![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the Thoracic Cavity contain |
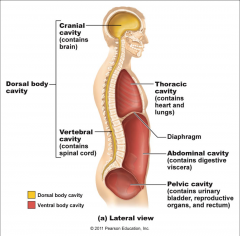
-heart, lungs, bronchi -separted from abdomino-pelvic cavity by the diaphragm |
|
|
What are the lungs enclosed by and what are the layers of this sac? |
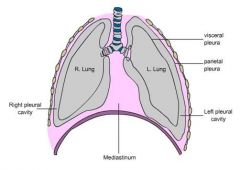
-pleural sac -visceral pleura: internal layer- adheres to each long -parietal pleura: external layer- adheres to chest wall, diaphragm and mediastinum |
|
|
Costophrenic Sinus |
-space between the costal and diaphragmatic portions of parietal pleura -lower than edge of lung -most common location for pleural fluid |
|
|
Mediastinum and where it extends |
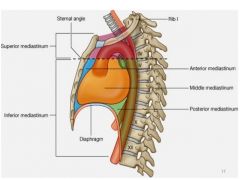
-middle portion of thoracic cavity: movable thick structure -superiorly: thoracic inlet (root of neck) -inferiotly: to diaphragm -anteriorly: to sternum -posterioly: 12th thoracic vertebra |
|
|
Structures within the Mediastinum |
-thymus -heart -great vessels (AO, IVC) -trachea -esophagus lymph nodes -nerves |
|
|
Normal sonographic appearance of Chest |
-lung-air/ visceral pleura interface is echogenic -diaphragm is thin continuous hyperechoic curved linear structure |
|
|
Pleural Effusion of thoracic cavity |
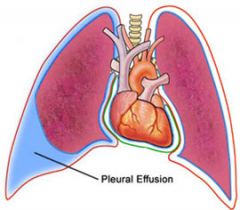
AKA Hydrothorax -fluid between visceral and parietal pleural -most common cause is CHF or metastatic dis -left side most commonly |
|
|
Clinical presentation of Pleural Effusion |
-dyspnea (difficulty beathing) -chest pain |
|
|
Complications of pleural effusion |
-inversion of diaphragm -pneumothorax |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Pleural Effusion |
-supradiaphragmatic fluid: most commonly located in costophrenic spaces -variable echogenicity -anechoic: inflammatory response -complex w septations: infectious or malignant |
|
|
Metastases of thoracic cavity |
-growth of malignant cells from primary site |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Metastases |
-pleural effusion - usually complex -pleural thickening -solid nodules in pleural cavity |
|
|
Mesothelioma |
-rare, fatal pleural tumor from exposure to asbestos |
|
|
Sonographic apparence ot Mesothelioma |
-pleural thickening -calcifications (post. shadowing) -pleural effusion |
|
|
Lung Abscess |
-pus from breakdown of tissue |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Lung Abscess? |
-thick, irregular walls -echogenic debris -expansion of mass with inspiration |
|
|
Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy |
-enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy |
-homogeneous masses -calcification -large homogeneous solid mass (we are not best modality bc can't see deep) |
|
|
Pericardial effusion |
-accumulation of fluid between layers of pericardium surrounding the heart |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Pericardial effusion |
-fluid in pericardial sac varying echogenicities |
|
|
Atelectasis |
-absence of air in all or part of lung |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Atelectasis |
-only if pleural effusion is present -wedge shaped, highly echogenic homogeneous lung floating within effusion -motion of lung with respirations -xray best modality |
|
|
Lung Consolidation |
-lung filled with fluid (don't even see lungs) |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Lung Consolidation |
-wedge shaped, solid, echo poor lung that lacks air -homogeneous texture with echogenicity similar to liver -motion of lung with respiration |

