variable deceleration |
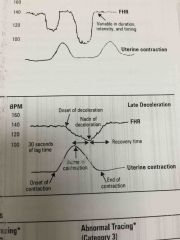
Variable onset, shape and duration and is the most common periodicity in labour. Due to compression of the cord or forceful contractions in second stage labour
COMPLICATED VARIBLE: slow return to baseline can be <70bpm for >60secs |
|
|
|
Late deceleration |
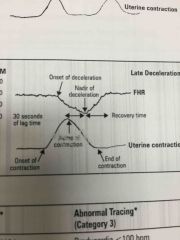
Uniform shape with onset late in contraction. Due to fetal hypoxia and acidic maternal hypotension Usually a sign of uteroplacental insufficiency |
|
|
|
Factors affecting fetal heart rate |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Contractions measured by _________ |
Tocometer |
|
|
|
Normal FHR |
110-160 |
|
|
|
FHR variability |
Measured over a 15min period and described as Absent Minimal (less than 6 per minute) Moderate 6-25 Marked >25 |
|
|
|
Managing an abnormal FHR |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Decceleration |
3 types 1. Early deceleration 2. Variable deceleration 3. Late deceleration |
|
|
|
Early deceleration |
Early onset and uniform shape and mirrors a contraction |
|

