![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
146 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Order of musculo exam? |
1 Inspection (visible deformity-step off) 2 Palpation -TOP (Tenderness on palpation)? Nodules? Spasms? 3 ROM 4 Strength 5 Sensation 6 Reflexes 7 Provacative maneuvers when indicated |
|
|
|
Abduction and internal rotation degree range? |
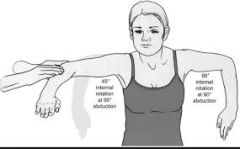
0-90° |
|
|
|
With Valgus of knee, which CL is being stressed? |

Valgus= gum=knock kneed MCL |
|
|
|
Degree of wrist extension? |

|
|
|
|
Low arch = excessive |
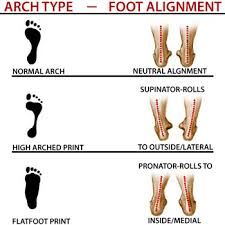
pronation eversion of foot ankles lean in flat footed
|
|
|
|
Deg of dorsiflexion |
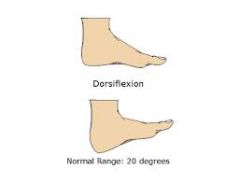
|
|
|
|
Degree of MCP flexion? |
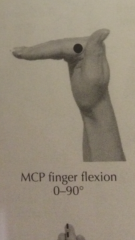
|
|
|
|
valgus vs varus |
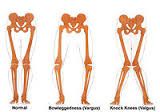
Valgus= gum (MCL) Varus= bowlegged/ rum (LCL) |
|
|
|
Inversion & eversion of the foot? |
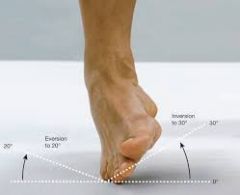
Inversion (5th digit near floor) Eversion (Big toe's near floor) |
|
|
|
Impingement sign tests? |
1 Neers |
|
|
|
Degree of wrist flexion? |

|
|
|
|
Infraspinatus Test?
|
Adduction +External Rotation Test |
|
|
|
Degree of PIP flexion? |
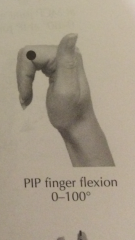
|
|
|
|
high arch = excessive |
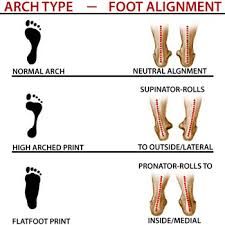
supination inversion of the foot pinky near floor ankles move away from each other |
|
|
|
O'Brien's test is + if? |
Pain or audible click at the AC joint or at the GH joint Obrien's test= Active Compression test |
|
|
|
External rotation should reach to approx which landmark? |
C7- T4 |
|
|
|
Degree for 1 MCP 2 PIP 3 DIP |
1 MCPis 0-90 2 PIP is 0-100 3 DIP is 0-30 |
|
|
|
Supraspinatus tests? |
1 Jobe |
|
|
|
Degree of DIP flexion? |
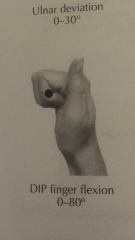
|
|
|
|
Subscapularis tests? |
1 Lift off test |
|
|
|
Signs of scoliosis |
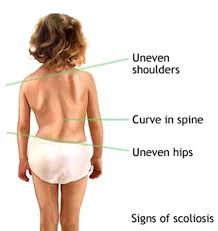
|
|
|
|
Assess Lumbar region for? |
1 Curvature 4 ROM? 5 Strength/ motor 6 Sensation 7 Reflexes 8 Leg length discrepancy 9 Provocative tests if indicated |
|
|
|
Provocative Tests for Lumbar region |
1 Straight leg test 4 Gaenslen's 6 Braggards 8 Patricks (Faber) 9 Fortis sign - SI joint gapping 10 Hoover's
|
|
|
|
Assess Cervical Region for? |
1 Inspection (visible deformity-step off) 2 Palpation -TOP? Nodules? Spasms? 3 ROM 4 Strength 5 Sensation 6 Reflexes 7 Provacative maneuvers when indicated
|
|
|
|
Provocative Tests for Cervical Region? |
1 Inspect for Deformities/ edema, swelling, ecchymosis 2 Palpation -Point tenderness? Nodules? 3 ROM 4 Strength? Shoulder Shrug? 5 Sensation 6 Reflexes 7 Provocative tests when indicated
|
|
|
|
Assess shoulders for? |
1 Inspect: Deformities/ edema, swelling, ecchymosis 2 Palpate: Point tenderness, Sulcus Sign 3 ROM? 4 Strength 6 Provocative tests when indicated
|
|
|
|
Provocative tests for shoulders |
1 Neers 2 Hawkins 3 Jobes- Empty Can Test 4 Belly Press 5 Lift off 6 Internal Rotation 7 External Rotation 8 Abduction & External Rotation 9 Check for anterior and posterior laxity 10 Sulcus sign (for inferior laxity) 11 Labral pathology (Obrien's test, Crank test, Clunk test) 12 Biceps ( Speed's test, yeargens test) |
|
|
|
Assess knees for? |
1 Inspect for Deformities/ edema, swelling, ecchymosis 2 Palpation Point tenderness, Crepitus 3 ROM 4 Strength 5 Provacative tests when indicated
|
|
|
|
Provacative tests for the knees? |
1 Valgus stress & Varus stress/ Strength 2 Anterior drawer |
|
|
|
Assess the ankle for? |
1 Inspect: Deformities/ edema, swelling, ecchymosis 2 Palpate: Point tenderness, 3 ROM? 4 Strength 6 Provocative tests when indicated
|
|
|
|
Provacative tests for the ankles? |
1 Anterior drawer |
|
|
|
Assess the hip for? |
1 Deformities/ edema, swelling, ecchymosis 2 Point tenderness 3 ROM? 4 Strength 5 Sensation 6 Patrick's (Faber test-Provocative)
|
|
|
|
Provacative tests for hips? |
1 Patrick's (Faber test-Provocative) |
|
|
|
Assess wrists for?
|
1 Inspect: Deformities/ edema, swelling, ecchymosis 2 Palpation-TOP, Nodules 3 ROM? 4 Strength 5 Sensation
|
|
|
|
Provacative tests for the wrists for? |
1 Phalen's test? 2 Tinel's sign?
|
|
|

|
hip internal rotation |
|
|
|
Cervical |
Neck forward |
|
|
|
Degree of radial deviation? |
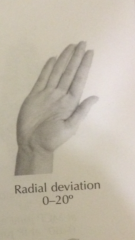
|
|
|
|
Cervical extension |
Neck back |
|
|
|
Cervical Rotation (R,L) |
Turn neck right to left |
|
|
|
Cervical Lateral flexion |
Ear to shoulders |
|
|
|
Tests for rotator cuff tear? |
1 Drop arm test 2 resisted external rotation |
|
|
|
R & L thoracic rotation |
50° |
|
|
|
signs of scoliosis |
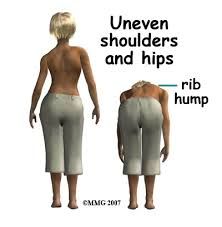
|
|
|
|
Lumbar Flexion |
>60° |
|
|
|
Lumbar Extension
|
>30° |
|
|
|
Lumbar Lateral Flexion (R&L)
|
>25° |
|
|
|
R,L Lumbar rotation |
30° |
|
|
|
Shoulder Flexion |
>150° (180°) |
|
|
|
Shoulder Extension |
>50° (45°) |
|
|
|
Shoulder ABduction |
>150° (170°) |
|
|
|
Shoulder ADduction |
30° (45°) |
|
|
|
Shoulder Internal Rotation |
90° |
|
|
|
Shoulder External Rotation |
90° |
|
|
|
Elbow Flexion |
150° |
|
|
|
Elbow Extension
|
0° |
|
|
|
hip external rotation |
|
|
|
Forearm Pronation
|
80°
|
|
|
|
Forearm Supination
|
80° (90° with elbow flexed) |
|
|
|
Wrist Flexion |
70° (90° with elbow flexed) |
|
|
|
Wrist Extension |
60° |
|
|
|
Wrist Radial Deviation |
20° |
|
|
|
Wrist Ulnar Deviation |
30° |
|
|
|
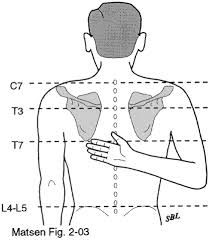
Internal rotation should reach to approx which landmark? |
|
|
|
|
O'brien's test is consistent with? |
-AC joint dysfunction if the pain is at the AC joint -Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) pathology if pain's at the GH joint |
|
|
|
Internal rotation should reach to approx which landmark? |
T4-T7 |
|
|
|
+ Apprehension test if |
test reproduces the patient's pain or gives the pt apprehension of reproduction of their pain or the feeling that their shoulder will dislocate or pop out of the socket. |
|
|
|
a over pronated foot is ________ arch type+________________ |
everted, with the big toe on the ground low arch= flat footed |
|
|
|
Hip ABduction
|
40° |
|
|
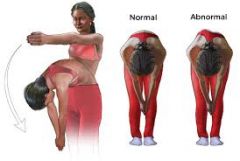
|
Scoliosis |
|
|
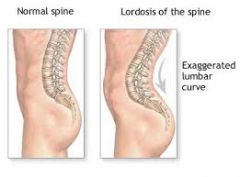
|
Lordosis |
|
|
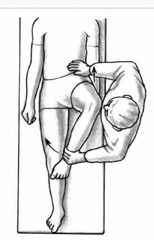
|
hip internal rotation |
|
|
|
Hip ADduction |

0° to 30° |
|
|
|
Degree of ulnar deviation? |
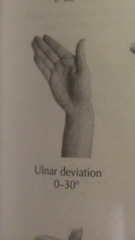
|
|
|
|
Hip Internal Rotation |
40° |
|
|
|
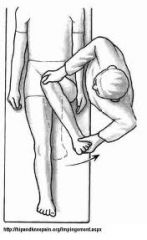
Hip External Rotation |
50° |

|
|
|
Knee Flexion
|
120° |
|
|
|
Knee Extension |
0°
|
|
|
|
Ankle Dorsiflexion |
Toes back toward shin |
|
|
|
Where is there lordosis and kyphosis of the spine? |
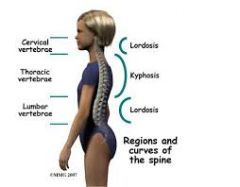
|
|
|
|
Ankle Plantarflexion
|
Foot pointed |
|
|
|
Ankle Inversion
|
30° |
|
|
|
Apprehension test |
Subluxation Dislocated shoulder
Relocation test would make them feel better |
|
|
|
high arch = excessive ________= ______ footed |
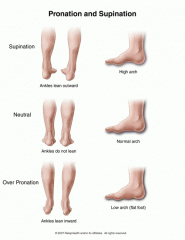
|
|
|
|
Apprehension test indicates? |
Anterior shoulder laxity or instability |
|
|
|
Ankle Eversion
|
20° |
|
|
|
Hoover’s sign
|
of leg paresis is one of two signs named for Charles Franklin Hoover. |
|
|
|
ROM of wrist? |
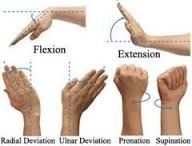
|
|
|
|
+ Drop arm test is indicative of? |
rotator cuff tear or significant tendinopathy |
|
|
|
knee valgus |
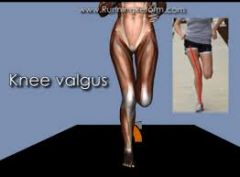
|
|
|
|
Deg of plantar and dorsiflexion? |
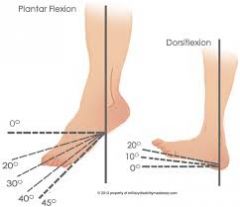
|
|
|
|
Hallus valgus |
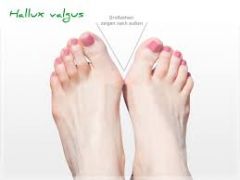
|
|
|
|
Test for bicipital tendonitis? |
Speed's test |
|
|
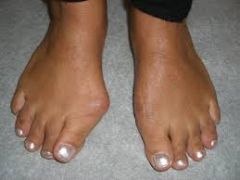
|
Hallux valgus= bunion |
|
|
|
Where are your DIP and PIPs? |
|
|
|
|
Dorsum of the hand? |
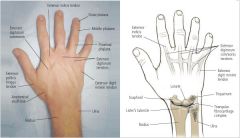
Pronated |
|
|
|
Volar aspect of the hand? |
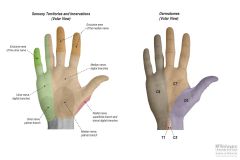
Palmar surface Supinated |
|
|
|
eversion of the foot |
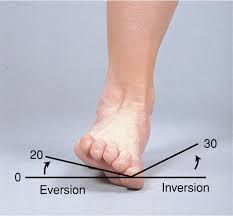
|
|
|
|
With Varus of knee, which CL is being stressed? |
Varus= rum & bowlegged LCL |
|
|
|
Your feet roll inward too much when you walk |
* Your feet roll inward too much when you walk =excessive pronation |
|
|
|
an oversupinated foot is _______ Arch type=__________ |
inverted, with the pinky toe on the ground high arch |
|
|
|
Plantar fasciitis can be caused by? |
Plantar fasciitis is caused by straining the ligament that supports your arch. Repeated strain can cause tiny tears in the ligament. These can lead to pain and swelling. This is more likely to happen if: * Your feet roll inward too much when you walk (excessive pronation ). |
|
|
|
Most people with plantar fasciitis have pain when they take their first steps after they get out of bed or sit for a long time. You may have less stiffness and pain after you take a few steps. But your foot may hurt more as the day goes on. It may hurt the most when you climb stairs or after you stand for a long time. If the foot pain is at night, it may be? |
If you have foot pain at night, you may have a different problem, such as arthritis, or a nerve problem such as tarsal tunnel syndrome. |
|
|
|
low arch = excessive ________= ______ footed |
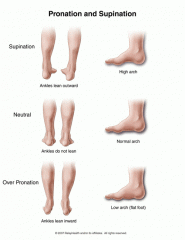
|
|
|
|
Postures |
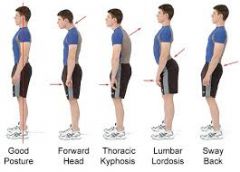
|
|
|
|
Other names for plantar faciitis? |
Plantar fasciitis (also known as plantar fasciopathy or jogger's heel) |
|
|
|
pronation of the foot? |
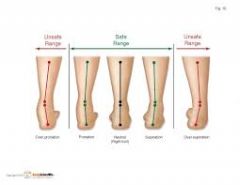
|
|
|
|
nerves of the feet? |
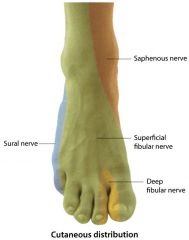
|
|
|
|
plantar flexion? foot eversion? |
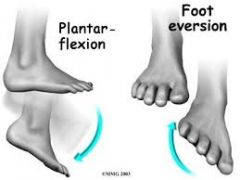
|
|
|
|
toe extension |
|
|
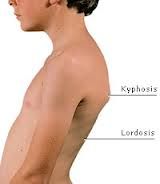
|
Kyphosis |
|
|
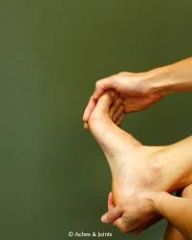
This is a pict of? |
inversion |
|
|
|
Test for Biceps? |
Speed's test & yeargens test |
|
|
|
Thumb MP Joint Flexion? |
60° |
|
|
|
Thumb IP Joint Flexion? |
80° |
|
|
|
1st MTP Extension |
0° to 70° |
|
|
|
1st MTP Flexion
|
0° to 45° |
|
|
|
Thumb MCP Extension
|
0° |
|
|
|
Thumb IP Flexion |
0° to 80° |
|
|
|
Thumb IP Extension |
0° to 20° |
|
|
|
Finger DIP Flexion
|
0° to 90° |
|
|
|
Finger PIP Extension |
0° |
|
|
|
Finger PIP Flexion
|
0°-100° |
|
|
|
Finger MCP Flexion
|
0°-90° |
|
|
|
Finger MCP Extension |
0° to 45° |
|
|
|
ROM of the elbow includes? |
Flexion Extension Supination Pronation |
|
|
|
antalgic gait |
a gait that develops as a way to avoid pain while walking gait abnormality where the stance phase of gait is abnormally shortened relative to the swing phase. It can be a good indication of pain with weight-bearing |
|
|
|
How to choose cane height? |
* Check your wrist height. With your arm hanging straight down at your side, the top of your cane should line up with the crease in your wrist. If your cane is too long, you'll need to work harder to pick it up and move it. If your cane is too short, you might lean to one side — which can throw you off balance. |
|
|
|
How to walk with a cane? |
For example, you might hold the cane in the opposite hand of the affected leg and move the cane in unison with the affected leg. Each time you step with the affected leg, move the cane, too — to give you support as you walk. When you step forward with the unaffected leg, keep the cane in place. |
|
|
|
How to walk up and down stairs with a cane |
Be careful when using steps with a cane. If you have an injury or disability affecting one leg, grasp the railing — if possible — and step up with your unaffected leg first. Then step up with your other leg as you move the cane. To move down steps, put your cane on the lower step first, then your affected leg and then your other leg — which carries your body weight. |
|
|
|
Muscle tone |
1. normal |
|
|
|
Flacid muscles are? |
hypotonic (soft/flabby) |
|
|
|
Spastic muscles are? |
initially resistant to passive movement but then comply |
|
|
|
Rigid muscles are? |
rigid and may have tremors |
|
|
|
Rigidity is a more constant state of? |
spasticity with fewer periods of release of resistance |
|
|
|
Coordination is the function of which part of the brain?
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
|
AC Joint testing |
Scarf Sign |
|
|
|
Coordination is assessed by? |
-asking client to perform repititious movements - close eyes repeatedly/rapidly |
|
|
|
Abnormal Posturing occurs when? |
Abnormal Posturing occurs when: injury to the motor tract |
|
|
|
Two types of Abnormal posturing are? |
Two types of Abnormal posturing are: 1. Flexion |
|
|
|
Flexion posturing is characterized by: 1. flexion of the arms |
Flexion posturing is characterized by: 1. flexion of the arms |
|
|
|
Flexion posturing is caused by? |
1. Lesions of the cerebral hemispheres |
|
|
|
Extension posturing is characterized by? |
Extension posturing is characterized by: 1. arching of the back |
|
|
|
Tests for Lumbar region |
1 Straight leg test 4 Gaenslen's 6 Braggards 8 Patricks (Faber) 9 Fortis sign - SI joint gapping 10 Hoover's
|
|
|
|
Provacative Tests for Cervical Region? |
1 Soto Hall 2 Spurlings 3 Shoulder depression |
|
|
|
Provocative tests for shoulders |
1 Impingement sign? (Neers, Hawkins, Drop Arm) 2 Supraspinatus test? (Jobe, Adduction/ External Rotation Test) |
|

