![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diazetrophs
|
Nitrogen fixing organisms that colonize root nodules leguminous plants
|
|
|
N2 reduction requires a lot of (?) and strong (?) like ferredoxin to (?)
|
ATP
Strong reducing agents Electrons |
|
|
Net reaction for N2 reduction
|
N2 + 8H + 8e- + 16ATP + 16H20 --> 2NH3 + H2 + 16ADP + 16Pi
|
|
|
(?)e- needed for nitrogenase reaction, but only (?) needed for formal nitrogen reduction. The remaining electrons are used to produce (?)
|
8
6 H2 |
|
|
Takes about (?) ATP per N2 reduced
|
20-30
|
|
|
What inactivates nitrogenase?
|
Oxygen
|
|
|
NO3- (Name?) is found in water and soils and is reduced by plants/fungi/bacteria
|
Nitrate
|
|
|
NO2-
|
Nitrite
|
|
|
Ammonia exists in protonated form as (?) and has a pK of (?)
|
NH4+
9.25 |
|
|
Nitrificaton
|
Production of nitrate by bacteria that oxidize NH4+ to NO2- to No3-
|
|
|
Nitrogen is assimilated into an (?) to produce Glu
|
Citric acid intermediate
|
|
|
What is deanimated to produce a second Glu?
|
Gln (Glutamine
|
|
|
Glutamine synthetase does what in bacteria/mammals?
|
Bacteria: Metabolic entry point for fixed nitrogen
Animals: Mop up excess ammonia |
|
|
Mammals produce glutamate via
|
Glutamate dehydrogenase
|
|
|
Glutamine synthetase reaction that introduces ammonia into biological compounds requires substrate called
|
Glutamate
|
|
|
What is the source of nitrogen in bacteria/plants?
|
Enzyme glutamate synthase
|
|
|
Transamination
|
Amino groups transferred from molecule to molecule with glutamate as amino group donor
|
|
|
A transaminase catalyzes transfer of what to what?
|
Amino group to alpha-keto acid
|
|
|
Transaminase example:
Glutamate + What <--> What + What? |
Glutamate + Pyruvate (alpha keto acid) <--> alpha-ketogluterate + Alanine
|
|
|
Most transaminases generate
|
Glutamate or aspartate
|
|
|
What is the only AA that can't be transaminated?
|
Lysine
|
|
|
Tyr is produced from _____ via what? By what enzyme?
|
Phe via hydroxylation...through phenylalanine hydroxylase
|
|
|
Aspartate --> Asparagine via what enzyme
|
Asparagine synthetase
|
|
|
Three common metabolic intermediates?
|
Pyruvate
Oxaloacetate alpha-ketoglutarate |
|
|
Glutamate can be converted to what and what?
|
Proline and Arginine
|
|
|
Serine can be derived from glycolytic intermediate ?
|
3-phosphoglycerate
|
|
|
Serine gives rise to what?
|
Glycine
|
|
|
Tetrahydrofolate?
|
Carrier of one-carbon units in several nitrogen rections
|
|
|
Deficiency in folate results in?
|
Neural tube defects like spina bifida
|
|
|
Pyruvate -->
Oxaloacetate --> alpha-ketoglutarate --> |
Alanine
Aspartate Glutamate |
|
|
Sulfur containing amino acids begin with
|
Serine + sulfur from inorganic sulfide
|
|
|
Synthesis of methionine
|
Serine --> Cysteine --> Homocysteine --> Methionine
IN PLANTS |
|
|
In humans, serine reacts with what to produce cysteine?
|
Homocysteine
|
|
|
GABA?
|
y-aminobutryic acid
|
|
|
Tyrosine gives rise to what three compunds? And what are these called?
|
Dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. Called catecholamines (resemble catechol)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tryptophan leads to ?
|
Serotonin
|
|
|
Degradation of carbon skeletons of ____ produces ____ and precursors for _____
|
Amino acids
Acetyl-CoA Gluconeogensis |
|
|
Glucogenic means
|
Giving rise to gluconeogenic precursors --> Glucose
|
|
|
Ketogenic means
|
Give rise to acetyl-CoA
|
|
|
Catabolism of AA does not proceed all the way to ?
|
CO2
|
|
|
Ketogenic AA
|
Leucine
Lysine |
|
|
Both ketogenic and glucogenic
|
Isoleucine
Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine |
|
|
Ketone bodies are made of ? and are synthesized in ?
|
Acetoacetate + beta-hydroxybutyrate
Liver mitochondria |
|
|
Acetoacetate can go to what two things?
|
3-hydroxybutyrate and acetone
|
|
|
Ammonia released by ? is concorporated into ?
|
Glutamate dehydrogenase
Carbamoyl phosphate |
|
|
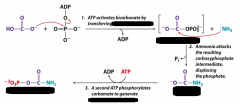
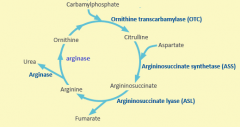
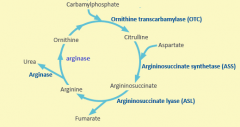
Starting substrate for urea cycle is produced by ?
|
Carbomyl phoshate synthetase
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
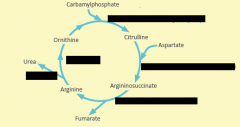
Urea production is controlled by
|
Carbomyl phosphate synthetase
|
|
|
When amino acids are being catabolized, increased ? and ? increase production of ?
|
Glu and acetyl-Coa
N-acetylglutamate |

