![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Thoracic cavity |
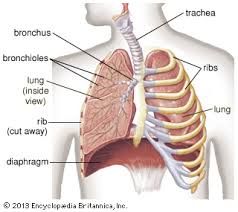
encompassing the heart, lungs, and bronchi |
|
|
What seperates the Thoracic cavity from the Abdomino-pelvic cavity? |
Diaphragm |
|
|
Pleural Sac |
Encloses the lungs |
|
|
2 layers of the Pleural Sac |
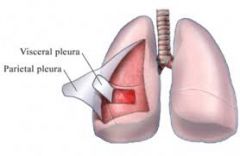
1. visceral - internal - adheres to each lung 2. parietal - external - adheres to chest wall, diaphragm, and mediastinum |
|
|
Costophrenic Sinus |
Space between costal and diaphragmatic portions that is MOST COMMON for pleural fluid accumulation |
|
|
Mediastinum |
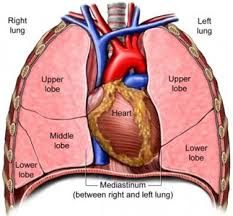
Movable, thick structure - Median partition of thoracic cavity |
|
|
Pleural Effusion AKA Hydrothorax |
Accumulation of fluid between visceral and parietal pleura |
|
|
What is Pleural Effusion most commonly caused by? |
CHF metastatic disease |
|
|
Which side does Pleural Effusion usually affect? |
LEFT |
|
|
Complications of Pleural Effusion |
- inversion of diaphragm - pneumothorax (collapsed lung) |
|
|
Clinical presentation of Pleural Effusion |
- dyspnea - chest pain |
|
|
Sonographic appearance of Pleural Effusion |
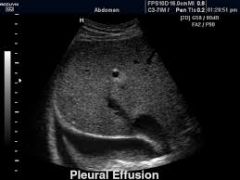
supradiaphragmatic fluid |
|
|
Treatment for Pleural Effusion |
Thoracentesis |
|
|
Sonographic Appearance of Metastases in Thoracic Cavity |
- pleural effusion - thickening - SOLID nodules |
|
|
Mesothelioma |
Rare, fatal pleural tumor from asbestos |
|
|
Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy |
Enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes - calcifications - large solid masses |
|
|
Pericardial Effusion |
Accumulation of fluid between the layers of the pericardium surrounding heart |
|
|
Atelectasis |
Absence of air in all or part of the lung - wedge-shaped, highly echogenic lung |
|
|
Lung Consolidation |
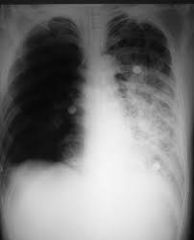
Lung filled with fluid - wedge-shaped, echo-poor lung |

