![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1000 kg/m3 |
Density of water |
|
|
1atm, 101325 Pa, 760 Torr |
Atmospheric Pressure |
|
|
Pascal's Principle |
A pressure due to a force on an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid |
|
|
F1/A1 = F2/A2 |
Pascal's Principle in formula |
|
|
Continuity Principle |
Fluids in constant pressure flow faster in narrower passages. |
|
|
A1v1 = A2v2 |
Continuity principle formula |
|
|
Venturi effect |
Faster moving fluids produce lower pressure and vice versa |
|
|
P1 + 1/2 pv1^2 + pgh = 2nd |
Bernoulli's principle formula |
|
|
U = Q -W |
First law of thermodynamics formula |
|
|
ΔL = α(L)ΔT |
Thermal expansion formula |
|
|
ΔQ/Δt= -kA(ΔT/ΔL) |
The rate of heat flow thru a conductor Formula |
|
|
Q= mcΔT |
Temperature change equation |
|
|
Q = mL |
Phase change equation |
|
|
8.987 x 10^9 (Nm^2)/c^2 |
Coulumb's constant |
|
|
F = k(q1q2) /r^2 |
Electrostatic force formula |
|
|
R = p (length/area) |
Resistance formula |
|
|
Series |
Type of circuit with same current |
|
|
Parallel |
Type of circuit with same voltage |
|
|
Parallel |
Type of circuit with reciprocal total resistance = sum of individual reciprocal resistance |
|
|
CV = q |
Capacitor equation with charge |
|
|
C = e (A/d) |
Capacitance equation of parallel plate capacitor |
|
|
1/Ct = 1/C1 + ... |
Capacitors in series formula |
|
|
Ct = C1 + C2 ... |
Capacitors in parallel |
|
|
3 x 10^8 m/s |
Speed of light |
|
|
f= c/wavelength |
Frequency of wave (light) formula |
|
|
n1sintheta1 = n2sintheta2 |
Law of refraction |
|
|
1.33 |
Index of refraction of water |
|
|
True |
T or F: The greater the refractive index, the more the light bends |
|
|
1/f = 1/d0 + 1/di |
Focal length formula |
|
|
M= hi/ho = -di/do |
Magnification formula |
|
|
False |
T or F: Higher energy light bends less when passing through a different material |
|
|
2 protons, 2 neutrons |
Alpha particle composition |
|
|
Beta decay |
Type of decay: Ejection of particle, changing of the charges of protons and neutrons |
|
|
Gamma decay |
Type of decay: Emission of gamma ray when excited nucleus releases excess energy |
|
|
d = vot + 1/2at^2 d = 1/2t (vf + vo) |
Uniformly accelarating linear motion formula for d |
|
|
vf = vo + at vf^2 = vi^2 + 2ad |
Uniformly accelerated motion formulas for v |
|
|
V = πrw |
Tangetial velocity formula |
|
|
α = v^2 / r |
Centripetal acceleration formula |
|
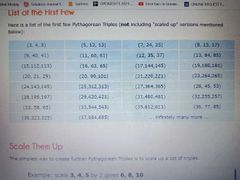
Try up to 10 |
Pythagorean triples |
|
|
p = mv |
Momentum formula |
|
|
I = Δp, Ft |
Impulse formula |
|
|
T = Fr, Iα |
Torque formua |
|
|
C + 273.15 |
Celsius to Kelvin |
|
|
Aufbau principle |
In the ground state of an atom, electrons fill the lowest available energy first |
|
|
Hund's rule |
Orbitals of equal energy are occupied by one electron first before any orbital is occupied by a second electron |
|
|
Pauli's exclusion principle |
No two electrons can have the same four electronic quantum numbers |
|
|
Electronegativity |
How well an atom atrracts an electron |
|
|
Ionization energy |
Energy needed to remove an electron |
|
|
Electron affinity |
Energy released when an electron is added |
|
|
Upper right |
Trend/position in the periodic table wherein electronegativity, ionization energy, and electron affinity are at its highest |
|
|
Lower left |
Trend/position in the periodic table wherein atomic size and metallic property are at its highest |
|
|
NaVa = NbVb |
Normality-Volume formula |
|
|
PV = nRT |
Ideal gas law formula |
|
|
0.0821 L•atm/mol•K |
Ideal gas constant |
|
|
273.15K, 1 atm |
STP |
|
|
22.4 L |
At STP, 1 mol of any gas occupies this volume (L) |
|
|
Moles = mass/molar mass |
Molar conversion formula |
|
|
Arrhenius acids/bases |
Acids: donates a H+ when dissolved in water Bases: breaks down in water to yield -OH |
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry acids/bases |
Acid: compound that breaks down to donate H+ Base: any atom or ion that accepts H+ |
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry acids/bases |
Acid: compound that breaks down to donate H+ Base: any atom or ion that accepts H+ |
|
|
Lewis acids/bases |
Acids: atom/molecule that accpets an electron pair Bases: electron pair donor |
|

|
Name strong acids and bases (6 each) |
|

|
Name weak acids (7) /bases(6) |
|
|
Superior/inferior vena cava , R atrium , R ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary vein, L atrium, L ventricle, aorta |
Flow of blood |
|
|
Tricuspid; Bicuspid |
Valve between r. atrium / ventricle; l. atrium/ ventricle |
|
|
Systole |
Contraction of the chambers of the heart |
|
|
Diastole |
Period of cardiac muscle relaxation |
|
|
SA node, AV node, bundle of His, Bundle branches, purkinje fibers |
Flow of cardiac impulse |
|
|
Dendrites |
Transmits signal towards cell body (neuron) |
|
|
Axon |
Transmits signal away from the cell body (neuron) |
|
|
Nodes of ranvier |
Where saltatory conduction occurs |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Part of brain: body's thermostat, secretion of hormones (sexual urges, pleasure, hunger, fight or flight response, etc) |
|
|
Pons |
Part of brain: bridge between cerebral cortex and medulla, breath holding |
|
|
Medulla oblongata |
Part of brain: involuntary functions important for living (breathing, heart rate, etc.) |
|
|
Cerebellum |
Part of brain: fine motor movement; non verbal learning and memory |
|
|
Sympathetic NS |
Type of autonomic nervous system: inhibit salivary glands, stimulate liver to release glucose, inhibit peristalsis and secretion, relaxes bladder |
|
|
Parasympathetic NS |
Type of autonomic nervous system: constrict pupils and bronchi, stimulates bile release, contracts bladder |
|
|
Stomach |
Site of main digestion of fats and proteins |
|
|
G cell |
Cell that secretes gastrin |
|
|
Gastrin |
Hormone that stimulates stomach to secrete gastric juices |
|
|
Parietal cells |
Secretes HCl |
|
|
Chief cells |
Secretes pepsinogen, renin, and lipase |
|
|
Pepsinogen |
This plus HCl = pepsin |
|
|
Renin |
Digests milk in young mammals |
|
|
Mucin |
Glycoprotein that protects stomach wall when activated (reaction with water) |
|
|
Mucin neck cell |
Produces mucin |
|
|
Hormones |
Long distance chemical signals |
|
|
Exocrine gland |
Has duct, secretes enzyme towards organ near gland |
|
|
Endocrine |
Ductless gland, secretes hormone |
|
|
Merocrine |
Type of exocrine gland: no part of cell is lost |
|
|
Apocrine |
Type of exocrine gland: part of cell is lost along with secretion |
|
|
Holocrine |
Type of exocrine gland: whole cell detaches with secretion |
|
|
Zygote, morula, blastula, gastrula |
Embryology steps |
|
|
4186 J/kg•C |
Heat capacity of water |

