![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
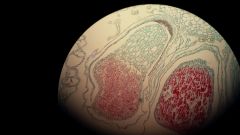
Embryo
|
An organism in the earliest stage of development
|
|
|
Sporic meiosis
|
Life cycle that has two multicellular generations
|
|
|
alternation of generation
|
the alternation between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte in a plant's life cycle
|
|
|
gametophyte
|
A haploid plant or plant structure that produces haploid gametes through mitosis.
|
|
|
Sporophyte
|
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism by meiosis
|
|
|
dominant gametophye
|
non-vascular plants
|
|
|
dominant sporophyte
|
vascular plants
|
|

thallus
|
tissue of non-vascular plant, simple sheet of cells (one or more layers thick)
|
|
|
gemma
|
small multicellular reproductive structures
|
|
|
gemma cup
|
Small cup-like structures bearing gemmae, Failsafe mechanism for liverwort lifecycle. Part of the gametophyte, can reproduce asexually when male and female gametes can't locate one another
|
|
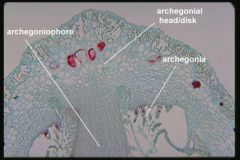
archegoniophore
|
in some liverworts, a stalk (gametophore) that bears archegonia, a multicellular structure in which a single egg is produced; found in the bryophytes and some vascular plants
|
|
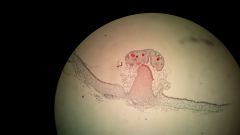
antheridiophore
|
stalk bearing antheridia as in certain mosses and liverworts
|
|
|
cuticle
|
A waxy layer that covers the outer epidermal wall, which prevents water loss
|
|
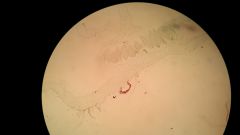
rhizoid
|
Threadlike structures that anchor nonvascular plants to the ground.
|
|
|
Air pore
|
gas exchange
|
|
|
air chamber
|
chamber under air pore
|
|
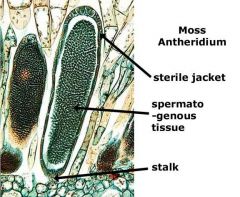
antheridium
|
In plants, the male gametangium, a moist chamber in which gametes develop.
|
|
Archegonium
|
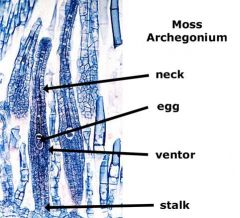
In plants, the female gametangium, a moist chamber in which gametes develop.
|
|
|
egg cell
|
the female reproductive cell
|
|
|
neck
|
elongated portion of archegonium
|
|
|
neck canal
|
where sperm swim up
|
|
|
neck canal cell
|
release chemical sperm attractant
|
|
|
sterile jacket layer
|
Protective layer over antheridia and archegonia
|
|
spermatogenous tissue
|
tissue of the male gametophyte, or pollen grain, of gymnosperms, which divides mitotically to form two sperm
|
|
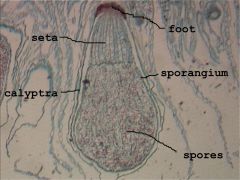
calyptra
|
protect sporophyte from mechanical injury and desiccation, develop from expanded venter and neck
|
|
|
foot
|
to absorb nutrients
|
|
|
seta
|
raise capsule for spore dispersal
|
|
|
sporangium
|
organ containing or producing spores, meiosis
|
|
|
sporogenous tissue
|
tissue on the inside of a sporangium that undergo meiosis to produce 1n spores
|
|
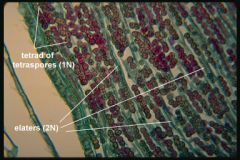
elater
|
long, twisted, moist cells that surround haploid spores of liverworts, when they dry out they twist and jerk around and scatter the spores they contain. Dead at maturity.
|
|
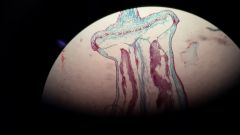
Columella
|
Central sterile tissue in moss capsule
|
|
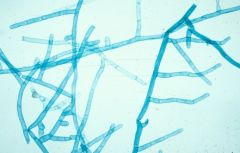
Protonema
|
A mass of green, branched, one-cell-thick filaments produced by germinating moss spores.
|
|
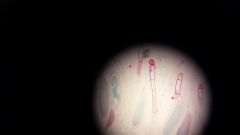
Paraphyses
|
sterile hair to protect gametangia from mechanical injuries and desiccation
|
|
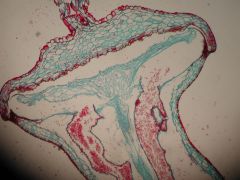
Operculum
|
cap like opening for spore to disperse
|
|
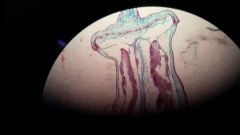
Peristome
|
teeth like structures that mediate dispersal of spores from sporangium when operculum opens
|
|
|
Characteristics of Non Vascular Plant
|
all have dominant gametophyte generation
all have complete or partially dependent sporophyte phase no true (lignified) vascular tissue gametophyte plant body is thallus sperm swims in liquid to egg asexual reproduction is by fragmentation or gemma |

